Standard Form Of Differential Equation - By a first order linear differential equation we understand a differential equation that can be brought into the standard form x0(t)+ p(t)x(t) =. A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form: The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. D y d x + p (x) y = q (x). The p and q in this.
D y d x + p (x) y = q (x). The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. The p and q in this. By a first order linear differential equation we understand a differential equation that can be brought into the standard form x0(t)+ p(t)x(t) =. A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form:
By a first order linear differential equation we understand a differential equation that can be brought into the standard form x0(t)+ p(t)x(t) =. The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. D y d x + p (x) y = q (x). The p and q in this. A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form:
Ordinary differential equation PPT
By a first order linear differential equation we understand a differential equation that can be brought into the standard form x0(t)+ p(t)x(t) =. The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. D y d x + p (x) y = q (x). A differential equation.
Differential Equations Definition, Formula, Types, Examples
By a first order linear differential equation we understand a differential equation that can be brought into the standard form x0(t)+ p(t)x(t) =. The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. D y d x + p (x) y = q (x). A differential equation.
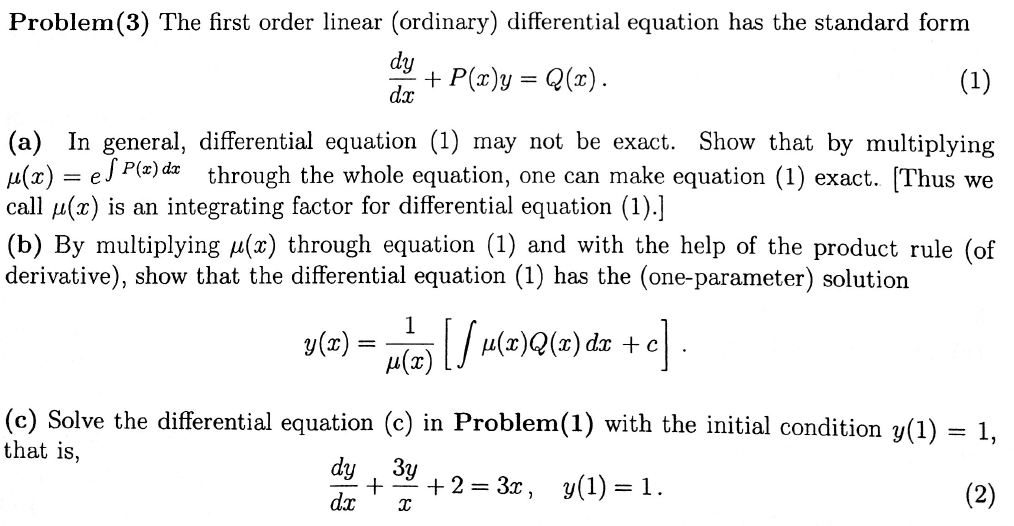
Solved The first order linear (ordinary) differential
The p and q in this. A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form: The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. By a first order linear differential equation we understand a differential equation that can.
Ordinary differential equation PPT
A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form: By a first order linear differential equation we understand a differential equation that can be brought into the standard form x0(t)+ p(t)x(t) =. The p and q in this. The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q,.
calculus Differential equation of non standard form. Mathematics
By a first order linear differential equation we understand a differential equation that can be brought into the standard form x0(t)+ p(t)x(t) =. The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using.
Solved Write the differential equation e^x y' + e^2x y = sin
By a first order linear differential equation we understand a differential equation that can be brought into the standard form x0(t)+ p(t)x(t) =. The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. The p and q in this. A differential equation can be identified as a.
Ordinary differential equation PPT
By a first order linear differential equation we understand a differential equation that can be brought into the standard form x0(t)+ p(t)x(t) =. The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. D y d x + p (x) y = q (x). A differential equation.
Ordinary differential equation PPT
A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form: The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. The p and q in this. D y d x + p (x) y = q (x). By a first.
Bernoulli’s differential equation Yawin
The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. The p and q in this. A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form: D y d x + p (x) y = q (x). By a first.
Report on differential equation PPT
D y d x + p (x) y = q (x). The p and q in this. A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form: By a first order linear differential equation we understand a differential equation that can be brought into the standard form x0(t)+ p(t)x(t) =. The standard form.
By A First Order Linear Differential Equation We Understand A Differential Equation That Can Be Brought Into The Standard Form X0(T)+ P(T)X(T) =.
The p and q in this. The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. D y d x + p (x) y = q (x). A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form: