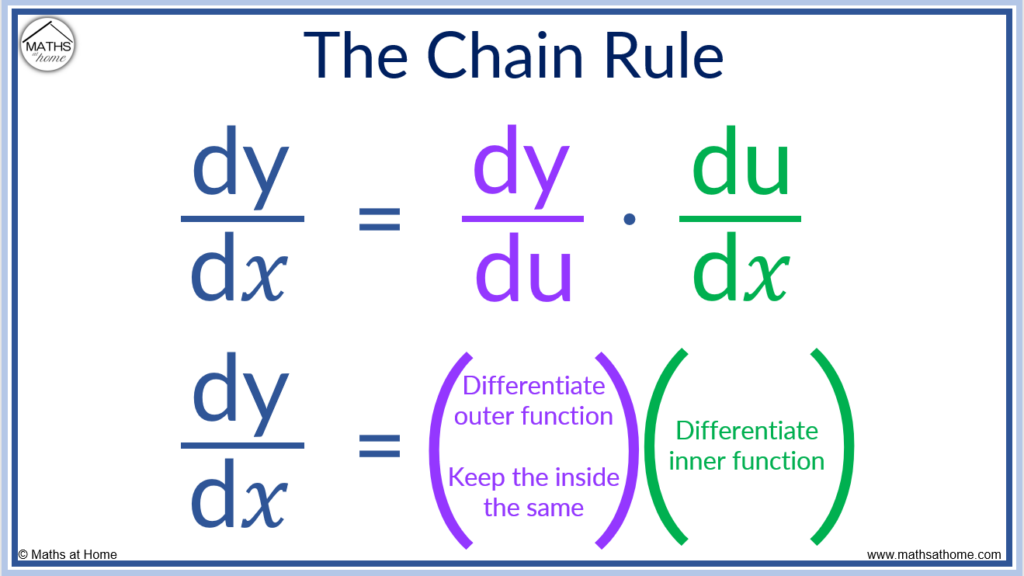
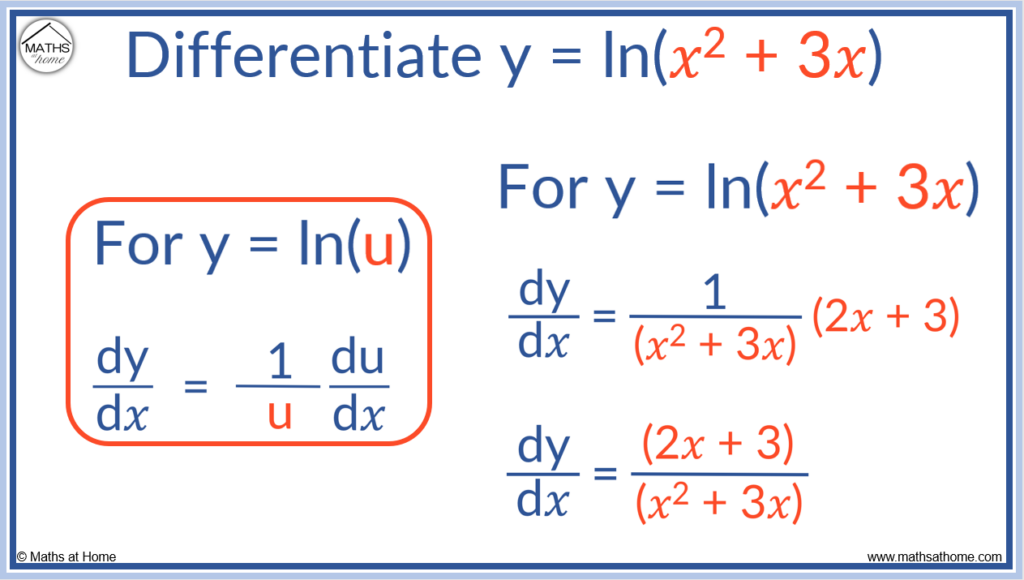
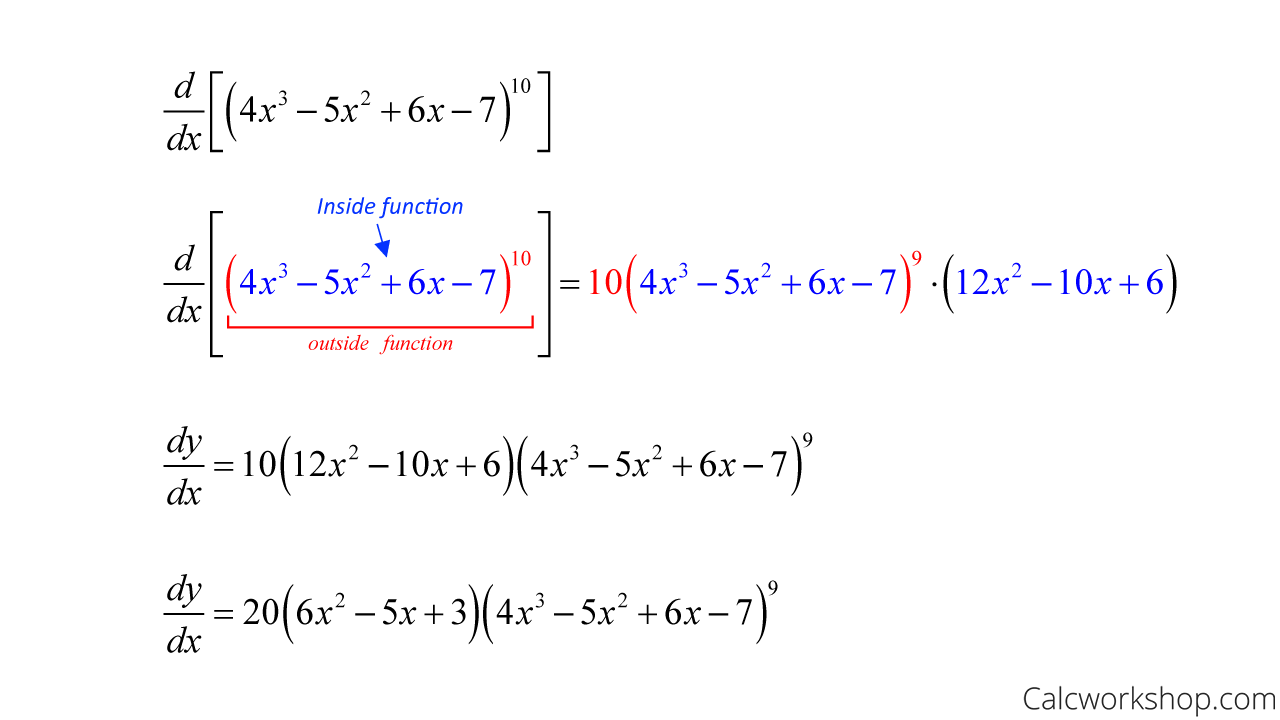Matrix Differentiation Chain Rule - Rk × k → rn × n as a(b) = c ′ bc. Use the chain rule to find relations between different partial derivatives of a function. The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. Denote also g(a) = [gij(a)], a = [aij], c = [cij]. The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. The purpose of this document is to help you learn to take derivatives of vectors, matrices, and. My problem is computing $\frac{\partial h}{\partial w_1}$.
The purpose of this document is to help you learn to take derivatives of vectors, matrices, and. Use the chain rule to find relations between different partial derivatives of a function. Denote also g(a) = [gij(a)], a = [aij], c = [cij]. The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. My problem is computing $\frac{\partial h}{\partial w_1}$. Rk × k → rn × n as a(b) = c ′ bc. The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point.
The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. The purpose of this document is to help you learn to take derivatives of vectors, matrices, and. Use the chain rule to find relations between different partial derivatives of a function. The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. Rk × k → rn × n as a(b) = c ′ bc. My problem is computing $\frac{\partial h}{\partial w_1}$. Denote also g(a) = [gij(a)], a = [aij], c = [cij].
calculus Automatic Differentiation Chain Rule Question
Denote also g(a) = [gij(a)], a = [aij], c = [cij]. The purpose of this document is to help you learn to take derivatives of vectors, matrices, and. My problem is computing $\frac{\partial h}{\partial w_1}$. The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. Rk × k → rn × n as a(b).
Chain Rule Applications of Chain Rule PDF Subtraction Syntax (Logic)
The purpose of this document is to help you learn to take derivatives of vectors, matrices, and. The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. Rk × k → rn × n as a(b) = c ′ bc. Use the chain rule to find relations between different partial derivatives of a function..
Lecture 2 Continue Intro Diff and Chain Rule PDF
Use the chain rule to find relations between different partial derivatives of a function. The purpose of this document is to help you learn to take derivatives of vectors, matrices, and. The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. My problem is computing $\frac{\partial h}{\partial w_1}$. Denote also g(a) = [gij(a)], a.
The Chain Rule Made Easy Examples and Solutions
