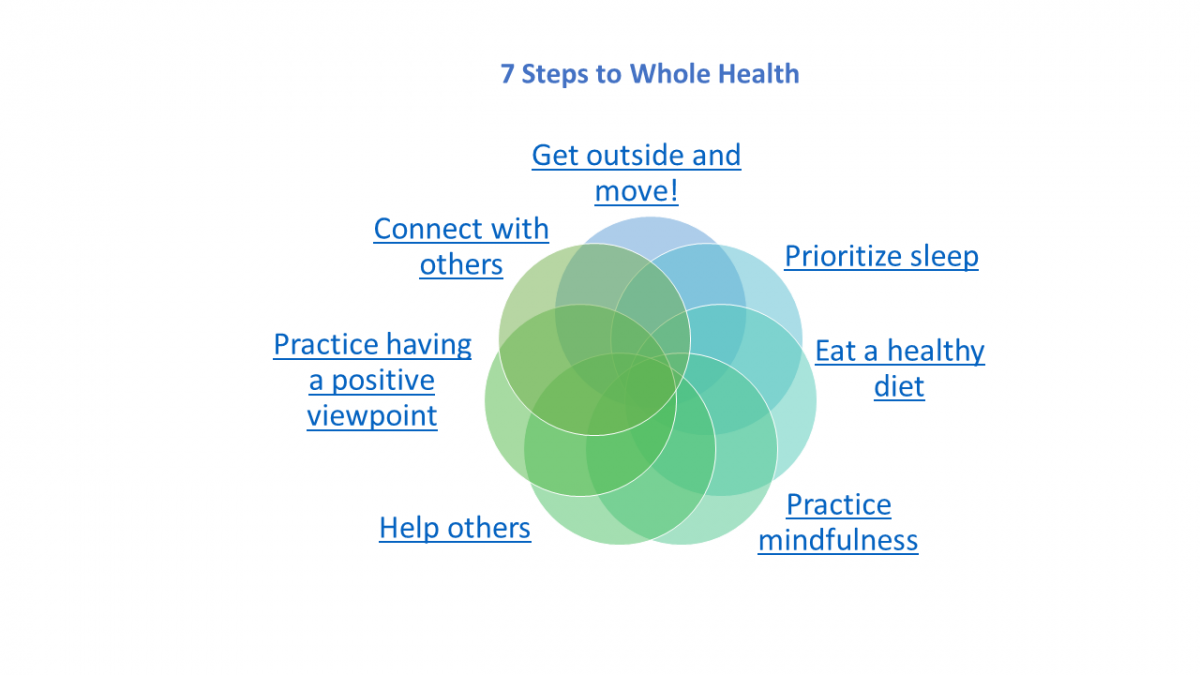
Primary Prevention Mental Health - Primary prevention occurs before any evidence of disease and aims to reduce or eliminate causal risk factors, prevent onset,. Primary prevention occurs before any evidence of disease and aims to reduce or eliminate causal risk factors, prevent onset, and thus reduce. Understanding the three levels of prevention in mental health. With the advent of digital technology and simultaneous traction on mental health promotion and prevention interventions, preventive. Primary mental health prevention can be described as the intentional interventions in reducing risk factors for mental health. Primary prevention—the avoidance of biological, social, and environmental factors that cause illness and disease (winslow, 1920)—is the. Classification as primary, secondary, or tertiary prevention is based on when during the course of disease the intervention is provided.
With the advent of digital technology and simultaneous traction on mental health promotion and prevention interventions, preventive. Primary mental health prevention can be described as the intentional interventions in reducing risk factors for mental health. Classification as primary, secondary, or tertiary prevention is based on when during the course of disease the intervention is provided. Primary prevention occurs before any evidence of disease and aims to reduce or eliminate causal risk factors, prevent onset, and thus reduce. Primary prevention occurs before any evidence of disease and aims to reduce or eliminate causal risk factors, prevent onset,. Understanding the three levels of prevention in mental health. Primary prevention—the avoidance of biological, social, and environmental factors that cause illness and disease (winslow, 1920)—is the.
Primary prevention occurs before any evidence of disease and aims to reduce or eliminate causal risk factors, prevent onset,. Primary prevention occurs before any evidence of disease and aims to reduce or eliminate causal risk factors, prevent onset, and thus reduce. Understanding the three levels of prevention in mental health. Primary prevention—the avoidance of biological, social, and environmental factors that cause illness and disease (winslow, 1920)—is the. Primary mental health prevention can be described as the intentional interventions in reducing risk factors for mental health. With the advent of digital technology and simultaneous traction on mental health promotion and prevention interventions, preventive. Classification as primary, secondary, or tertiary prevention is based on when during the course of disease the intervention is provided.
