Process That Inhibits Or Prevents The Growth Of Pathogenic Organisms - Process that kills or destroys pathogenic. Process that destroys or kills pathogens organisms,not always effective agains spores and viruses. A substance that prevents or inhibits the growth of microorganisms, especially bacteria. A cidal agent kills the organism while a static agent inhibits the organism's growth long enough for body defenses to remove it. Examples include refrigeration and freezing. Low temperature inhibits microbial growth by slowing down microbial metabolism. Prevent or inhibit growth of pathogenic organisms but are not effective against spores and viruses. A cidal agent kills the organism while a static agent inhibits the organism's growth long enough for body defenses to remove it.
Prevent or inhibit growth of pathogenic organisms but are not effective against spores and viruses. Examples include refrigeration and freezing. Low temperature inhibits microbial growth by slowing down microbial metabolism. A cidal agent kills the organism while a static agent inhibits the organism's growth long enough for body defenses to remove it. Process that destroys or kills pathogens organisms,not always effective agains spores and viruses. Process that kills or destroys pathogenic. A substance that prevents or inhibits the growth of microorganisms, especially bacteria. A cidal agent kills the organism while a static agent inhibits the organism's growth long enough for body defenses to remove it.
Prevent or inhibit growth of pathogenic organisms but are not effective against spores and viruses. A substance that prevents or inhibits the growth of microorganisms, especially bacteria. A cidal agent kills the organism while a static agent inhibits the organism's growth long enough for body defenses to remove it. Process that kills or destroys pathogenic. A cidal agent kills the organism while a static agent inhibits the organism's growth long enough for body defenses to remove it. Process that destroys or kills pathogens organisms,not always effective agains spores and viruses. Low temperature inhibits microbial growth by slowing down microbial metabolism. Examples include refrigeration and freezing.
Non Pathogenic
A cidal agent kills the organism while a static agent inhibits the organism's growth long enough for body defenses to remove it. Examples include refrigeration and freezing. A cidal agent kills the organism while a static agent inhibits the organism's growth long enough for body defenses to remove it. Process that destroys or kills pathogens organisms,not always effective agains spores.
Non Pathogenic
Examples include refrigeration and freezing. Low temperature inhibits microbial growth by slowing down microbial metabolism. A substance that prevents or inhibits the growth of microorganisms, especially bacteria. Process that kills or destroys pathogenic. Process that destroys or kills pathogens organisms,not always effective agains spores and viruses.
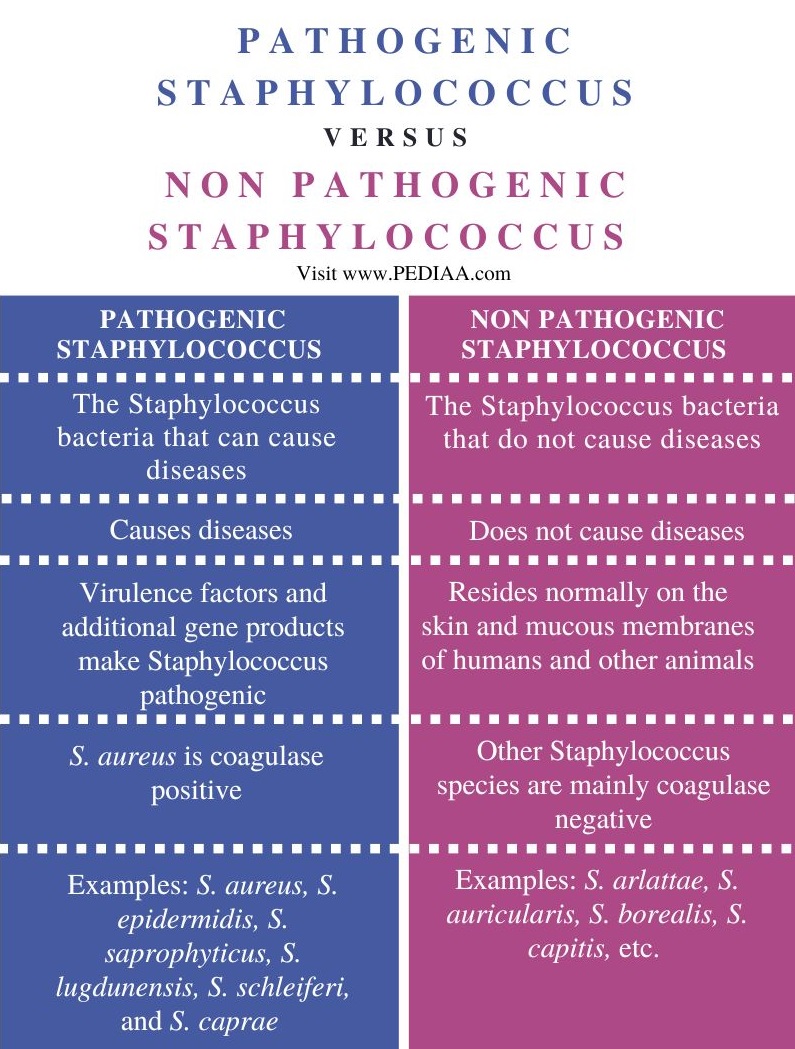
What is the Difference Between Pathogenic and Nonpathogenic
A cidal agent kills the organism while a static agent inhibits the organism's growth long enough for body defenses to remove it. Examples include refrigeration and freezing. A substance that prevents or inhibits the growth of microorganisms, especially bacteria. Process that destroys or kills pathogens organisms,not always effective agains spores and viruses. Process that kills or destroys pathogenic.
