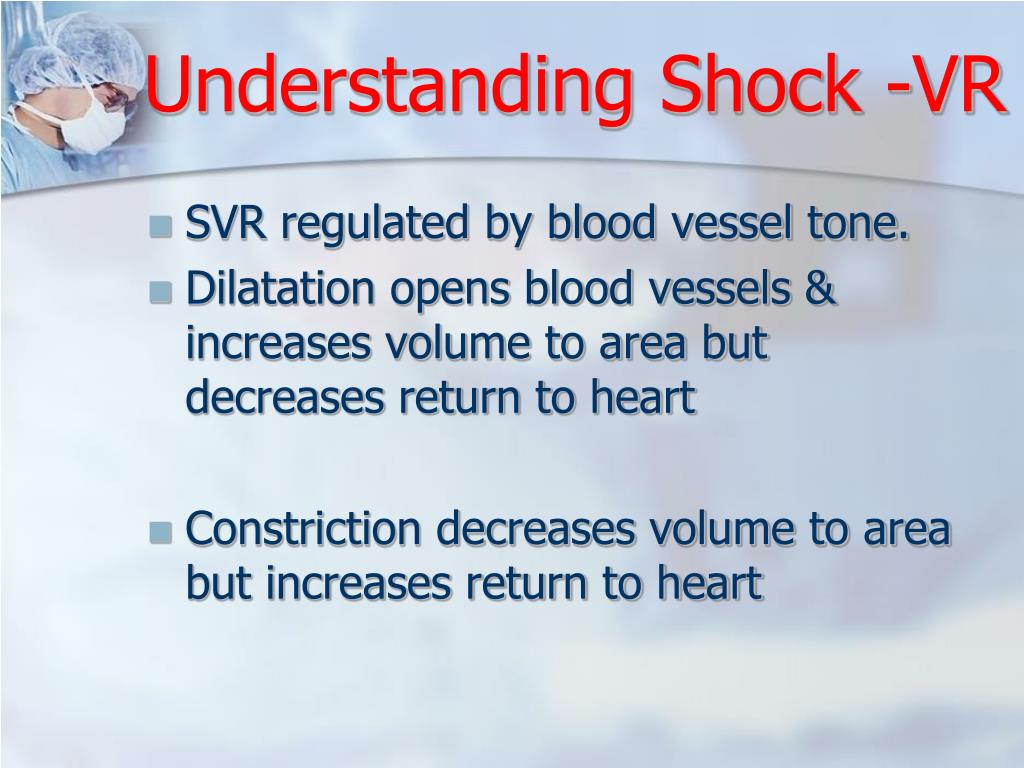
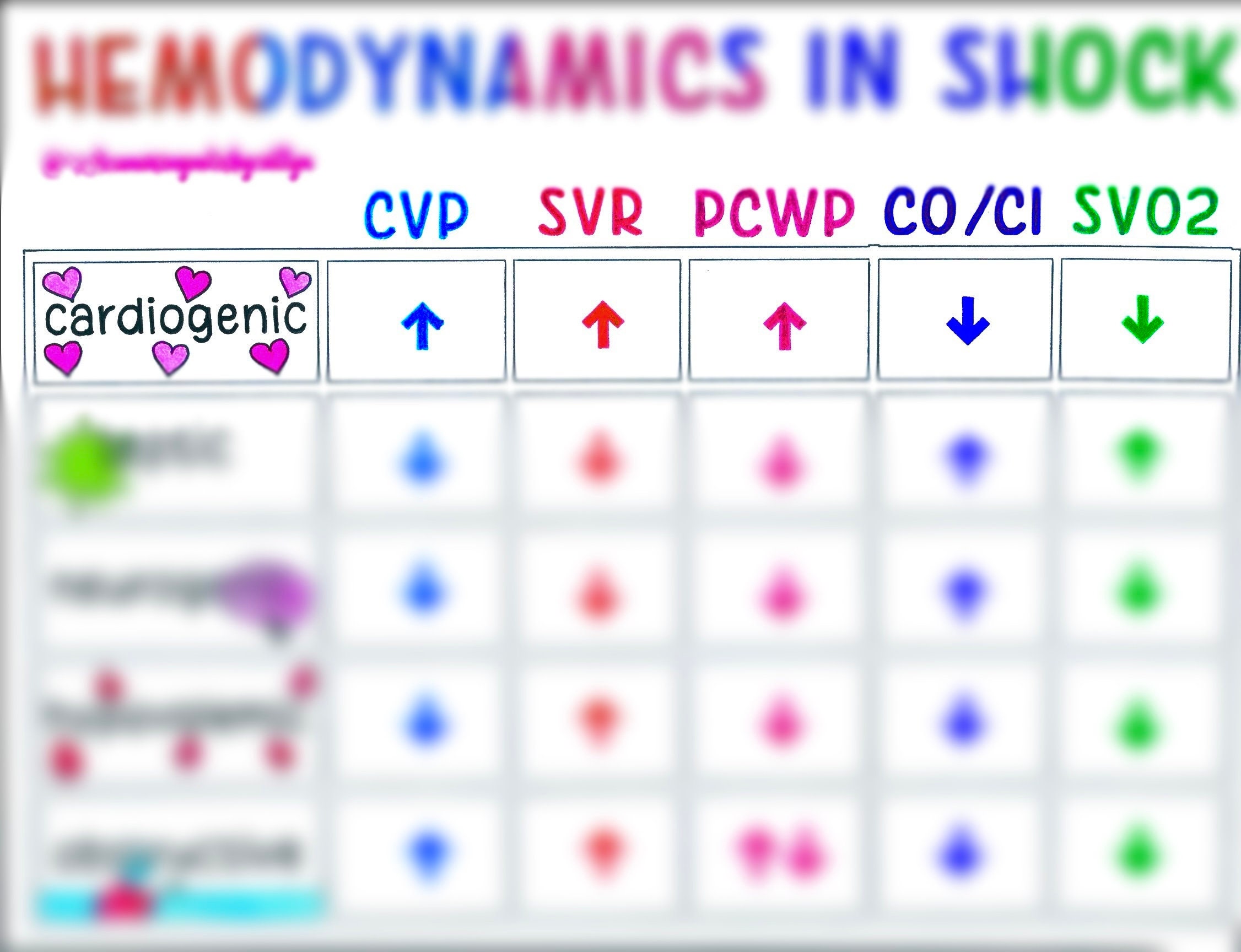
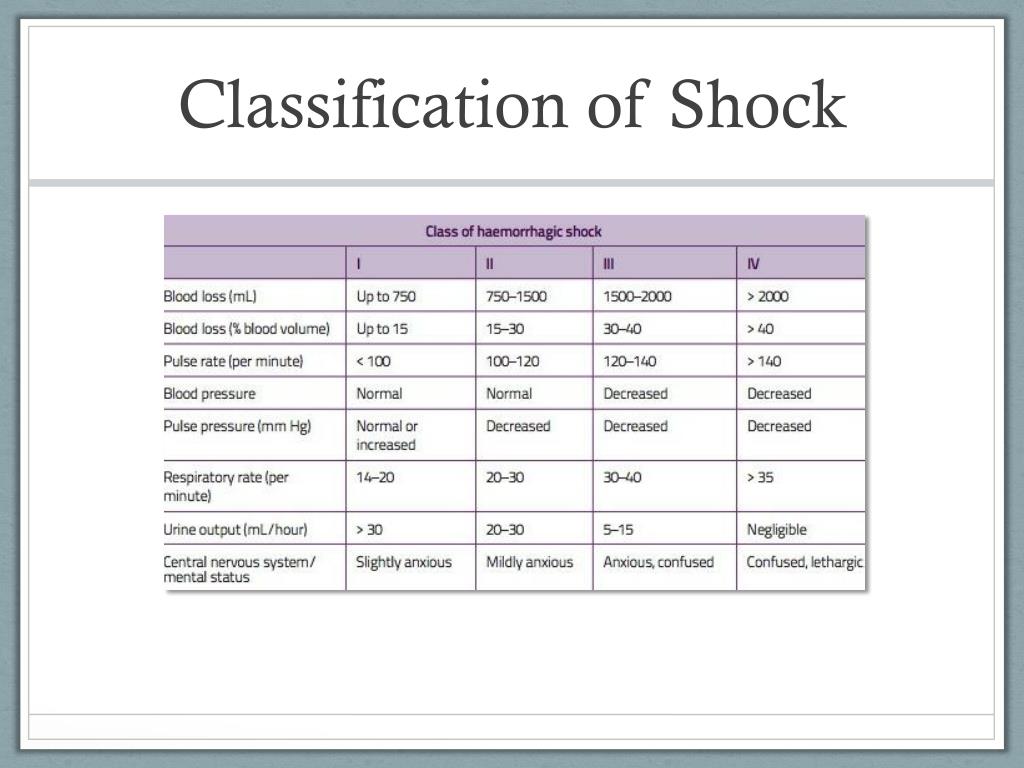
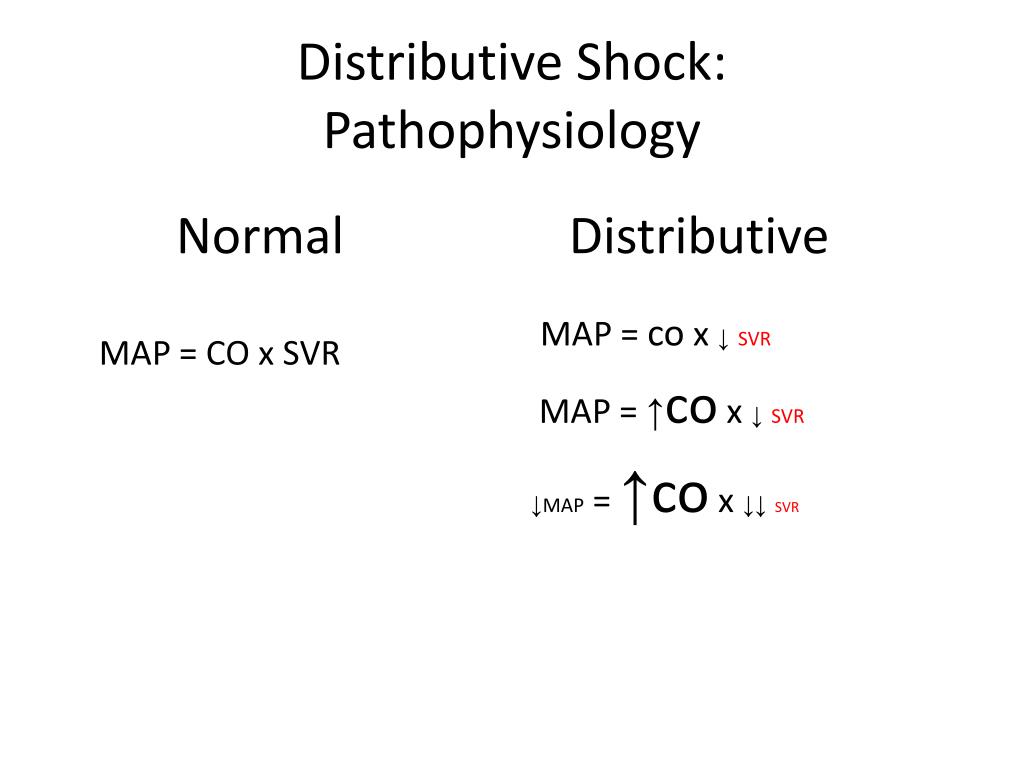
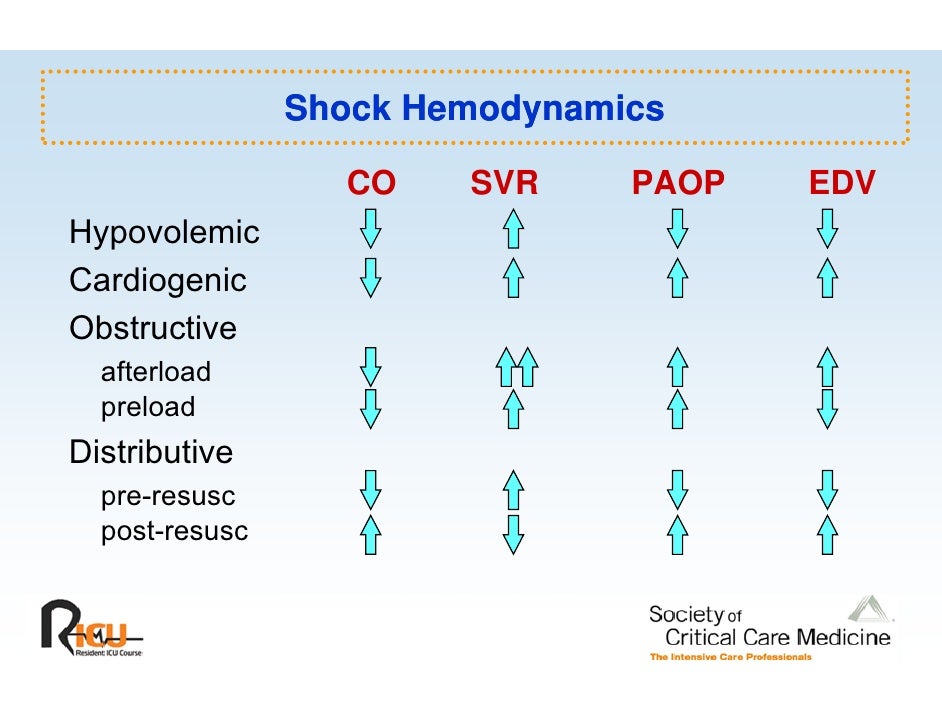
Shock Ci And Svr Differential - Systemic vascular resistance (svr) is proportional to vessel length and blood viscosity, while it is inversely proportional to vessel. Both cardiac output (co) and systemic vascular resistance (svr) contribute to bp, as demonstrated by the equation bp = co × svr. In this study, we sought to determine the accuracy and interobserver variability of pediatric physician's assessment of ci and.
