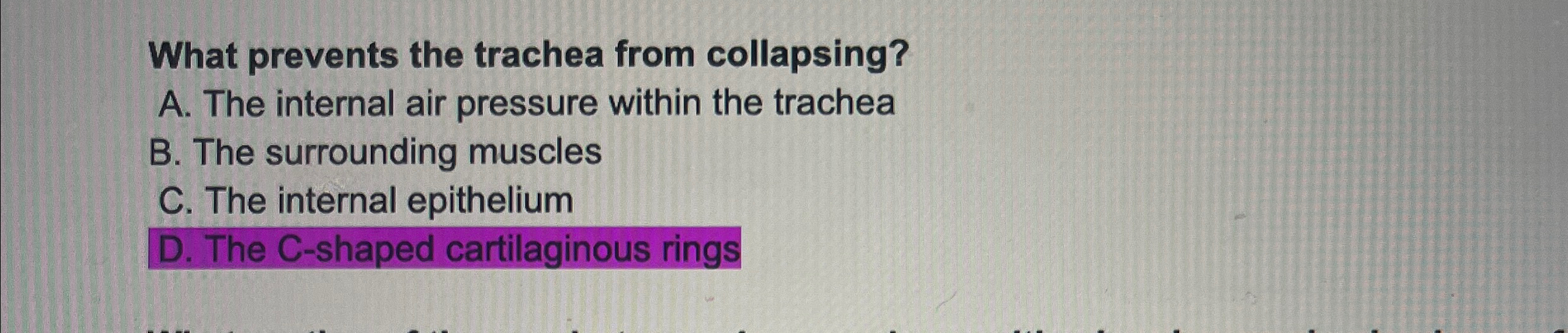
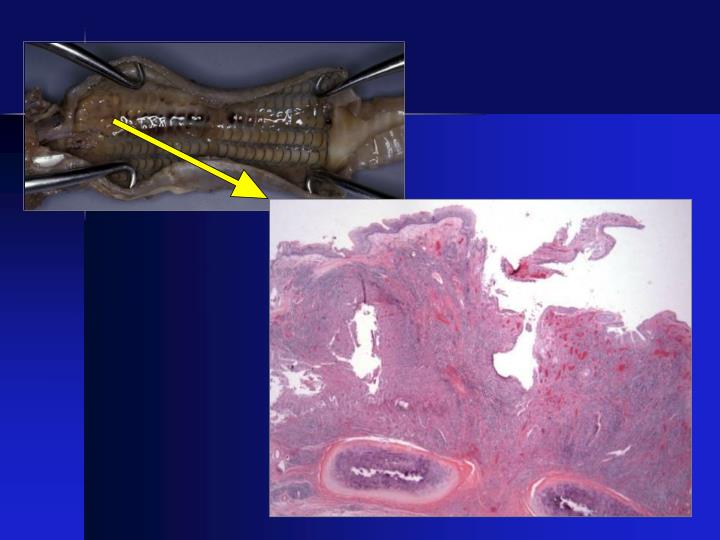
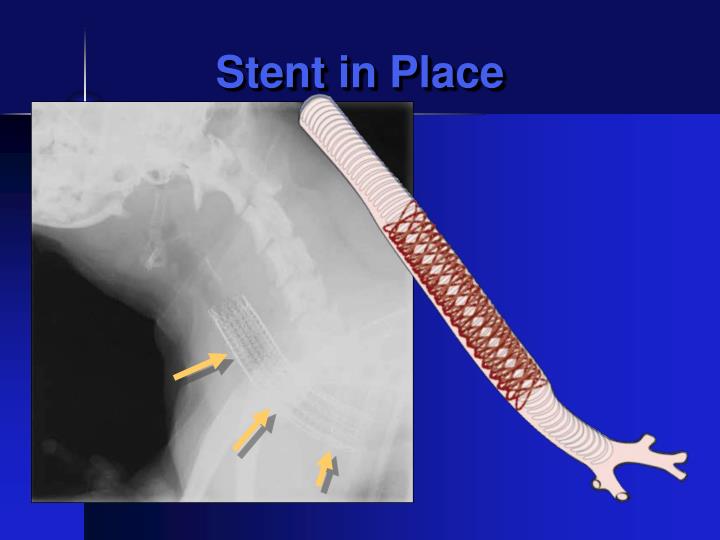
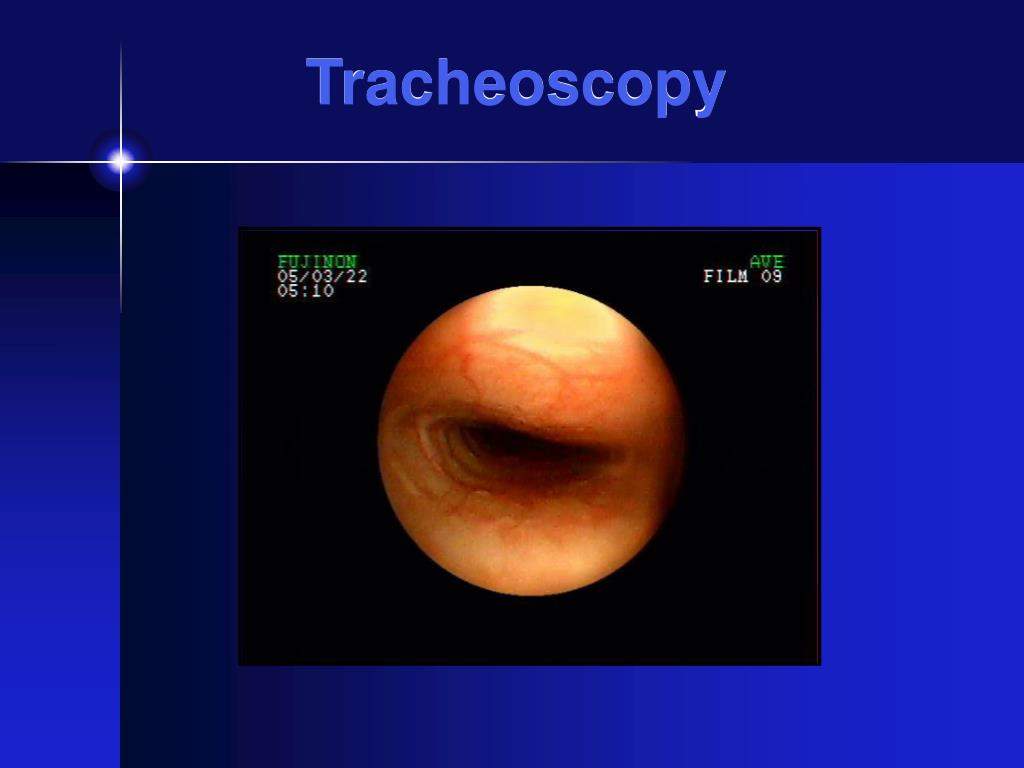
What Prevents The Trachea From Collapsing - As the thoracic cavity (and therefore the lungs) increase in size, the pressure inside increases. The hyaline cartilage layer is sturdy but flexible and prevents the collapse of the. The fibroelastic membrane allows the trachea to stretch and expand slightly during inhalation. The rigidity of the trachea is maintained by a series of incomplete cartilaginous rings. The trachea, primary, secondary and tertiary bronchi, and initial bronchioles are supported by. The cartilage rings in the trachea prevent the trachea from collapsing during the absence of. The trachea is a tube that connects the larynx to the lungs, providing a pathway for.
The fibroelastic membrane allows the trachea to stretch and expand slightly during inhalation. The cartilage rings in the trachea prevent the trachea from collapsing during the absence of. The trachea is a tube that connects the larynx to the lungs, providing a pathway for. The rigidity of the trachea is maintained by a series of incomplete cartilaginous rings. The trachea, primary, secondary and tertiary bronchi, and initial bronchioles are supported by. As the thoracic cavity (and therefore the lungs) increase in size, the pressure inside increases. The hyaline cartilage layer is sturdy but flexible and prevents the collapse of the.
The trachea is a tube that connects the larynx to the lungs, providing a pathway for. The fibroelastic membrane allows the trachea to stretch and expand slightly during inhalation. As the thoracic cavity (and therefore the lungs) increase in size, the pressure inside increases. The cartilage rings in the trachea prevent the trachea from collapsing during the absence of. The hyaline cartilage layer is sturdy but flexible and prevents the collapse of the. The trachea, primary, secondary and tertiary bronchi, and initial bronchioles are supported by. The rigidity of the trachea is maintained by a series of incomplete cartilaginous rings.
