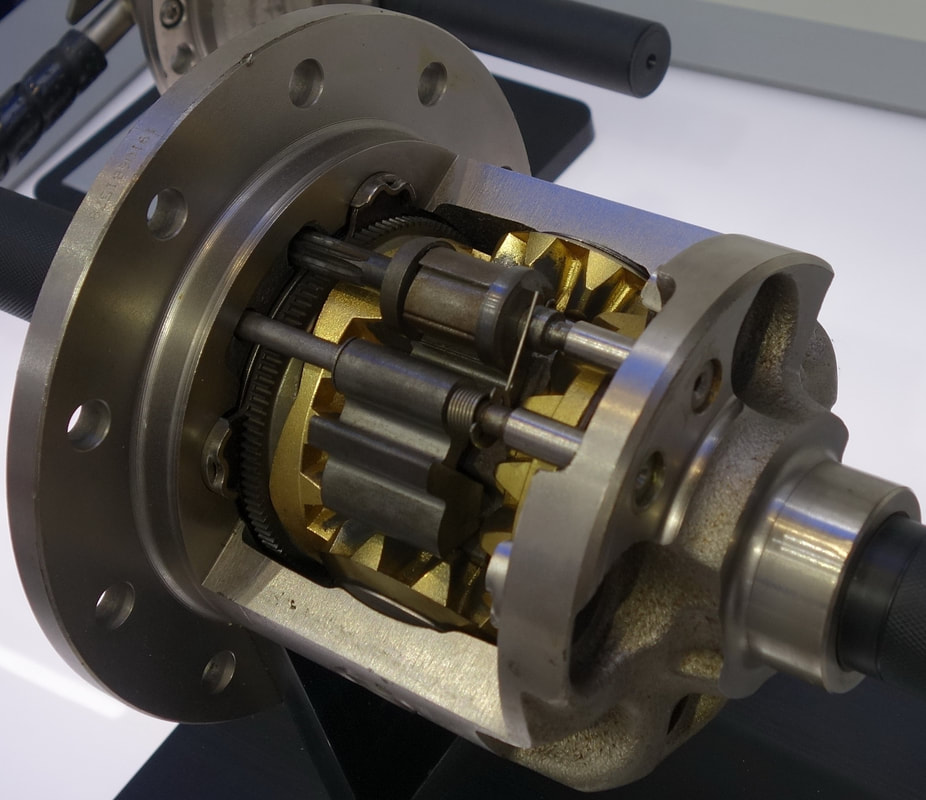
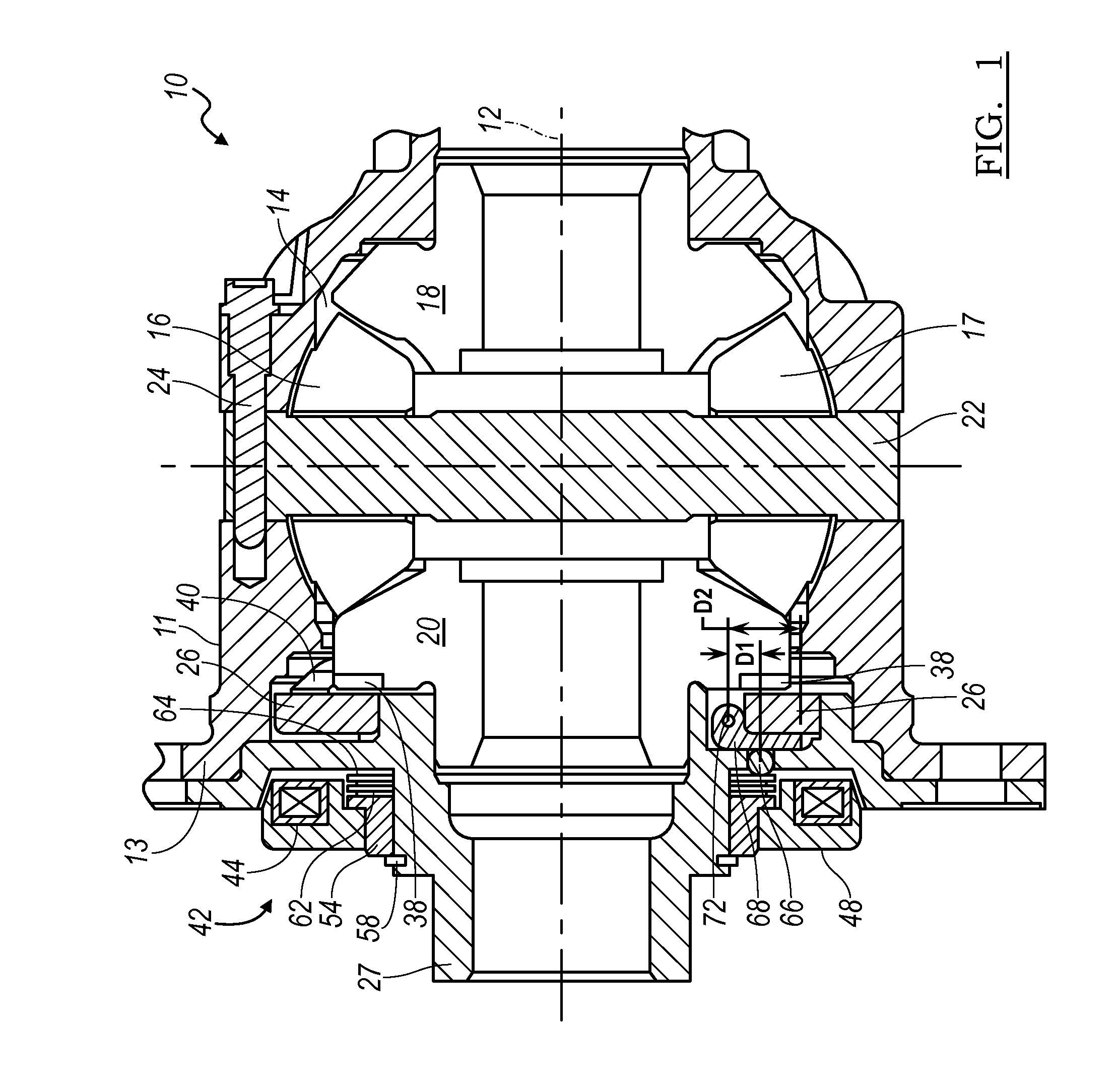
Locking Differential - The complicated answer is that locking differentials affect the torque directed to your wheels to prevent them from spinning uselessly when you. But what is a locking differential? A locking differential is a mechanical component, commonly used in vehicles, designed to overcome the chief limitation of a standard open differential by essentially locking both wheels on an axle. They increase traction by forcing both tires on an axle to turn. Its primary function is to ensure that power is evenly distributed to both wheels on an axle, regardless of the traction conditions. Locking differentials (or “lockers”) are a mechanical feature that locks both wheels on an axle together so they travel at the same speed. This means that when one wheel loses traction, the. When traction is lost for one wheel, all.
A locking differential is a mechanical component, commonly used in vehicles, designed to overcome the chief limitation of a standard open differential by essentially locking both wheels on an axle. This means that when one wheel loses traction, the. The complicated answer is that locking differentials affect the torque directed to your wheels to prevent them from spinning uselessly when you. Locking differentials (or “lockers”) are a mechanical feature that locks both wheels on an axle together so they travel at the same speed. But what is a locking differential? When traction is lost for one wheel, all. They increase traction by forcing both tires on an axle to turn. Its primary function is to ensure that power is evenly distributed to both wheels on an axle, regardless of the traction conditions.
Its primary function is to ensure that power is evenly distributed to both wheels on an axle, regardless of the traction conditions. They increase traction by forcing both tires on an axle to turn. The complicated answer is that locking differentials affect the torque directed to your wheels to prevent them from spinning uselessly when you. A locking differential is a mechanical component, commonly used in vehicles, designed to overcome the chief limitation of a standard open differential by essentially locking both wheels on an axle. Locking differentials (or “lockers”) are a mechanical feature that locks both wheels on an axle together so they travel at the same speed. This means that when one wheel loses traction, the. When traction is lost for one wheel, all. But what is a locking differential?
