Inhomogeneous First Order Differential Equation - A first order linear equation is homogeneous if the right hand side is zero: X ̇ + p(t)x = 0. In order to be able to investigate these precisely we first express them in a standard way. An example of a first order linear non. First order linear equations in the previous session we. Variation of parameters can be used to solve 2nd order odes, whereas if does not generalize. The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations. Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1.
A first order linear equation is homogeneous if the right hand side is zero: The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations. First order linear equations in the previous session we. Variation of parameters can be used to solve 2nd order odes, whereas if does not generalize. In order to be able to investigate these precisely we first express them in a standard way. An example of a first order linear non. Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1. X ̇ + p(t)x = 0.
A first order linear equation is homogeneous if the right hand side is zero: The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations. Variation of parameters can be used to solve 2nd order odes, whereas if does not generalize. Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1. In order to be able to investigate these precisely we first express them in a standard way. An example of a first order linear non. X ̇ + p(t)x = 0. First order linear equations in the previous session we.
Differential Equation Calculator
X ̇ + p(t)x = 0. An example of a first order linear non. Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1. First order linear equations in the previous session we. Variation of parameters can be used to solve 2nd order odes, whereas if does not generalize.
Inhomogeneous second order differential equation question r/askmath
Variation of parameters can be used to solve 2nd order odes, whereas if does not generalize. In order to be able to investigate these precisely we first express them in a standard way. X ̇ + p(t)x = 0. The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations. A first order linear equation is.
The second order inhomogeneous differential StudyX
Variation of parameters can be used to solve 2nd order odes, whereas if does not generalize. X ̇ + p(t)x = 0. An example of a first order linear non. First order linear equations in the previous session we. Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1.
[Solved] 1. A firstorder differential equation is homogenous if it can
Variation of parameters can be used to solve 2nd order odes, whereas if does not generalize. X ̇ + p(t)x = 0. An example of a first order linear non. In order to be able to investigate these precisely we first express them in a standard way. Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1.
(PDF) Digital Film Music Creation Model Based on Inhomogeneous First
X ̇ + p(t)x = 0. An example of a first order linear non. Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1. Variation of parameters can be used to solve 2nd order odes, whereas if does not generalize. A first order linear equation is homogeneous if the right hand side is zero:
Homogeneous Differential Equation First Order Lesson 4 Homogeneous
X ̇ + p(t)x = 0. The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations. First order linear equations in the previous session we. Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1. An example of a first order linear non.
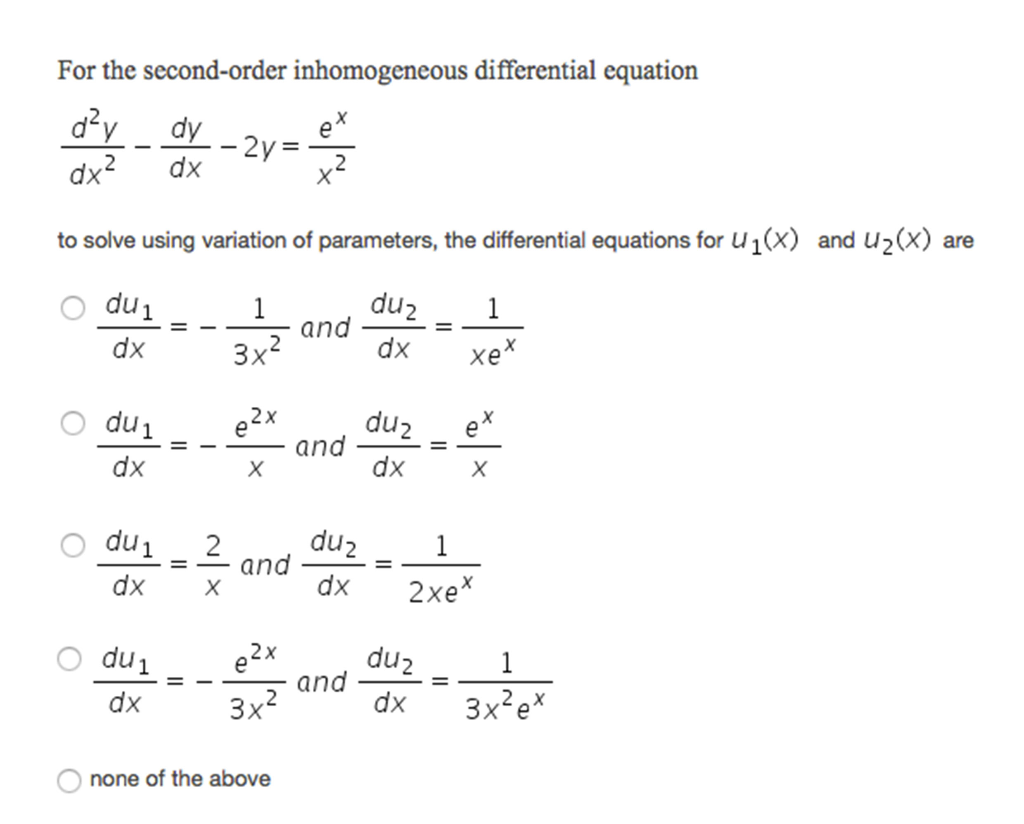
Solved For the secondorder inhomogeneous differential
Variation of parameters can be used to solve 2nd order odes, whereas if does not generalize. The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations. X ̇ + p(t)x = 0. An example of a first order linear non. In order to be able to investigate these precisely we first express them in a.
Solved Consider the inhomogeneous partial differential
In order to be able to investigate these precisely we first express them in a standard way. First order linear equations in the previous session we. Variation of parameters can be used to solve 2nd order odes, whereas if does not generalize. X ̇ + p(t)x = 0. A first order linear equation is homogeneous if the right hand side.
SOLUTION Differential equation homogeneous first order example 2
Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1. The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations. An example of a first order linear non. X ̇ + p(t)x = 0. First order linear equations in the previous session we.
Second Order Inhomogeneous Differential Equations
X ̇ + p(t)x = 0. An example of a first order linear non. The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations. Variation of parameters can be used to solve 2nd order odes, whereas if does not generalize. Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1.
Variation Of Parameters Can Be Used To Solve 2Nd Order Odes, Whereas If Does Not Generalize.
A first order linear equation is homogeneous if the right hand side is zero: Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1. First order linear equations in the previous session we. The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations.
In Order To Be Able To Investigate These Precisely We First Express Them In A Standard Way.
An example of a first order linear non. X ̇ + p(t)x = 0.