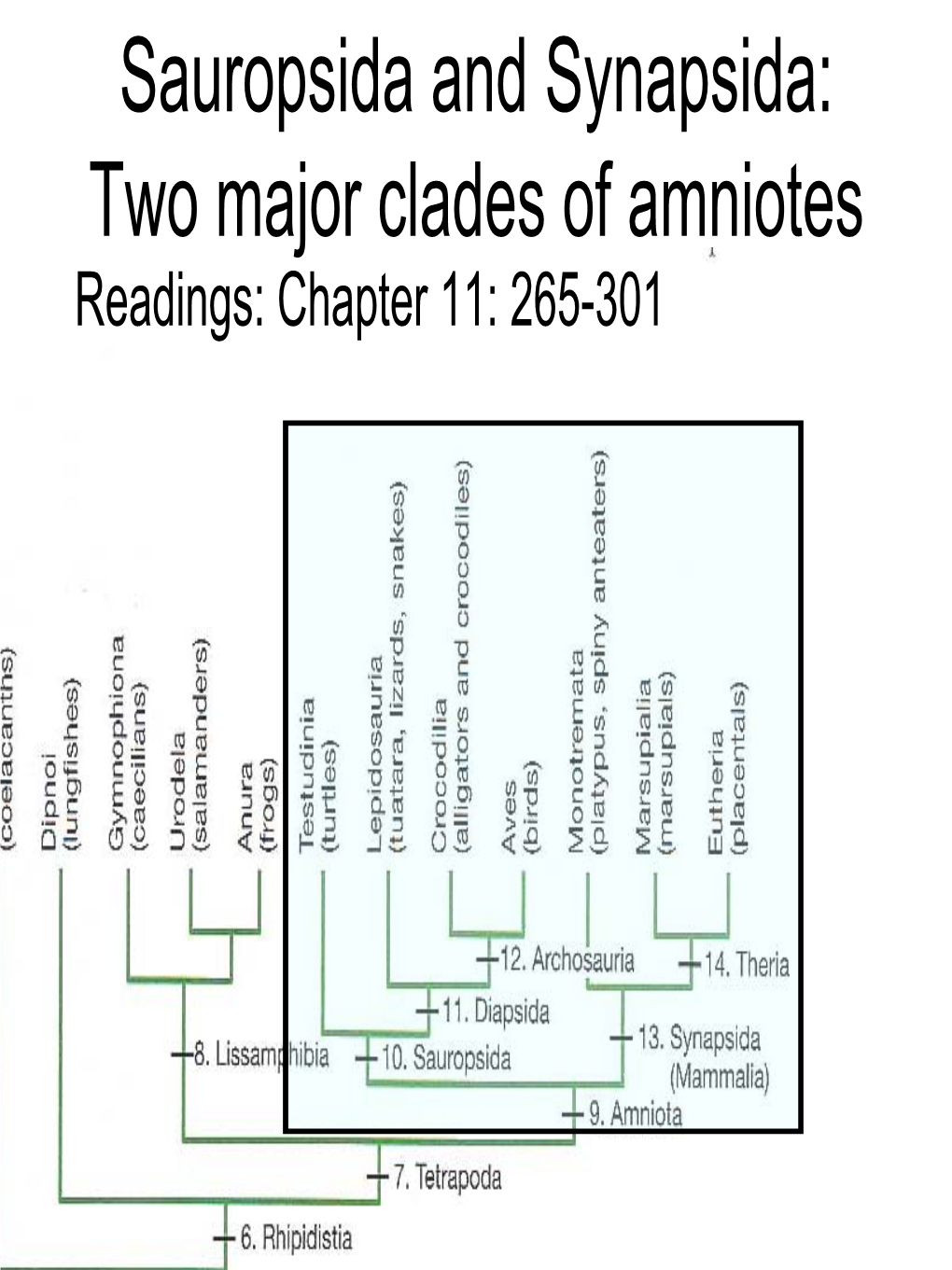
The Two Major Clades Of Amniotes Are The And The - The above statement means that reptiles (clade reptilia) are members of the clades amniota, tetrapoda, osteichthyes, gnathostomata,. (the term diapsid refers to the. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what is the key innovation of amniota?, list the major synapomorphies of. The two major clades of amniota are the synapsida and the sauropsida. Lepidosauria and archosauria, with their immediate ancestors, constitute the diapsida. What is the distinct trait of the frontal bone in amniotes? What are the two major clades of the amniota? The amniotes are the evolutionary branch (called clade) of the tetrapods (which are superclass tetrapoda), where the embryo develops within a. Humans belong to the synapsida, which is the clade that.