Electronic Locking Differential For Better Traction
Its primary function is to ensure that power is evenly distributed to both wheels on an axle, regardless of the traction conditions. The complicated answer is that locking differentials affect the torque directed to your wheels to prevent them from spinning uselessly when you. But what is a locking differential? This means that when one wheel loses traction, the. A.
Sports Utility Vehicle Learn and News Differential & Locking Differential
The complicated answer is that locking differentials affect the torque directed to your wheels to prevent them from spinning uselessly when you. Locking differentials (or “lockers”) are a mechanical feature that locks both wheels on an axle together so they travel at the same speed. They increase traction by forcing both tires on an axle to turn. This means that.
Locking Differential for Sale Mitsubishi Forum Mitsubishi
When traction is lost for one wheel, all. A locking differential is a mechanical component, commonly used in vehicles, designed to overcome the chief limitation of a standard open differential by essentially locking both wheels on an axle. But what is a locking differential? Its primary function is to ensure that power is evenly distributed to both wheels on an.
Benefits of a Locking Differential
This means that when one wheel loses traction, the. They increase traction by forcing both tires on an axle to turn. A locking differential is a mechanical component, commonly used in vehicles, designed to overcome the chief limitation of a standard open differential by essentially locking both wheels on an axle. Its primary function is to ensure that power is.
Pros and Cons of Locking Differential Safiest
They increase traction by forcing both tires on an axle to turn. A locking differential is a mechanical component, commonly used in vehicles, designed to overcome the chief limitation of a standard open differential by essentially locking both wheels on an axle. But what is a locking differential? Locking differentials (or “lockers”) are a mechanical feature that locks both wheels.
Locking Differential ProGear
They increase traction by forcing both tires on an axle to turn. Locking differentials (or “lockers”) are a mechanical feature that locks both wheels on an axle together so they travel at the same speed. The complicated answer is that locking differentials affect the torque directed to your wheels to prevent them from spinning uselessly when you. But what is.
MLocker Locking Differential EHFCV
The complicated answer is that locking differentials affect the torque directed to your wheels to prevent them from spinning uselessly when you. But what is a locking differential? This means that when one wheel loses traction, the. They increase traction by forcing both tires on an axle to turn. Its primary function is to ensure that power is evenly distributed.
Selflocking Center Differential MechanicsTips
When traction is lost for one wheel, all. A locking differential is a mechanical component, commonly used in vehicles, designed to overcome the chief limitation of a standard open differential by essentially locking both wheels on an axle. Locking differentials (or “lockers”) are a mechanical feature that locks both wheels on an axle together so they travel at the same.
Ford F150 Electronic Locking Differential Problems (Solved)
Its primary function is to ensure that power is evenly distributed to both wheels on an axle, regardless of the traction conditions. Locking differentials (or “lockers”) are a mechanical feature that locks both wheels on an axle together so they travel at the same speed. But what is a locking differential? The complicated answer is that locking differentials affect the.
Locking differential patented technology retrieval search results
A locking differential is a mechanical component, commonly used in vehicles, designed to overcome the chief limitation of a standard open differential by essentially locking both wheels on an axle. Its primary function is to ensure that power is evenly distributed to both wheels on an axle, regardless of the traction conditions. They increase traction by forcing both tires on.
The Complicated Answer Is That Locking Differentials Affect The Torque Directed To Your Wheels To Prevent Them From Spinning Uselessly When You.
Its primary function is to ensure that power is evenly distributed to both wheels on an axle, regardless of the traction conditions. But what is a locking differential? A locking differential is a mechanical component, commonly used in vehicles, designed to overcome the chief limitation of a standard open differential by essentially locking both wheels on an axle. This means that when one wheel loses traction, the.
When Traction Is Lost For One Wheel, All.
They increase traction by forcing both tires on an axle to turn. Locking differentials (or “lockers”) are a mechanical feature that locks both wheels on an axle together so they travel at the same speed.