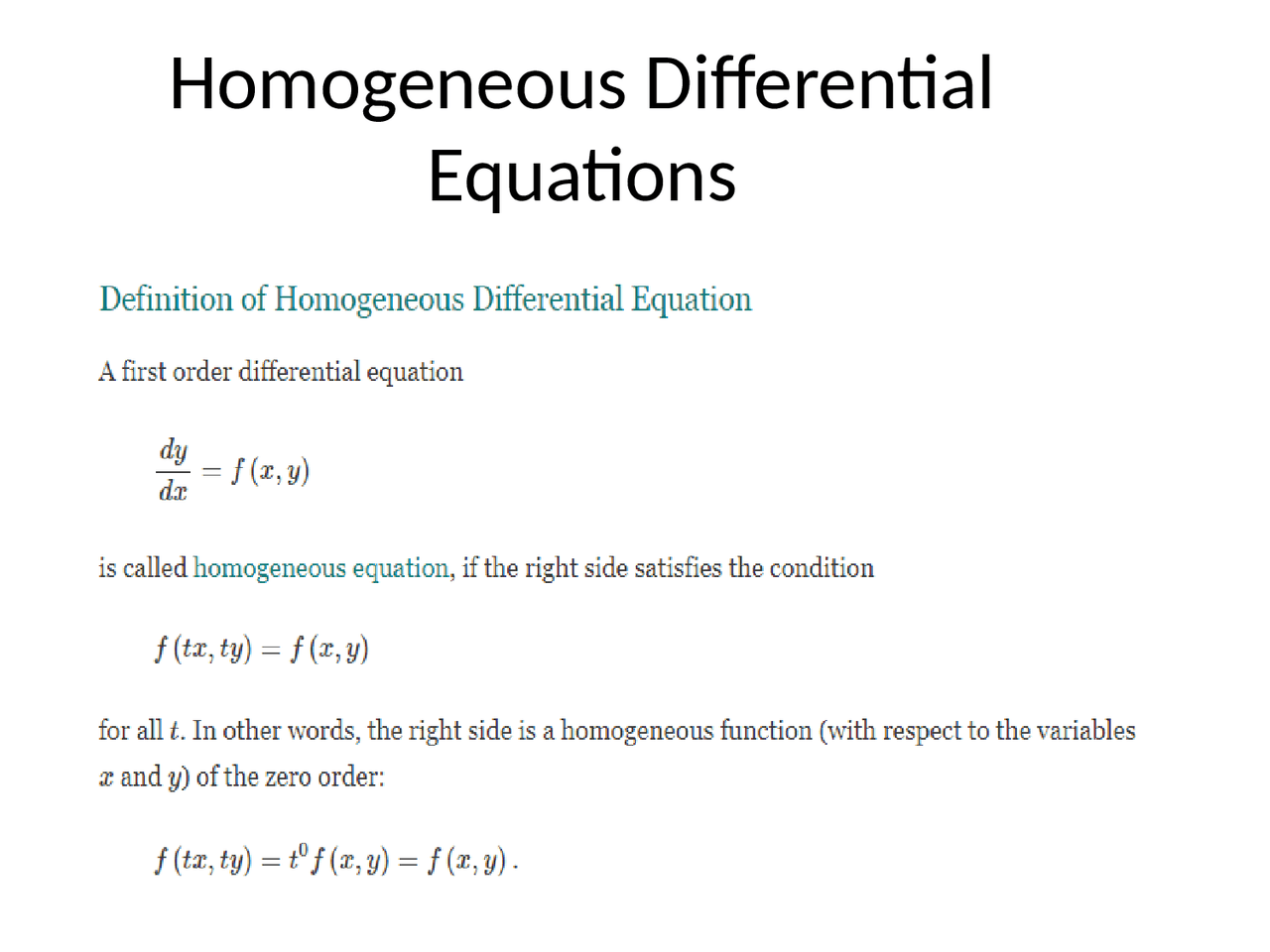
Solving Homogeneous Differential Equations - In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g (x, y) is. A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by making the substitution. Homogenous differential equations are equations that contain a homogenous. Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential equations a first.
Homogenous differential equations are equations that contain a homogenous. A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g (x, y) is. A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by making the substitution. Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential equations a first. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,.
Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential equations a first. Homogenous differential equations are equations that contain a homogenous. A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by making the substitution. A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g (x, y) is. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,.
2nd Order Homogeneous Equations
In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential equations a first. A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g (x, y) is. Homogenous differential equations are equations that contain a homogenous. A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by.
Particular Solution of NonHomogeneous Differential Equations Mr
In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. Homogenous differential equations are equations that contain a homogenous. Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential equations a first. A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g (x, y) is. A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by.
Homogeneous Differential Equations Docsity
In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. Homogenous differential equations are equations that contain a homogenous. A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g (x, y) is. A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by making the substitution. Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential.
Solved Solving Homogeneous Linear Systems of Differential
Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential equations a first. A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g (x, y) is. A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by making the substitution. Homogenous differential equations are equations that contain a homogenous. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving.
Homogeneous Differential Equation2 PDF Waves Applied And
In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential equations a first. A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by making the substitution. Homogenous differential equations are equations that contain a homogenous. A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g.
Homogeneous Linear Differential Equations KZHU.ai 🚀
A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g (x, y) is. Homogenous differential equations are equations that contain a homogenous. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by making the substitution. Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential.
[Solved] Determine whether the given differential equations are
In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential equations a first. A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g (x, y) is. Homogenous differential equations are equations that contain a homogenous. A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by.
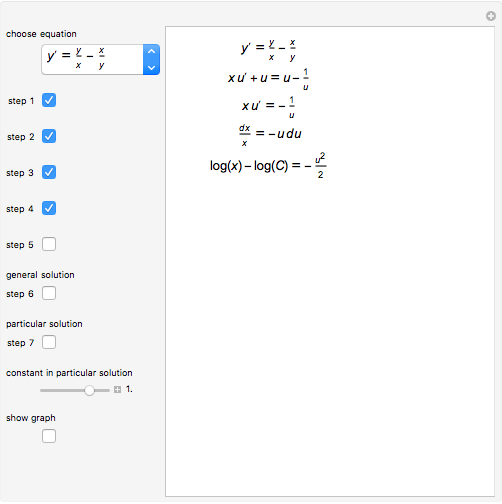
Some Homogeneous Ordinary Differential Equations Wolfram
Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential equations a first. A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g (x, y) is. A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by making the substitution. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. Homogenous differential equations are equations that.
Solving Homogeneous Differential Equations Maths Science
Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential equations a first. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g (x, y) is. Homogenous differential equations are equations that contain a homogenous. A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by.
[Solved] . Use the method for solving homogeneous equations to solve
Here we look at a special method for solving homogeneous differential equations a first. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g (x, y) is. A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by making the substitution. Homogenous differential equations are equations that.
Here We Look At A Special Method For Solving Homogeneous Differential Equations A First.
A homogeneous differential equation can often be solved by making the substitution. Homogenous differential equations are equations that contain a homogenous. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. A differential equation of the form dy/dx = f (x, y)/ g (x, y) is.