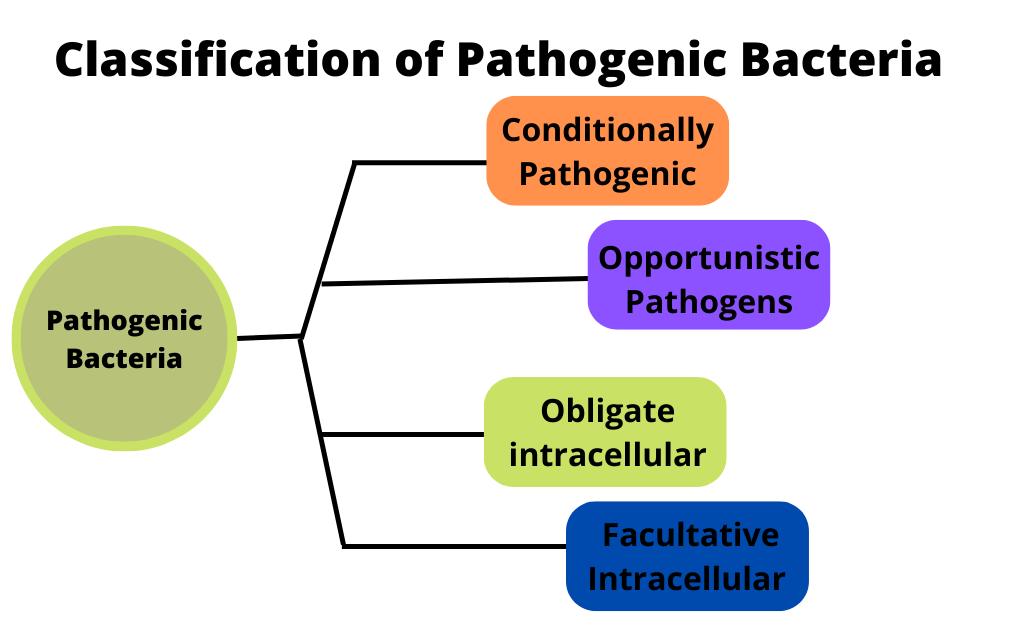
Pathogenic targeted by complex cellular communications
A cidal agent kills the organism while a static agent inhibits the organism's growth long enough for body defenses to remove it. A substance that prevents or inhibits the growth of microorganisms, especially bacteria. Prevent or inhibit growth of pathogenic organisms but are not effective against spores and viruses. Low temperature inhibits microbial growth by slowing down microbial metabolism. A.
Difference Between Pathogenic and Nonpathogenic Bacteria
A cidal agent kills the organism while a static agent inhibits the organism's growth long enough for body defenses to remove it. Prevent or inhibit growth of pathogenic organisms but are not effective against spores and viruses. Examples include refrigeration and freezing. Low temperature inhibits microbial growth by slowing down microbial metabolism. Process that destroys or kills pathogens organisms,not always.
Non Pathogenic
A cidal agent kills the organism while a static agent inhibits the organism's growth long enough for body defenses to remove it. Process that destroys or kills pathogens organisms,not always effective agains spores and viruses. Process that kills or destroys pathogenic. A cidal agent kills the organism while a static agent inhibits the organism's growth long enough for body defenses.
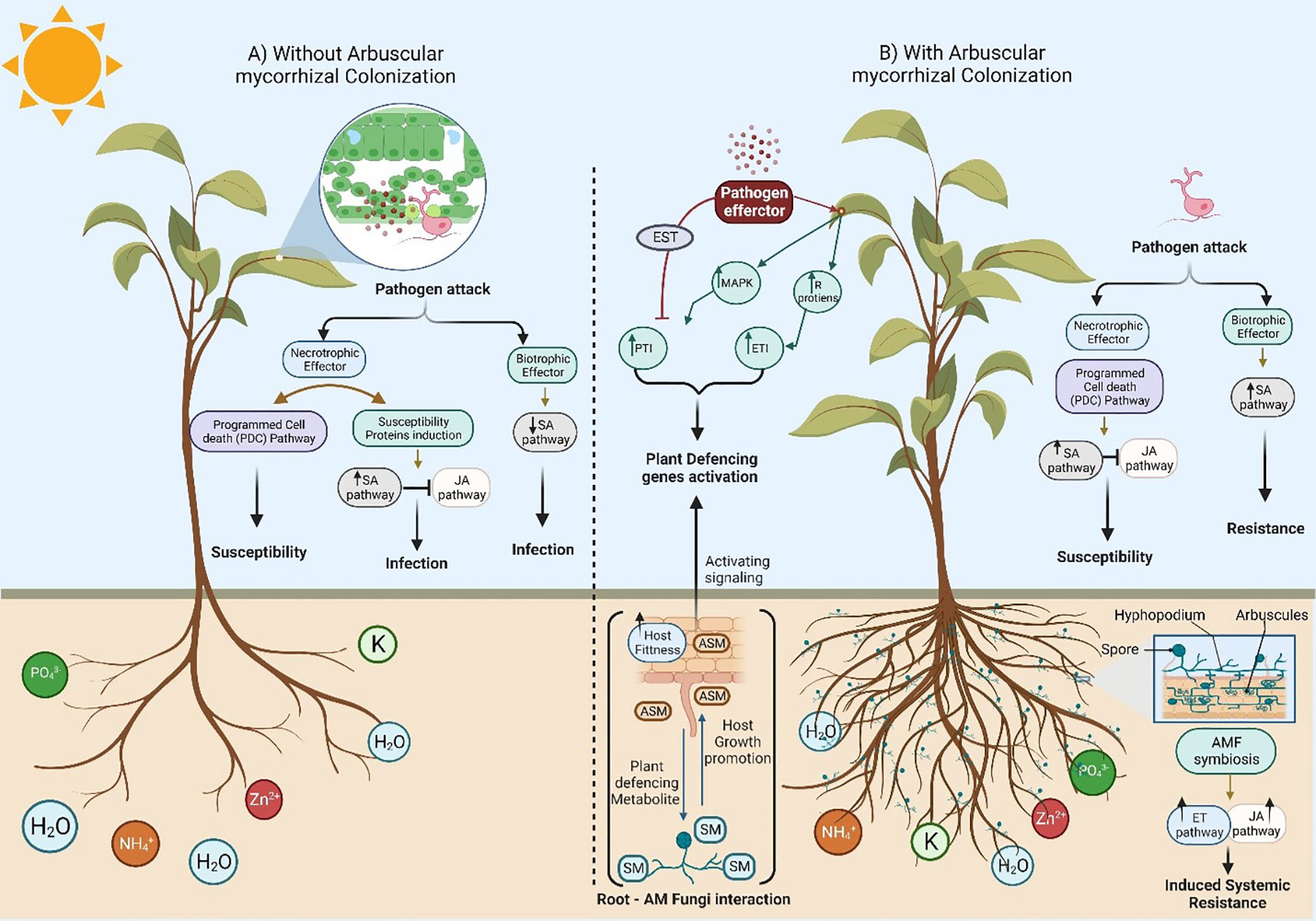
The possible mechanisms involved in growth inhibition of plant
Prevent or inhibit growth of pathogenic organisms but are not effective against spores and viruses. Process that destroys or kills pathogens organisms,not always effective agains spores and viruses. A cidal agent kills the organism while a static agent inhibits the organism's growth long enough for body defenses to remove it. Examples include refrigeration and freezing. Process that kills or destroys.
