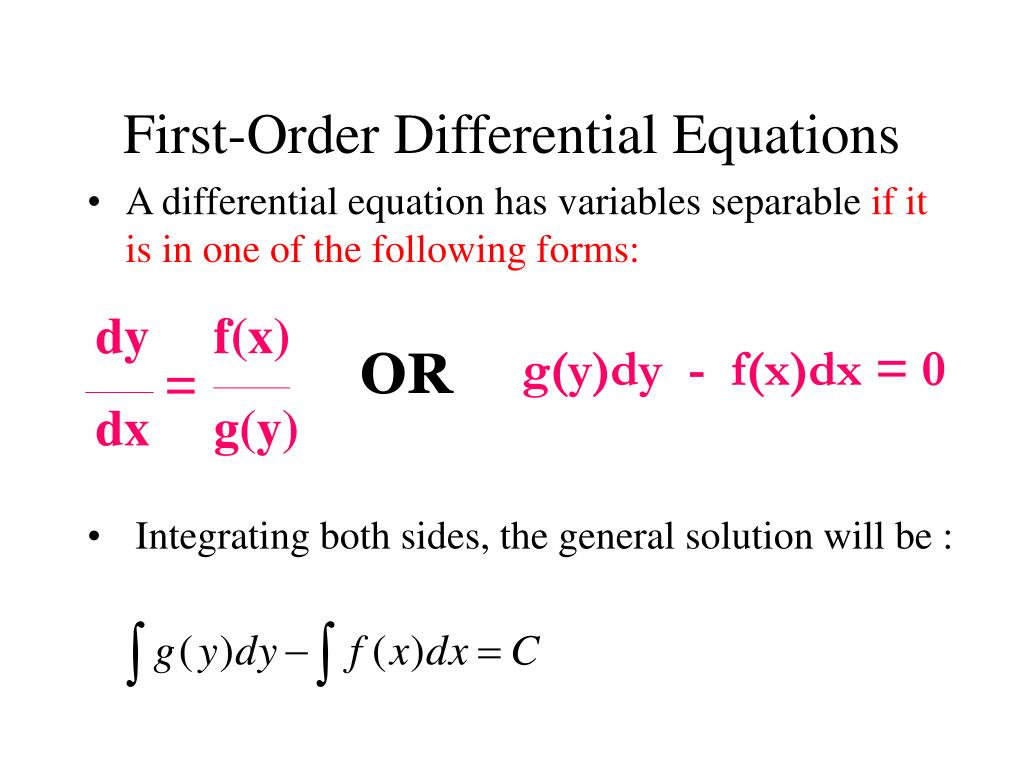
Inhomogeneous Differential Equation First Order - Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1. Y’ + ky = q(t) where: The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations. First order linear equations in the previous session we. The equation has the form y0+ ay= g(t) (1) where ais a constant. You can think of this as a. The inhomogeneous first order linear ode we wish to solve is x˙ + tx = (1+ t)e t.
The inhomogeneous first order linear ode we wish to solve is x˙ + tx = (1+ t)e t. First order linear equations in the previous session we. Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1. The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations. You can think of this as a. The equation has the form y0+ ay= g(t) (1) where ais a constant. Y’ + ky = q(t) where:
First order linear equations in the previous session we. The inhomogeneous first order linear ode we wish to solve is x˙ + tx = (1+ t)e t. You can think of this as a. The equation has the form y0+ ay= g(t) (1) where ais a constant. Y’ + ky = q(t) where: Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1. The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations.
Solved Consider the inhomogeneous partial differential
The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations. The equation has the form y0+ ay= g(t) (1) where ais a constant. Y’ + ky = q(t) where: You can think of this as a. The inhomogeneous first order linear ode we wish to solve is x˙ + tx = (1+ t)e t.
Differential Equation Calculator
You can think of this as a. The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations. The equation has the form y0+ ay= g(t) (1) where ais a constant. The inhomogeneous first order linear ode we wish to solve is x˙ + tx = (1+ t)e t. First order linear equations in the previous.
(PDF) Digital Film Music Creation Model Based on Inhomogeneous First
First order linear equations in the previous session we. The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations. Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1. The inhomogeneous first order linear ode we wish to solve is x˙ + tx = (1+ t)e t. The equation has the form y0+ ay= g(t) (1) where ais.
Inhomogeneous Linear Differential Equations KZHU.ai 🚀
The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations. Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1. Y’ + ky = q(t) where: The equation has the form y0+ ay= g(t) (1) where ais a constant. The inhomogeneous first order linear ode we wish to solve is x˙ + tx = (1+ t)e t.
