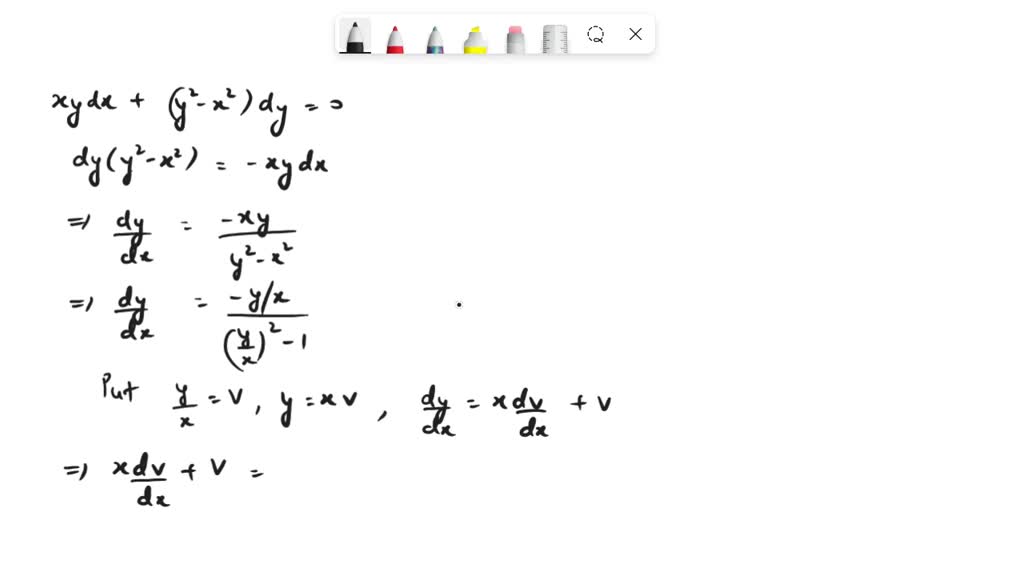Solve Homogeneous Differential Equation - In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential. The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0. Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. Learn how to identify and solve homogeneous differential equations of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx, where f and g are homogeneous. If $$$ g(x)=0 $$$, the equation is homogeneous; An example will show how it is all done: Homogeneous and nonhomogeneous differential equations:
In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. An example will show how it is all done: The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0. Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential. Homogeneous and nonhomogeneous differential equations: If $$$ g(x)=0 $$$, the equation is homogeneous; Learn how to identify and solve homogeneous differential equations of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx, where f and g are homogeneous. Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation.
Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0. An example will show how it is all done: Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. Homogeneous and nonhomogeneous differential equations: If $$$ g(x)=0 $$$, the equation is homogeneous; Learn how to identify and solve homogeneous differential equations of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx, where f and g are homogeneous.
[Solved] Solve the HOMOGENEOUS differential equation in step by step
Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. Homogeneous and nonhomogeneous differential equations: An example will show how it is all done: Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential. The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0.
[Solved] Solve the HOMOGENEOUS differential equation in step by step
Learn how to identify and solve homogeneous differential equations of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx, where f and g are homogeneous. Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0. Homogeneous and nonhomogeneous differential.
SOLUTION How to make differential equation from general equation what
If $$$ g(x)=0 $$$, the equation is homogeneous; The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0. An example will show how it is all done: Homogeneous and nonhomogeneous differential equations: In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher.
SOLUTION How to make differential equation from general equation what
Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. An example will show how it is all done: If $$$ g(x)=0 $$$, the equation is homogeneous; Homogeneous and nonhomogeneous differential equations:
SOLUTION How to make differential equation from general equation what
Homogeneous and nonhomogeneous differential equations: Learn how to identify and solve homogeneous differential equations of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx, where f and g are homogeneous. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. An example will show how it is all done: If $$$ g(x)=0 $$$, the equation is.
Homogeneous Differential Equations HandWritten Notes in JPG Format
Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. Let us learn more about the homogeneous.
Homogeneous Differential Equation2 PDF Waves Applied And
Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential. Learn how to identify and solve homogeneous differential equations of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx, where f and g are homogeneous. Homogeneous and nonhomogeneous differential equations: Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. An example will show how it is.
Homogeneous Differential Equation Know types, Steps to solve
If $$$ g(x)=0 $$$, the equation is homogeneous; In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential. Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. Homogeneous and nonhomogeneous differential equations:
SOLUTION How to make differential equation from general equation what
Homogeneous and nonhomogeneous differential equations: If $$$ g(x)=0 $$$, the equation is homogeneous; An example will show how it is all done: Learn how to identify and solve homogeneous differential equations of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx, where f and g are homogeneous. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to.
SOLVED In the given equation , solve the homogeneous differential
Learn how to identify and solve homogeneous differential equations of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx, where f and g are homogeneous. Homogeneous and nonhomogeneous differential equations: Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential. The general form of a homogeneous differential.
Using Y = Vx And Dy Dx = V + X Dv Dx We Can Solve The Differential Equation.
Homogeneous and nonhomogeneous differential equations: An example will show how it is all done: Learn how to identify and solve homogeneous differential equations of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx, where f and g are homogeneous. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher.
If $$$ G(X)=0 $$$, The Equation Is Homogeneous;
The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0. Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential.