Math Differentials - In this section we study what differential equations are, how to verify their. In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function = with. Given a function \(y = f\left( x \right)\) we call \(dy\) and \(dx\) differentials.
Given a function \(y = f\left( x \right)\) we call \(dy\) and \(dx\) differentials. In this section we study what differential equations are, how to verify their. In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function = with.
In this section we study what differential equations are, how to verify their. In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function = with. Given a function \(y = f\left( x \right)\) we call \(dy\) and \(dx\) differentials.
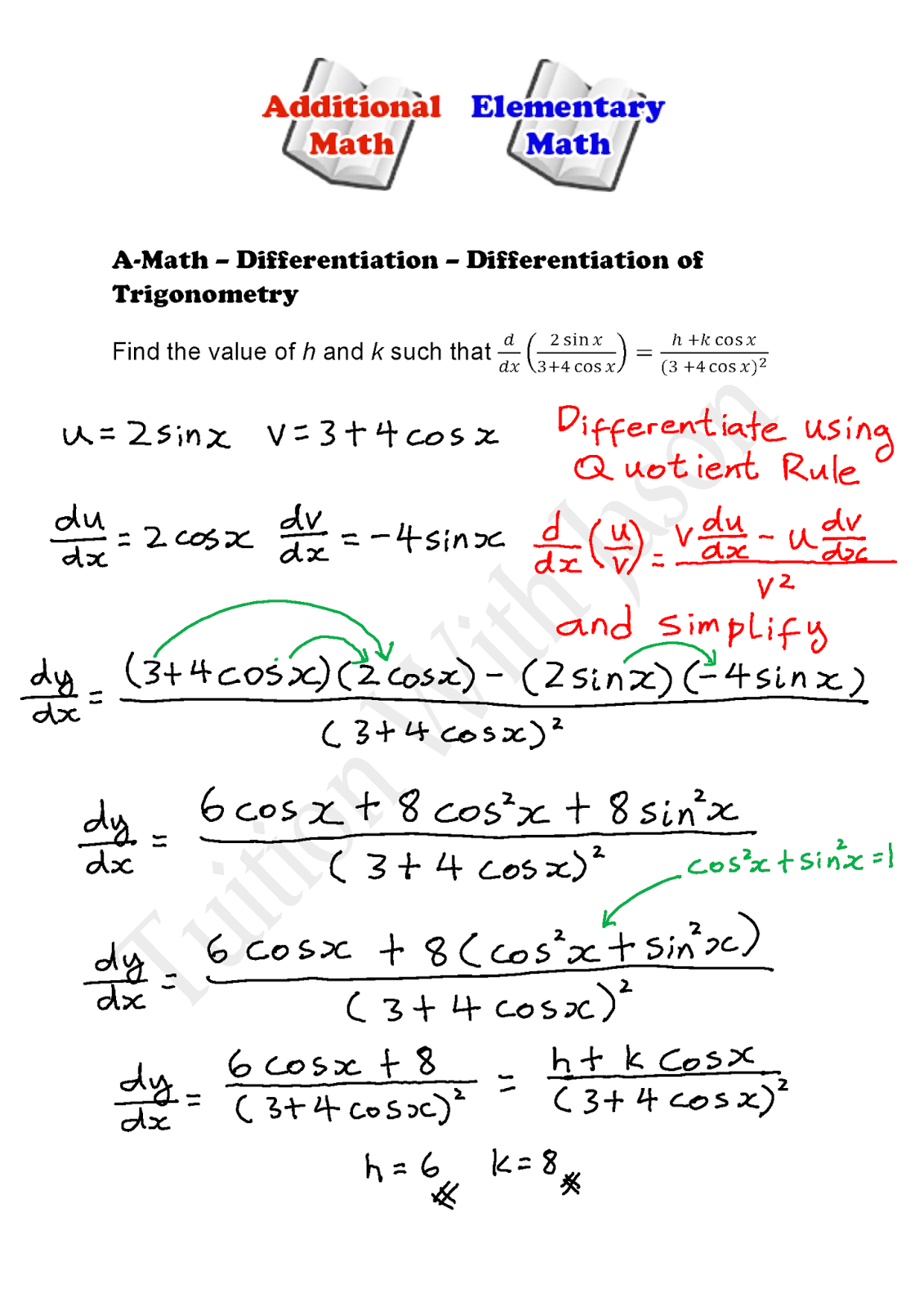
AMath Differentiation Differentiation of Trigonometry (2
Given a function \(y = f\left( x \right)\) we call \(dy\) and \(dx\) differentials. In this section we study what differential equations are, how to verify their. In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function = with.
