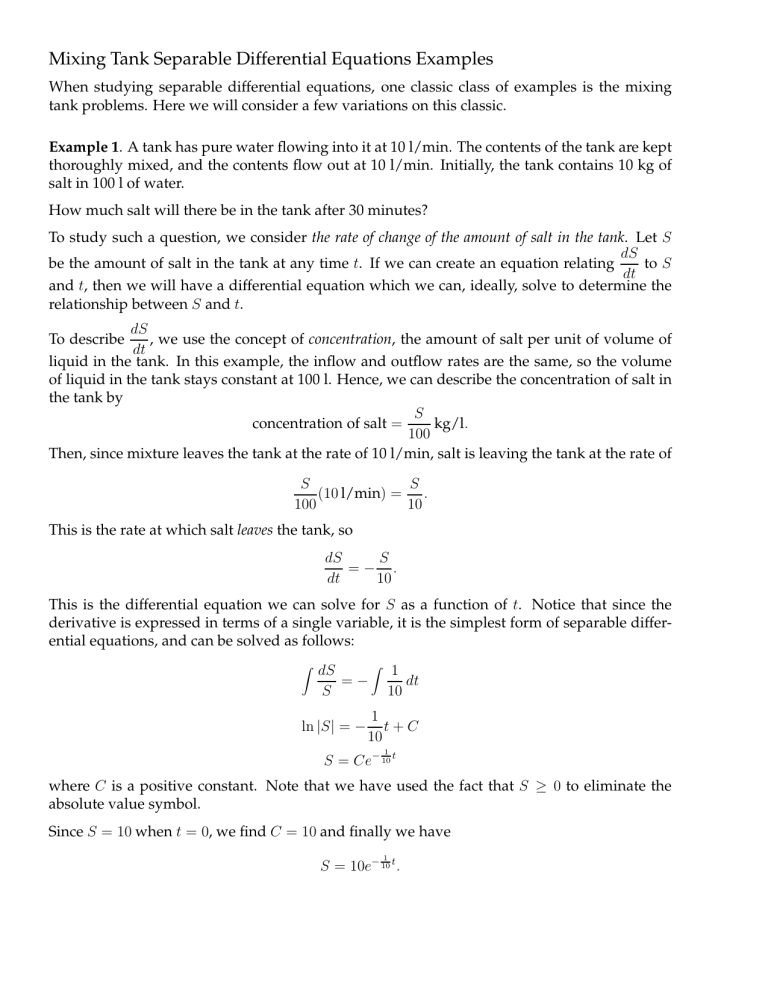
Tank Problem Differential Equations - A typical mixing problem deals with the amount of salt in a mixing tank. Salt and water enter the tank at a certain rate, are mixed with what is already. Find the diferential equation for the mango concentration m(t). Now we have each terms (components) of governing law for tank a,tank b and tank c. Mixing problems with two tanks di erential equations 4 / 5 summary to solve the inhomogeneousinitial. A tank initially contains 50 litres of water with 5kg of salt dissolved in it. A salt solution with a concentration of 0.2 kg/l flows into the tank at. If you just combine those components according to.
Find the diferential equation for the mango concentration m(t). Salt and water enter the tank at a certain rate, are mixed with what is already. Mixing problems with two tanks di erential equations 4 / 5 summary to solve the inhomogeneousinitial. A typical mixing problem deals with the amount of salt in a mixing tank. A tank initially contains 50 litres of water with 5kg of salt dissolved in it. Now we have each terms (components) of governing law for tank a,tank b and tank c. A salt solution with a concentration of 0.2 kg/l flows into the tank at. If you just combine those components according to.
A tank initially contains 50 litres of water with 5kg of salt dissolved in it. Now we have each terms (components) of governing law for tank a,tank b and tank c. Mixing problems with two tanks di erential equations 4 / 5 summary to solve the inhomogeneousinitial. If you just combine those components according to. A salt solution with a concentration of 0.2 kg/l flows into the tank at. Salt and water enter the tank at a certain rate, are mixed with what is already. A typical mixing problem deals with the amount of salt in a mixing tank. Find the diferential equation for the mango concentration m(t).