What Is Primary Prevention Of Mental Health? Dreamscure
Understanding the three levels of prevention in mental health. Primary prevention—the avoidance of biological, social, and environmental factors that cause illness and disease (winslow, 1920)—is the. Classification as primary, secondary, or tertiary prevention is based on when during the course of disease the intervention is provided. Primary mental health prevention can be described as the intentional interventions in reducing risk.
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Prevention Campus Advocacy, Resources
Primary prevention—the avoidance of biological, social, and environmental factors that cause illness and disease (winslow, 1920)—is the. Primary prevention occurs before any evidence of disease and aims to reduce or eliminate causal risk factors, prevent onset, and thus reduce. Primary prevention occurs before any evidence of disease and aims to reduce or eliminate causal risk factors, prevent onset,. Classification as.
Understanding primary prevention SAFEU
Understanding the three levels of prevention in mental health. With the advent of digital technology and simultaneous traction on mental health promotion and prevention interventions, preventive. Primary prevention occurs before any evidence of disease and aims to reduce or eliminate causal risk factors, prevent onset, and thus reduce. Classification as primary, secondary, or tertiary prevention is based on when during.
2o C Parte 3 Primary Prevention Mental Health Programs
Understanding the three levels of prevention in mental health. Primary mental health prevention can be described as the intentional interventions in reducing risk factors for mental health. Primary prevention occurs before any evidence of disease and aims to reduce or eliminate causal risk factors, prevent onset, and thus reduce. Primary prevention occurs before any evidence of disease and aims to.
2o C Parte 3 Primary Prevention Mental Health Programs
Primary mental health prevention can be described as the intentional interventions in reducing risk factors for mental health. With the advent of digital technology and simultaneous traction on mental health promotion and prevention interventions, preventive. Primary prevention occurs before any evidence of disease and aims to reduce or eliminate causal risk factors, prevent onset, and thus reduce. Primary prevention occurs.
Mental Health Promotion and Suicide Prevention
Understanding the three levels of prevention in mental health. Primary mental health prevention can be described as the intentional interventions in reducing risk factors for mental health. Classification as primary, secondary, or tertiary prevention is based on when during the course of disease the intervention is provided. Primary prevention occurs before any evidence of disease and aims to reduce or.
(PDF) Primary Prevention Mental Health Programs for Children and
Understanding the three levels of prevention in mental health. Primary prevention—the avoidance of biological, social, and environmental factors that cause illness and disease (winslow, 1920)—is the. Primary prevention occurs before any evidence of disease and aims to reduce or eliminate causal risk factors, prevent onset, and thus reduce. Classification as primary, secondary, or tertiary prevention is based on when during.
Prevention and Promotion Department of Mental Health
Primary mental health prevention can be described as the intentional interventions in reducing risk factors for mental health. Primary prevention occurs before any evidence of disease and aims to reduce or eliminate causal risk factors, prevent onset, and thus reduce. Classification as primary, secondary, or tertiary prevention is based on when during the course of disease the intervention is provided..
2o C Parte 3 Primary Prevention Mental Health Programs
Classification as primary, secondary, or tertiary prevention is based on when during the course of disease the intervention is provided. Primary mental health prevention can be described as the intentional interventions in reducing risk factors for mental health. Primary prevention occurs before any evidence of disease and aims to reduce or eliminate causal risk factors, prevent onset, and thus reduce..
2o C Parte 3 Primary Prevention Mental Health Programs
Primary mental health prevention can be described as the intentional interventions in reducing risk factors for mental health. Primary prevention—the avoidance of biological, social, and environmental factors that cause illness and disease (winslow, 1920)—is the. Classification as primary, secondary, or tertiary prevention is based on when during the course of disease the intervention is provided. Understanding the three levels of.
With The Advent Of Digital Technology And Simultaneous Traction On Mental Health Promotion And Prevention Interventions, Preventive.
Primary mental health prevention can be described as the intentional interventions in reducing risk factors for mental health. Primary prevention occurs before any evidence of disease and aims to reduce or eliminate causal risk factors, prevent onset,. Classification as primary, secondary, or tertiary prevention is based on when during the course of disease the intervention is provided. Primary prevention occurs before any evidence of disease and aims to reduce or eliminate causal risk factors, prevent onset, and thus reduce.
Understanding The Three Levels Of Prevention In Mental Health.
Primary prevention—the avoidance of biological, social, and environmental factors that cause illness and disease (winslow, 1920)—is the.