Systemic vascular resistance (svr) is proportional to vessel length and blood viscosity, while it is inversely proportional to vessel. Both cardiac output (co) and systemic vascular resistance (svr) contribute to bp, as demonstrated by the equation bp = co × svr. In this study, we sought to determine the accuracy and interobserver variability of pediatric physician's assessment of ci and.
Systemic vascular resistance (svr) is proportional to vessel length and blood viscosity, while it is inversely proportional to vessel. Both cardiac output (co) and systemic vascular resistance (svr) contribute to bp, as demonstrated by the equation bp = co × svr. In this study, we sought to determine the accuracy and interobserver variability of pediatric physician's assessment of ci and.
Figure S1 CISVR plot for all patients Note Different perfusion
Systemic vascular resistance (svr) is proportional to vessel length and blood viscosity, while it is inversely proportional to vessel. In this study, we sought to determine the accuracy and interobserver variability of pediatric physician's assessment of ci and. Both cardiac output (co) and systemic vascular resistance (svr) contribute to bp, as demonstrated by the equation bp = co × svr.
Shock
In this study, we sought to determine the accuracy and interobserver variability of pediatric physician's assessment of ci and. Systemic vascular resistance (svr) is proportional to vessel length and blood viscosity, while it is inversely proportional to vessel. Both cardiac output (co) and systemic vascular resistance (svr) contribute to bp, as demonstrated by the equation bp = co × svr.
PPT Shock PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5178538
Both cardiac output (co) and systemic vascular resistance (svr) contribute to bp, as demonstrated by the equation bp = co × svr. In this study, we sought to determine the accuracy and interobserver variability of pediatric physician's assessment of ci and. Systemic vascular resistance (svr) is proportional to vessel length and blood viscosity, while it is inversely proportional to vessel.
Types of Shock Concise Medical Knowledge
Systemic vascular resistance (svr) is proportional to vessel length and blood viscosity, while it is inversely proportional to vessel. Both cardiac output (co) and systemic vascular resistance (svr) contribute to bp, as demonstrated by the equation bp = co × svr. In this study, we sought to determine the accuracy and interobserver variability of pediatric physician's assessment of ci and.
Hemodynamics in Shock Etsy
In this study, we sought to determine the accuracy and interobserver variability of pediatric physician's assessment of ci and. Systemic vascular resistance (svr) is proportional to vessel length and blood viscosity, while it is inversely proportional to vessel. Both cardiac output (co) and systemic vascular resistance (svr) contribute to bp, as demonstrated by the equation bp = co × svr.
PPT Shock and Trauma Resuscitation PowerPoint Presentation, free
Both cardiac output (co) and systemic vascular resistance (svr) contribute to bp, as demonstrated by the equation bp = co × svr. Systemic vascular resistance (svr) is proportional to vessel length and blood viscosity, while it is inversely proportional to vessel. In this study, we sought to determine the accuracy and interobserver variability of pediatric physician's assessment of ci and.
USMLE wizard Hemodynamics in Shock Notes Distributive Shock...
In this study, we sought to determine the accuracy and interobserver variability of pediatric physician's assessment of ci and. Systemic vascular resistance (svr) is proportional to vessel length and blood viscosity, while it is inversely proportional to vessel. Both cardiac output (co) and systemic vascular resistance (svr) contribute to bp, as demonstrated by the equation bp = co × svr.
Pediatric Shock Ii
In this study, we sought to determine the accuracy and interobserver variability of pediatric physician's assessment of ci and. Both cardiac output (co) and systemic vascular resistance (svr) contribute to bp, as demonstrated by the equation bp = co × svr. Systemic vascular resistance (svr) is proportional to vessel length and blood viscosity, while it is inversely proportional to vessel.
Map Co X Svr Maping Resources
In this study, we sought to determine the accuracy and interobserver variability of pediatric physician's assessment of ci and. Systemic vascular resistance (svr) is proportional to vessel length and blood viscosity, while it is inversely proportional to vessel. Both cardiac output (co) and systemic vascular resistance (svr) contribute to bp, as demonstrated by the equation bp = co × svr.
shock
Both cardiac output (co) and systemic vascular resistance (svr) contribute to bp, as demonstrated by the equation bp = co × svr. Systemic vascular resistance (svr) is proportional to vessel length and blood viscosity, while it is inversely proportional to vessel. In this study, we sought to determine the accuracy and interobserver variability of pediatric physician's assessment of ci and.
In This Study, We Sought To Determine The Accuracy And Interobserver Variability Of Pediatric Physician's Assessment Of Ci And.
Both cardiac output (co) and systemic vascular resistance (svr) contribute to bp, as demonstrated by the equation bp = co × svr. Systemic vascular resistance (svr) is proportional to vessel length and blood viscosity, while it is inversely proportional to vessel.