[Solved] DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS APPLICATIONS A tank initially contains
Salt and water enter the tank at a certain rate, are mixed with what is already. Mixing problems with two tanks di erential equations 4 / 5 summary to solve the inhomogeneousinitial. A typical mixing problem deals with the amount of salt in a mixing tank. If you just combine those components according to. Find the diferential equation for the.
Mixing Problem in Tank using Differential Equations
If you just combine those components according to. Find the diferential equation for the mango concentration m(t). A typical mixing problem deals with the amount of salt in a mixing tank. Now we have each terms (components) of governing law for tank a,tank b and tank c. A tank initially contains 50 litres of water with 5kg of salt dissolved.
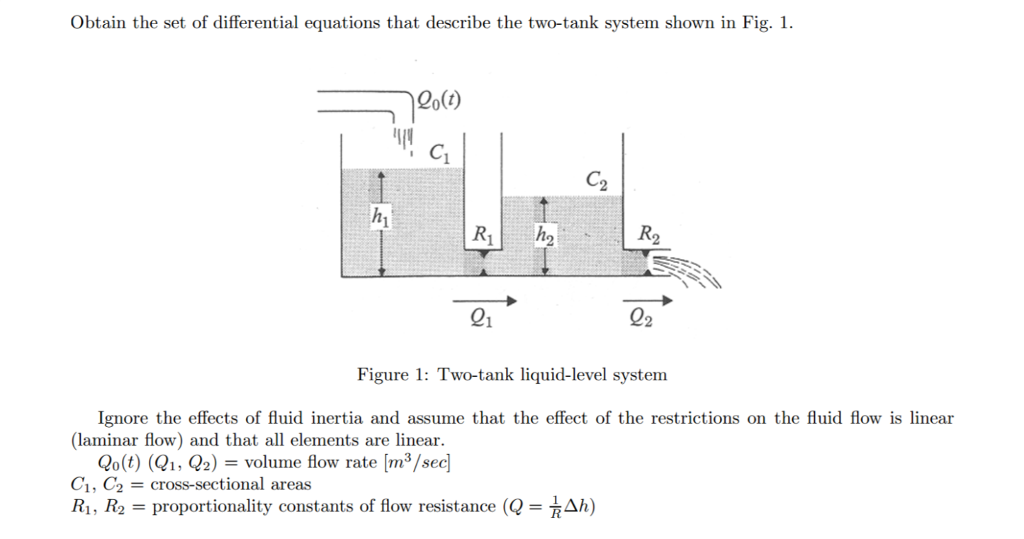
Solved Problem One Coupled TankThe coupled tank problem is
Mixing problems with two tanks di erential equations 4 / 5 summary to solve the inhomogeneousinitial. A salt solution with a concentration of 0.2 kg/l flows into the tank at. A typical mixing problem deals with the amount of salt in a mixing tank. If you just combine those components according to. Find the diferential equation for the mango concentration.
Solved 2. [10 points] Obtain the differential equations for
Now we have each terms (components) of governing law for tank a,tank b and tank c. A salt solution with a concentration of 0.2 kg/l flows into the tank at. Salt and water enter the tank at a certain rate, are mixed with what is already. Mixing problems with two tanks di erential equations 4 / 5 summary to solve.
[Solved] differential equations. 12 Consider a tank used in Certain
Now we have each terms (components) of governing law for tank a,tank b and tank c. A typical mixing problem deals with the amount of salt in a mixing tank. Salt and water enter the tank at a certain rate, are mixed with what is already. If you just combine those components according to. A tank initially contains 50 litres.
Linear Differential Equations Tank Problem Mathematics Stack Exchange
Find the diferential equation for the mango concentration m(t). A typical mixing problem deals with the amount of salt in a mixing tank. Salt and water enter the tank at a certain rate, are mixed with what is already. Mixing problems with two tanks di erential equations 4 / 5 summary to solve the inhomogeneousinitial. Now we have each terms.
Mixing Tank Separable Differential Equations Examples
If you just combine those components according to. Salt and water enter the tank at a certain rate, are mixed with what is already. Now we have each terms (components) of governing law for tank a,tank b and tank c. A salt solution with a concentration of 0.2 kg/l flows into the tank at. A tank initially contains 50 litres.
Solved 3 Brine tank problem a) Derive differential
Salt and water enter the tank at a certain rate, are mixed with what is already. Find the diferential equation for the mango concentration m(t). A tank initially contains 50 litres of water with 5kg of salt dissolved in it. Now we have each terms (components) of governing law for tank a,tank b and tank c. Mixing problems with two.
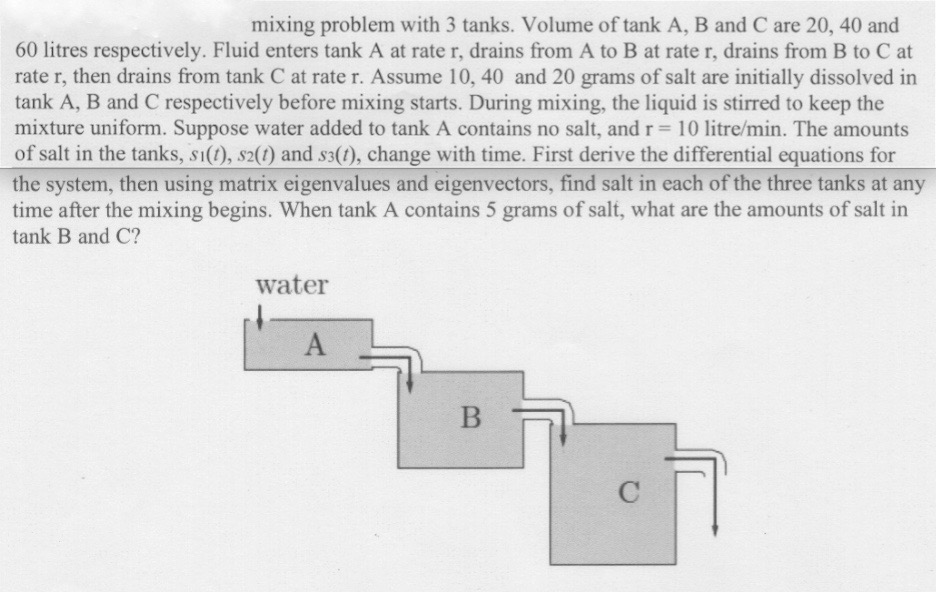
Solved Obtain The Set Of Differential Equations That Desc...
Mixing problems with two tanks di erential equations 4 / 5 summary to solve the inhomogeneousinitial. Find the diferential equation for the mango concentration m(t). A tank initially contains 50 litres of water with 5kg of salt dissolved in it. A typical mixing problem deals with the amount of salt in a mixing tank. If you just combine those components.
(PDF) Differential Equations Water Tank Problems
If you just combine those components according to. Mixing problems with two tanks di erential equations 4 / 5 summary to solve the inhomogeneousinitial. Salt and water enter the tank at a certain rate, are mixed with what is already. A salt solution with a concentration of 0.2 kg/l flows into the tank at. Find the diferential equation for the.
If You Just Combine Those Components According To.
Now we have each terms (components) of governing law for tank a,tank b and tank c. A typical mixing problem deals with the amount of salt in a mixing tank. Mixing problems with two tanks di erential equations 4 / 5 summary to solve the inhomogeneousinitial. A tank initially contains 50 litres of water with 5kg of salt dissolved in it.
Find The Diferential Equation For The Mango Concentration M(T).
A salt solution with a concentration of 0.2 kg/l flows into the tank at. Salt and water enter the tank at a certain rate, are mixed with what is already.

![Solved 2. [10 points] Obtain the differential equations for](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/c10/c103e9da-b075-4126-af4b-07ac067dfd96/phpne9W8Y)