Solved What prevents the trachea from collapsing?A. The
As the thoracic cavity (and therefore the lungs) increase in size, the pressure inside increases. The hyaline cartilage layer is sturdy but flexible and prevents the collapse of the. The trachea, primary, secondary and tertiary bronchi, and initial bronchioles are supported by. The trachea is a tube that connects the larynx to the lungs, providing a pathway for. The fibroelastic.
PPT Collapsing Trachea PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID326019
The cartilage rings in the trachea prevent the trachea from collapsing during the absence of. As the thoracic cavity (and therefore the lungs) increase in size, the pressure inside increases. The trachea, primary, secondary and tertiary bronchi, and initial bronchioles are supported by. The rigidity of the trachea is maintained by a series of incomplete cartilaginous rings. The trachea is.
PPT Collapsing Trachea PowerPoint Presentation ID326019
The trachea, primary, secondary and tertiary bronchi, and initial bronchioles are supported by. The cartilage rings in the trachea prevent the trachea from collapsing during the absence of. The fibroelastic membrane allows the trachea to stretch and expand slightly during inhalation. The hyaline cartilage layer is sturdy but flexible and prevents the collapse of the. The trachea is a tube.
SOLVED A structural difference between the trachea and esophagus that
The cartilage rings in the trachea prevent the trachea from collapsing during the absence of. The fibroelastic membrane allows the trachea to stretch and expand slightly during inhalation. The trachea is a tube that connects the larynx to the lungs, providing a pathway for. The trachea, primary, secondary and tertiary bronchi, and initial bronchioles are supported by. The hyaline cartilage.
SOLVED A structural difference between the trachea and esophagus that
The trachea is a tube that connects the larynx to the lungs, providing a pathway for. The fibroelastic membrane allows the trachea to stretch and expand slightly during inhalation. The trachea, primary, secondary and tertiary bronchi, and initial bronchioles are supported by. The hyaline cartilage layer is sturdy but flexible and prevents the collapse of the. The rigidity of the.
What prevents the trachea from collapsing?The
The rigidity of the trachea is maintained by a series of incomplete cartilaginous rings. The cartilage rings in the trachea prevent the trachea from collapsing during the absence of. The trachea is a tube that connects the larynx to the lungs, providing a pathway for. As the thoracic cavity (and therefore the lungs) increase in size, the pressure inside increases..
PPT Collapsing Trachea PowerPoint Presentation ID326019
The trachea is a tube that connects the larynx to the lungs, providing a pathway for. The trachea, primary, secondary and tertiary bronchi, and initial bronchioles are supported by. The hyaline cartilage layer is sturdy but flexible and prevents the collapse of the. The cartilage rings in the trachea prevent the trachea from collapsing during the absence of. The rigidity.
PPT Collapsing Trachea PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID326019
The cartilage rings in the trachea prevent the trachea from collapsing during the absence of. As the thoracic cavity (and therefore the lungs) increase in size, the pressure inside increases. The trachea is a tube that connects the larynx to the lungs, providing a pathway for. The rigidity of the trachea is maintained by a series of incomplete cartilaginous rings..
PPT Collapsing Trachea PowerPoint Presentation ID326019
The cartilage rings in the trachea prevent the trachea from collapsing during the absence of. As the thoracic cavity (and therefore the lungs) increase in size, the pressure inside increases. The trachea, primary, secondary and tertiary bronchi, and initial bronchioles are supported by. The fibroelastic membrane allows the trachea to stretch and expand slightly during inhalation. The hyaline cartilage layer.
PPT Collapsing Trachea PowerPoint Presentation ID326019
The trachea is a tube that connects the larynx to the lungs, providing a pathway for. The hyaline cartilage layer is sturdy but flexible and prevents the collapse of the. The trachea, primary, secondary and tertiary bronchi, and initial bronchioles are supported by. The rigidity of the trachea is maintained by a series of incomplete cartilaginous rings. The fibroelastic membrane.
As The Thoracic Cavity (And Therefore The Lungs) Increase In Size, The Pressure Inside Increases.
The fibroelastic membrane allows the trachea to stretch and expand slightly during inhalation. The trachea is a tube that connects the larynx to the lungs, providing a pathway for. The rigidity of the trachea is maintained by a series of incomplete cartilaginous rings. The cartilage rings in the trachea prevent the trachea from collapsing during the absence of.
The Hyaline Cartilage Layer Is Sturdy But Flexible And Prevents The Collapse Of The.
The trachea, primary, secondary and tertiary bronchi, and initial bronchioles are supported by.