10 Math Courses at Clark University OneClass Blog
Given a function \(y = f\left( x \right)\) we call \(dy\) and \(dx\) differentials. In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function = with. In this section we study what differential equations are, how to verify their.
What is Differential? Types of Differentials, Function & How They Work
In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function = with. Given a function \(y = f\left( x \right)\) we call \(dy\) and \(dx\) differentials. In this section we study what differential equations are, how to verify their.
(PDF) Using Differentials to Differentiate Trigonometric …math
In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function = with. Given a function \(y = f\left( x \right)\) we call \(dy\) and \(dx\) differentials. In this section we study what differential equations are, how to verify their.
PPT Section 3.9 Differentials PowerPoint Presentation, free
In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function = with. In this section we study what differential equations are, how to verify their. Given a function \(y = f\left( x \right)\) we call \(dy\) and \(dx\) differentials.
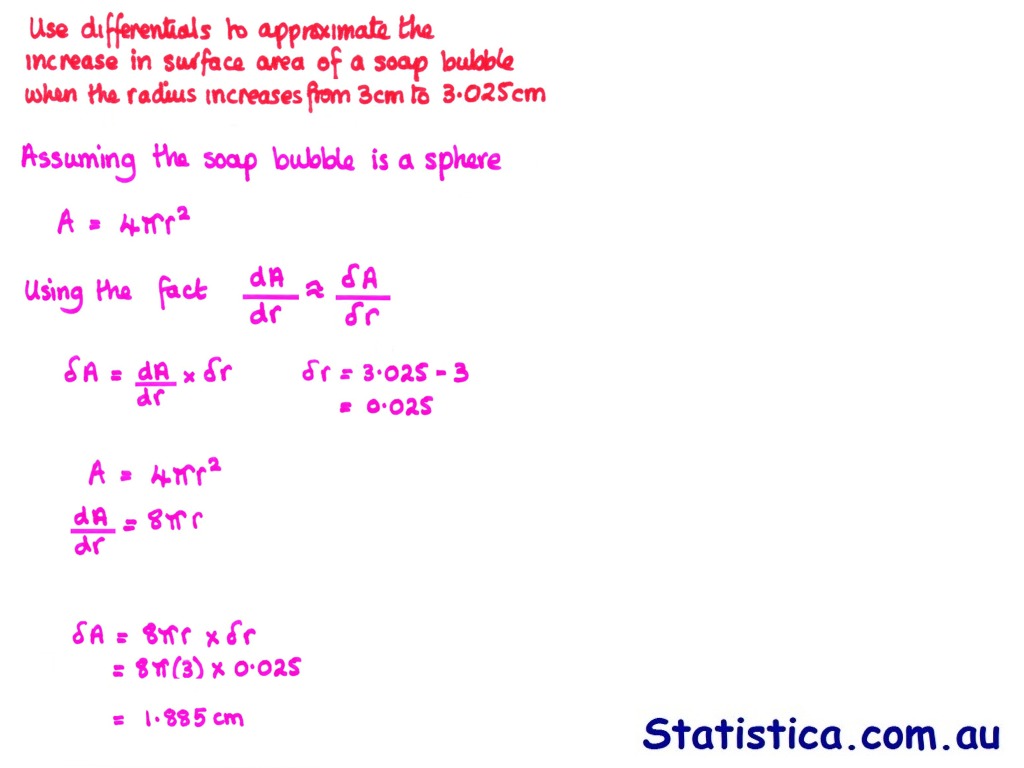
Differentials and Error Propagation
Given a function \(y = f\left( x \right)\) we call \(dy\) and \(dx\) differentials. In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function = with. In this section we study what differential equations are, how to verify their.
ShowMe differentials
In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function = with. In this section we study what differential equations are, how to verify their. Given a function \(y = f\left( x \right)\) we call \(dy\) and \(dx\) differentials.
A level Maths DIFFERENTIATION Rules (Edexcel) Teaching Resources
In this section we study what differential equations are, how to verify their. Given a function \(y = f\left( x \right)\) we call \(dy\) and \(dx\) differentials. In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function = with.