First Order Differential Equation Form example download
The equation has the form y0+ ay= g(t) (1) where ais a constant. You can think of this as a. First order linear equations in the previous session we. Y’ + ky = q(t) where: The inhomogeneous first order linear ode we wish to solve is x˙ + tx = (1+ t)e t.
The second order inhomogeneous differential StudyX
You can think of this as a. The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations. The equation has the form y0+ ay= g(t) (1) where ais a constant. The inhomogeneous first order linear ode we wish to solve is x˙ + tx = (1+ t)e t. First order linear equations in the previous.
SOLUTION Differential equation homogeneous first order example 2
You can think of this as a. The inhomogeneous first order linear ode we wish to solve is x˙ + tx = (1+ t)e t. Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1. Y’ + ky = q(t) where: The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations.
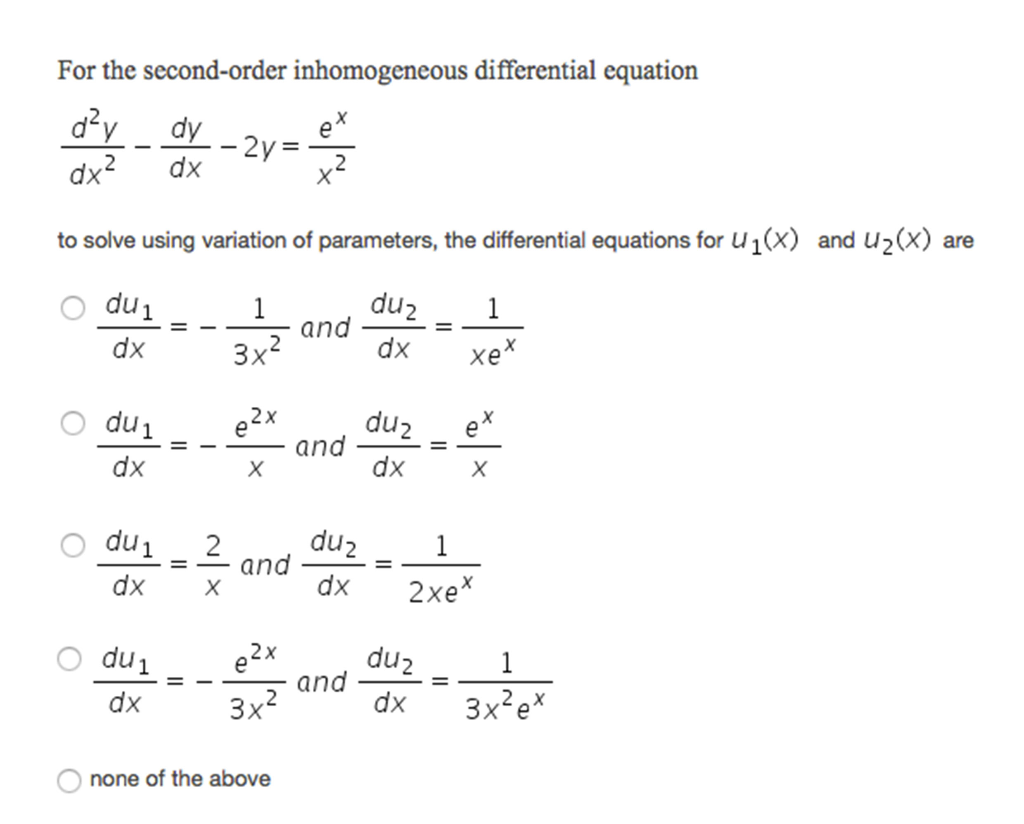
Solved For the secondorder inhomogeneous differential
Y’ + ky = q(t) where: Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1. The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations. The inhomogeneous first order linear ode we wish to solve is x˙ + tx = (1+ t)e t. The equation has the form y0+ ay= g(t) (1) where ais a constant.
Inhomogeneous second order differential equation question r/askmath
You can think of this as a. The inhomogeneous first order linear ode we wish to solve is x˙ + tx = (1+ t)e t. The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations. Y’ + ky = q(t) where: The equation has the form y0+ ay= g(t) (1) where ais a constant.
Second Order Inhomogeneous Differential Equations
The inhomogeneous first order linear ode we wish to solve is x˙ + tx = (1+ t)e t. You can think of this as a. The essential difference between first and second order equations is that for first order equations. First order linear equations in the previous session we. Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1.
You Can Think Of This As A.
Y’ + ky = q(t) where: First order linear equations in the previous session we. The inhomogeneous first order linear ode we wish to solve is x˙ + tx = (1+ t)e t. The equation has the form y0+ ay= g(t) (1) where ais a constant.
The Essential Difference Between First And Second Order Equations Is That For First Order Equations.
Solutions to linear first order ode’s 1.