The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. My problem is computing $\frac{\partial h}{\partial w_1}$. The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. The purpose of this document is to help you learn to take derivatives of vectors, matrices, and. Denote also g(a) =.
The Chain Rule Made Easy Examples and Solutions
Use the chain rule to find relations between different partial derivatives of a function. Rk × k → rn × n as a(b) = c ′ bc. The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. The.
14.5 The Chain Rule PDF Derivative Function (Mathematics)
Use the chain rule to find relations between different partial derivatives of a function. The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. Rk × k → rn × n as a(b) = c ′ bc. The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. Denote.
M53 Lec2.2 The Chain Rule and Differentiability PDF
Denote also g(a) = [gij(a)], a = [aij], c = [cij]. The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. My problem is computing $\frac{\partial h}{\partial w_1}$. Use the chain rule to find relations between different partial.
Formula of Differentiation by chain rule With solved example
Denote also g(a) = [gij(a)], a = [aij], c = [cij]. Rk × k → rn × n as a(b) = c ′ bc. My problem is computing $\frac{\partial h}{\partial w_1}$. The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. Use the chain rule to find relations between different partial derivatives of a.
The Chain Rule Made Easy Examples and Solutions
The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. The purpose of this document is to help you learn to take derivatives of vectors, matrices, and. Denote also g(a) = [gij(a)], a = [aij], c = [cij]. Use the chain rule to find relations between different partial derivatives of a function. Rk ×.
Chain Rule Differentiation Benytr
The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. Rk × k → rn × n as a(b) = c ′ bc. The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. The purpose of this document is to help you learn to take derivatives of vectors,.
The Matrices Df(Y) 2 M(N;P) And Dr(X) 2M(P;M) Combine To The Matrix Product Dfdrat A Point.
The matrices df(y) 2 m(n;p) and dr(x) 2m(p;m) combine to the matrix product dfdrat a point. The purpose of this document is to help you learn to take derivatives of vectors, matrices, and. My problem is computing $\frac{\partial h}{\partial w_1}$. Rk × k → rn × n as a(b) = c ′ bc.
Use The Chain Rule To Find Relations Between Different Partial Derivatives Of A Function.
Denote also g(a) = [gij(a)], a = [aij], c = [cij].