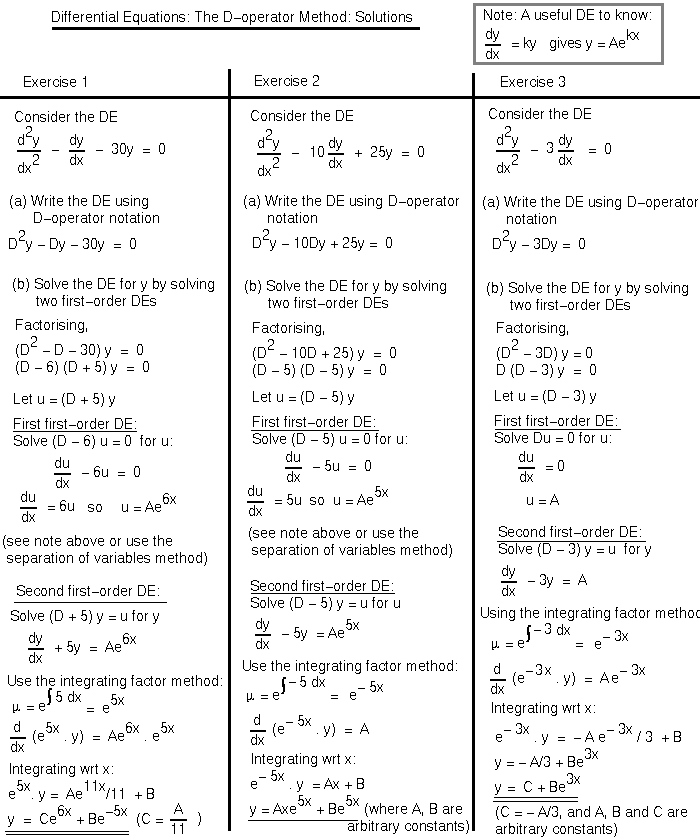
Differential Equations MATH100 Revision Exercises Resources
In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function = with. Given a function \(y = f\left( x \right)\) we call \(dy\) and \(dx\) differentials. In this section we study what differential equations are, how to verify their.
partial derivative Total differential definition help Mathematics
In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function = with. In this section we study what differential equations are, how to verify their. Given a function \(y = f\left( x \right)\) we call \(dy\) and \(dx\) differentials.
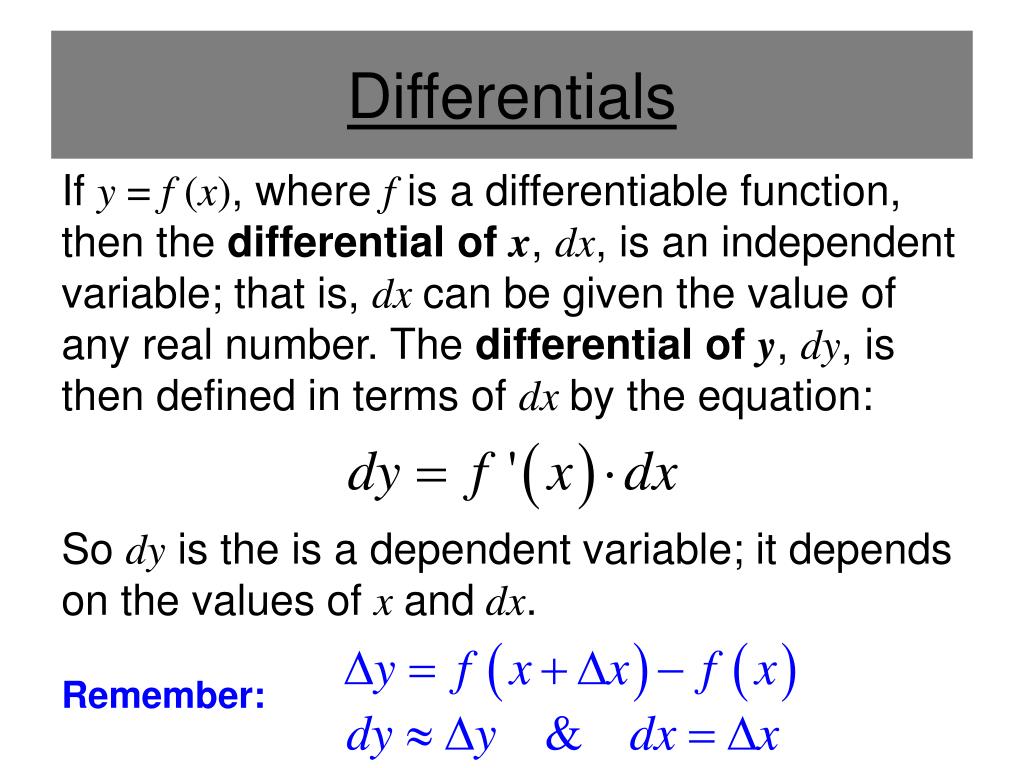
Given A Function \(Y = F\Left( X \Right)\) We Call \(Dy\) And \(Dx\) Differentials.
In this section we study what differential equations are, how to verify their. In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function = with.