Humans belong to the synapsida, which is the clade that. (the term diapsid refers to the. The amniotes are the evolutionary branch (called clade) of the tetrapods (which are superclass tetrapoda), where the embryo develops within a. The two major clades of amniota are the synapsida and the sauropsida. What is the distinct trait of the frontal bone in amniotes? What are the two major clades of the amniota? Lepidosauria and archosauria, with their immediate ancestors, constitute the diapsida. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what is the key innovation of amniota?, list the major synapomorphies of. The above statement means that reptiles (clade reptilia) are members of the clades amniota, tetrapoda, osteichthyes, gnathostomata,.
The above statement means that reptiles (clade reptilia) are members of the clades amniota, tetrapoda, osteichthyes, gnathostomata,. (the term diapsid refers to the. Lepidosauria and archosauria, with their immediate ancestors, constitute the diapsida. The amniotes are the evolutionary branch (called clade) of the tetrapods (which are superclass tetrapoda), where the embryo develops within a. Humans belong to the synapsida, which is the clade that. The two major clades of amniota are the synapsida and the sauropsida. What is the distinct trait of the frontal bone in amniotes? What are the two major clades of the amniota? Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what is the key innovation of amniota?, list the major synapomorphies of.
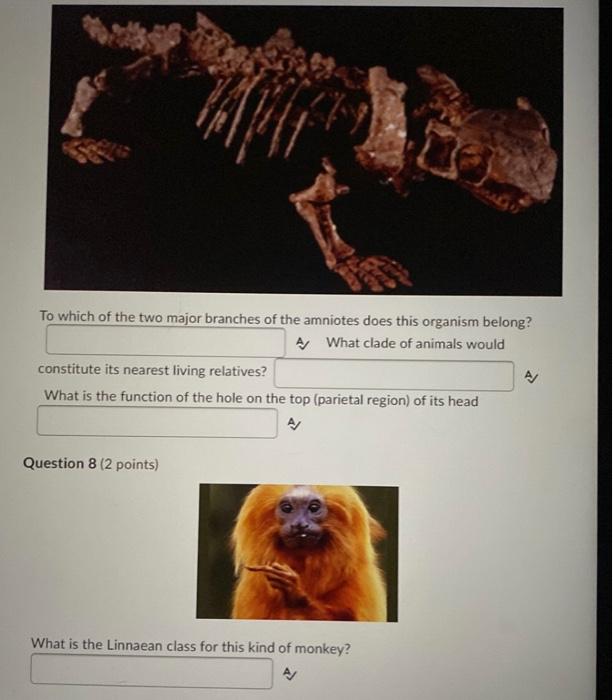
Solved To which of the two major branches of the amniotes
Humans belong to the synapsida, which is the clade that. The amniotes are the evolutionary branch (called clade) of the tetrapods (which are superclass tetrapoda), where the embryo develops within a. The above statement means that reptiles (clade reptilia) are members of the clades amniota, tetrapoda, osteichthyes, gnathostomata,. What is the distinct trait of the frontal bone in amniotes? What.