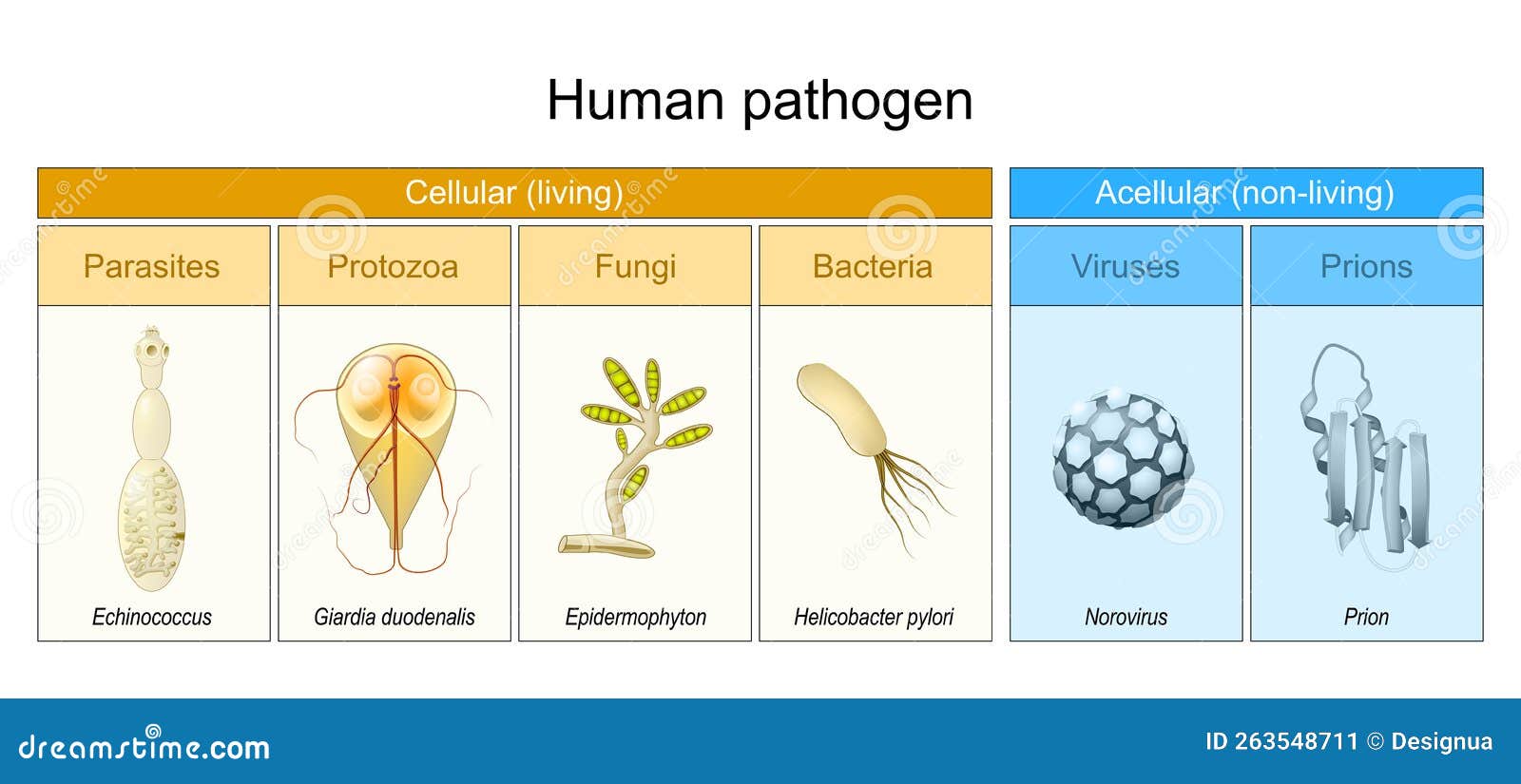
Pathogenic organisms (categorized into bacteria, parasites, and
Process that kills or destroys pathogenic. A cidal agent kills the organism while a static agent inhibits the organism's growth long enough for body defenses to remove it. A substance that prevents or inhibits the growth of microorganisms, especially bacteria. Process that destroys or kills pathogens organisms,not always effective agains spores and viruses. Examples include refrigeration and freezing.
Examples of harmful and pathogenic organisms Download Table
Low temperature inhibits microbial growth by slowing down microbial metabolism. Process that destroys or kills pathogens organisms,not always effective agains spores and viruses. Process that kills or destroys pathogenic. A cidal agent kills the organism while a static agent inhibits the organism's growth long enough for body defenses to remove it. Examples include refrigeration and freezing.
Distribution of pathogenic organisms in different periods. Download
A substance that prevents or inhibits the growth of microorganisms, especially bacteria. Process that destroys or kills pathogens organisms,not always effective agains spores and viruses. Prevent or inhibit growth of pathogenic organisms but are not effective against spores and viruses. A cidal agent kills the organism while a static agent inhibits the organism's growth long enough for body defenses to.
Low Temperature Inhibits Microbial Growth By Slowing Down Microbial Metabolism.
A substance that prevents or inhibits the growth of microorganisms, especially bacteria. Prevent or inhibit growth of pathogenic organisms but are not effective against spores and viruses. A cidal agent kills the organism while a static agent inhibits the organism's growth long enough for body defenses to remove it. Examples include refrigeration and freezing.
A Cidal Agent Kills The Organism While A Static Agent Inhibits The Organism's Growth Long Enough For Body Defenses To Remove It.
Process that destroys or kills pathogens organisms,not always effective agains spores and viruses. Process that kills or destroys pathogenic.