Amniotes Biology for Majors II
Humans belong to the synapsida, which is the clade that. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what is the key innovation of amniota?, list the major synapomorphies of. (the term diapsid refers to the. The amniotes are the evolutionary branch (called clade) of the tetrapods (which are superclass tetrapoda), where the embryo develops within a. What are.
Evolution of the chordates
What is the distinct trait of the frontal bone in amniotes? What are the two major clades of the amniota? The two major clades of amniota are the synapsida and the sauropsida. Lepidosauria and archosauria, with their immediate ancestors, constitute the diapsida. (the term diapsid refers to the.
Solved amniotes?The chorionThe allantoisThe endodermThe
Humans belong to the synapsida, which is the clade that. The above statement means that reptiles (clade reptilia) are members of the clades amniota, tetrapoda, osteichthyes, gnathostomata,. The two major clades of amniota are the synapsida and the sauropsida. The amniotes are the evolutionary branch (called clade) of the tetrapods (which are superclass tetrapoda), where the embryo develops within a..
(5) Questions for Amniotes Was it a fish or amphibian? a. Tikaalik
Lepidosauria and archosauria, with their immediate ancestors, constitute the diapsida. What are the two major clades of the amniota? The amniotes are the evolutionary branch (called clade) of the tetrapods (which are superclass tetrapoda), where the embryo develops within a. The above statement means that reptiles (clade reptilia) are members of the clades amniota, tetrapoda, osteichthyes, gnathostomata,. The two major.
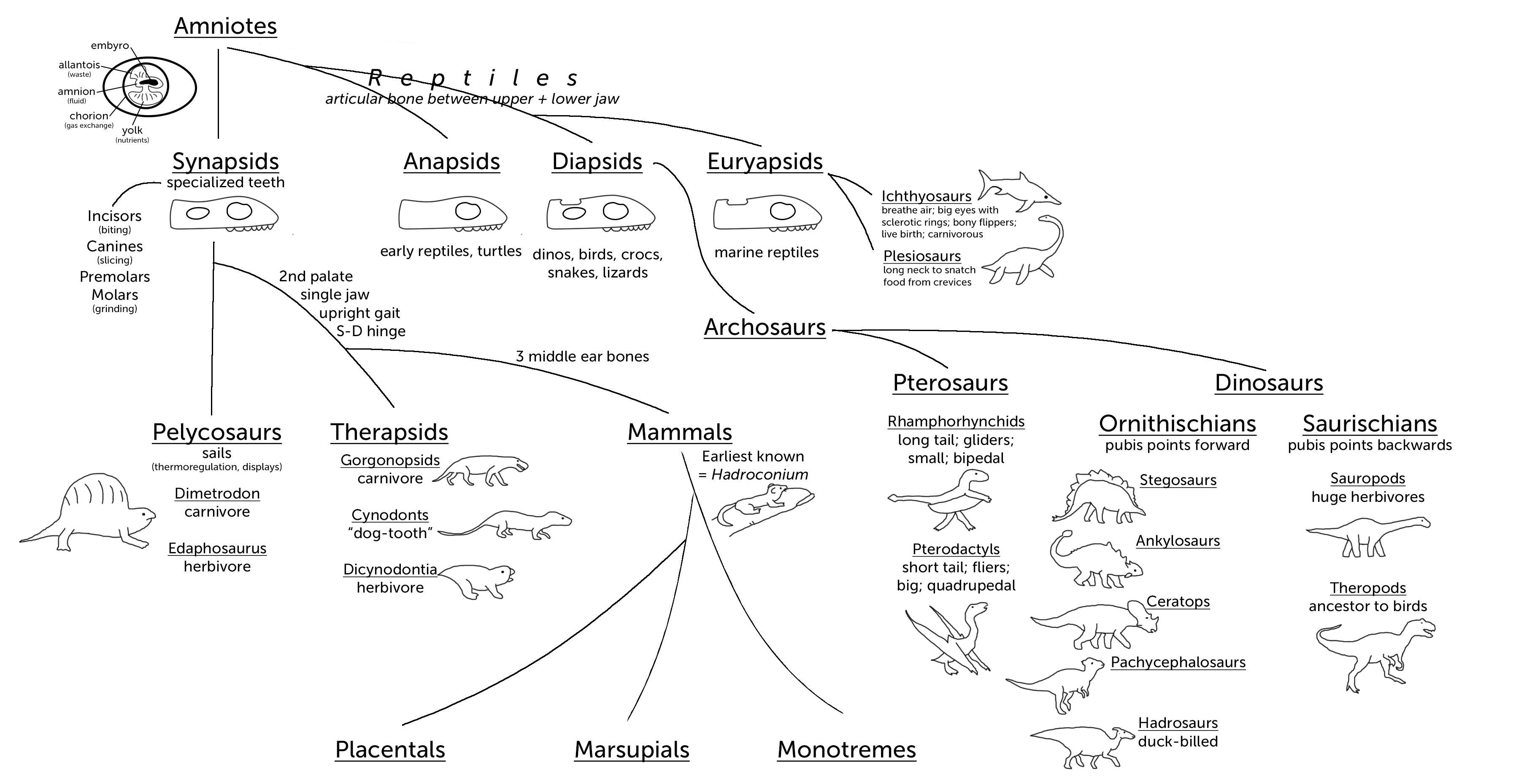
Phylogeny of selected major groups of amniotes. Selected
The above statement means that reptiles (clade reptilia) are members of the clades amniota, tetrapoda, osteichthyes, gnathostomata,. What is the distinct trait of the frontal bone in amniotes? The two major clades of amniota are the synapsida and the sauropsida. (the term diapsid refers to the. What are the two major clades of the amniota?
Nicolás Naves 12.2 Amniotes 3 Column Chart PDF Mammals Reptile
Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what is the key innovation of amniota?, list the major synapomorphies of. Humans belong to the synapsida, which is the clade that. (the term diapsid refers to the. Lepidosauria and archosauria, with their immediate ancestors, constitute the diapsida. The above statement means that reptiles (clade reptilia) are members of the clades.
Amniotes of the Late Paleozoic & Mesozoic Lucky Sci
Lepidosauria and archosauria, with their immediate ancestors, constitute the diapsida. The amniotes are the evolutionary branch (called clade) of the tetrapods (which are superclass tetrapoda), where the embryo develops within a. The above statement means that reptiles (clade reptilia) are members of the clades amniota, tetrapoda, osteichthyes, gnathostomata,. What are the two major clades of the amniota? (the term diapsid.
Sauropsida and Synapsida Two Major Clades of Amniotes DocsLib
Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what is the key innovation of amniota?, list the major synapomorphies of. The two major clades of amniota are the synapsida and the sauropsida. What are the two major clades of the amniota? Lepidosauria and archosauria, with their immediate ancestors, constitute the diapsida. What is the distinct trait of the frontal.
Phylogeny of selected major groups of amniotes. Selected
What are the two major clades of the amniota? The above statement means that reptiles (clade reptilia) are members of the clades amniota, tetrapoda, osteichthyes, gnathostomata,. Humans belong to the synapsida, which is the clade that. (the term diapsid refers to the. What is the distinct trait of the frontal bone in amniotes?
The Above Statement Means That Reptiles (Clade Reptilia) Are Members Of The Clades Amniota, Tetrapoda, Osteichthyes, Gnathostomata,.
The amniotes are the evolutionary branch (called clade) of the tetrapods (which are superclass tetrapoda), where the embryo develops within a. Lepidosauria and archosauria, with their immediate ancestors, constitute the diapsida. What is the distinct trait of the frontal bone in amniotes? Humans belong to the synapsida, which is the clade that.
What Are The Two Major Clades Of The Amniota?
(the term diapsid refers to the. The two major clades of amniota are the synapsida and the sauropsida. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what is the key innovation of amniota?, list the major synapomorphies of.