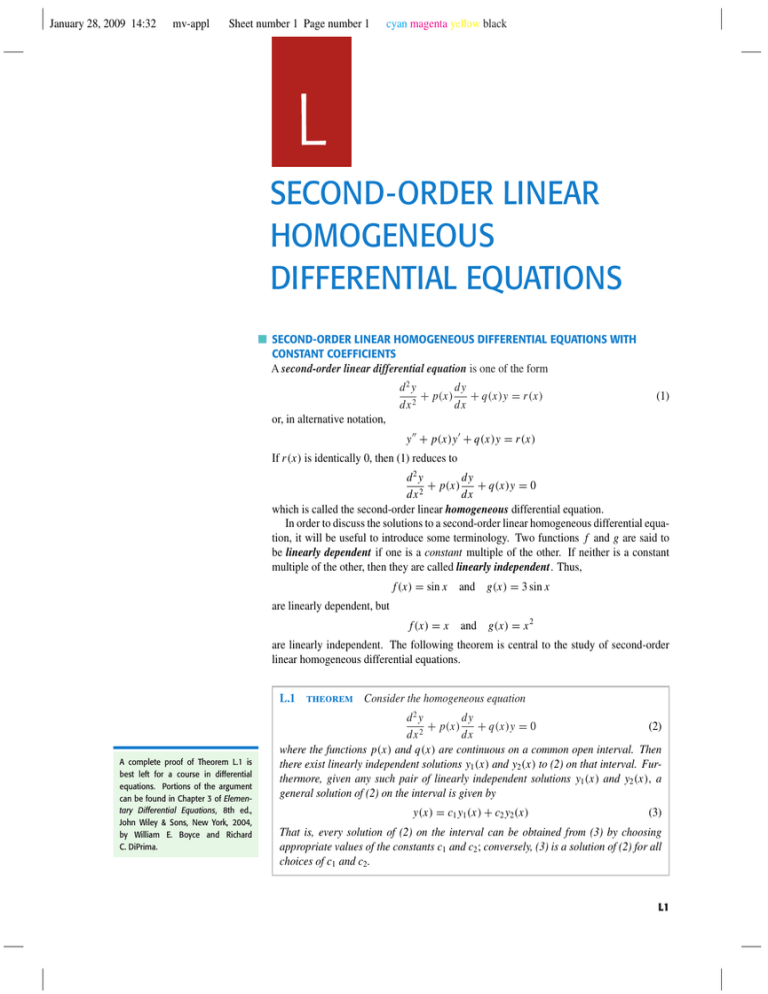
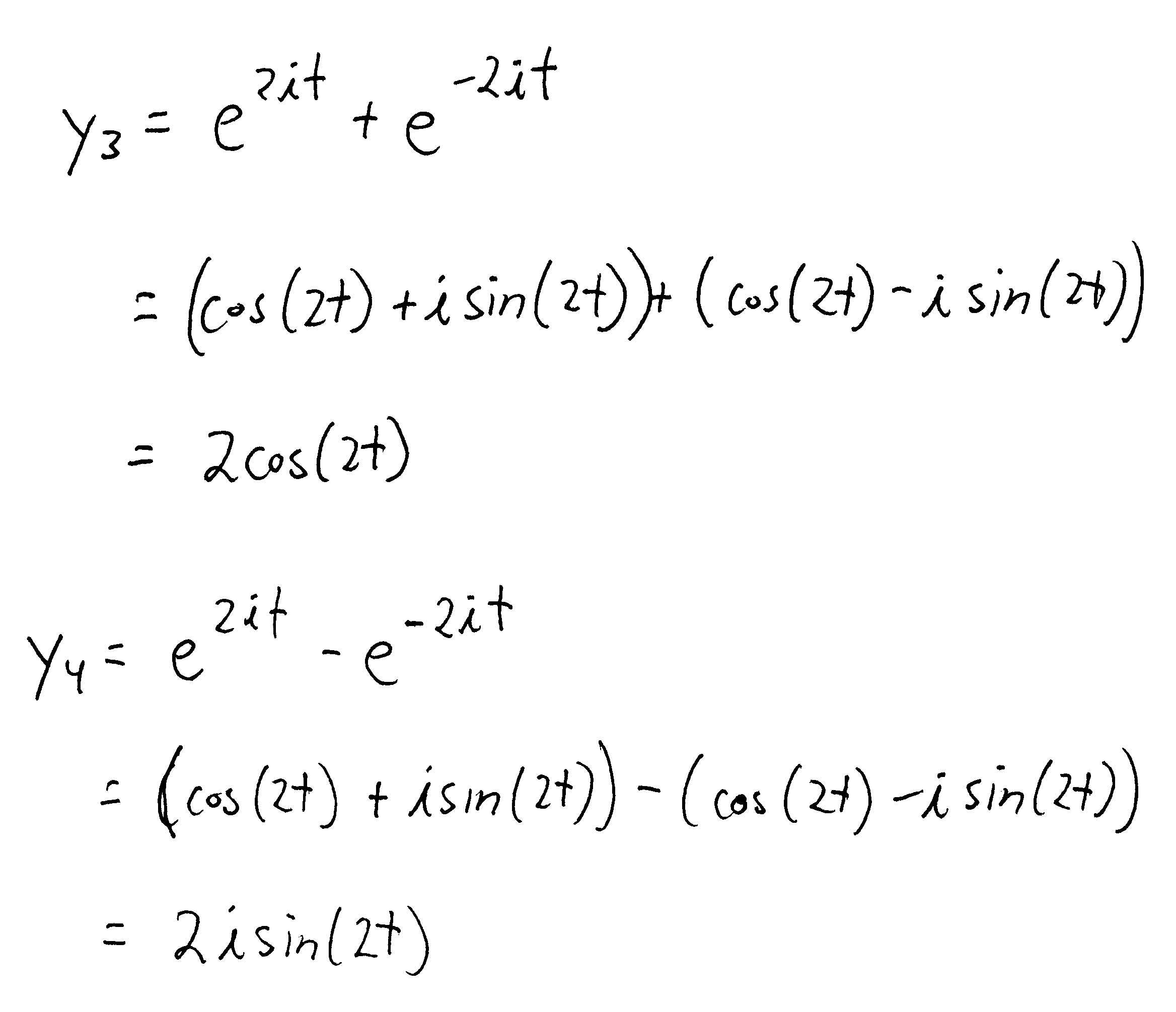Homogeneous Second Order Differential Equations - A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. Second order (the highest derivative is of. In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form: A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form:
We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form: Second order (the highest derivative is of.
We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form: A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. Second order (the highest derivative is of.
Solved Second Order NonHomogeneous Differential Equations
A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. Second order (the highest derivative is of. A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. In this tutorial, we will.
SOLUTION Second order homogeneous linear differential equation Studypool
A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. Second order (the highest derivative is of. In this tutorial, we will.
2nd Order Homogeneous Equations
A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: Second order (the highest derivative is of. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form: A d2y dx2.
Homogeneous Linear Differential Equations KZHU.ai 🚀
Second order (the highest derivative is of. A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form: A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a.
College Park Tutors Blog Differential Equations Solving a second
In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form: Second order (the highest derivative is of. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an.
Solving secondorder differential equations. Mathematics Stack Exchange
We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. Second order (the highest derivative is of. A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: In this tutorial, we will.
Particular Solution of NonHomogeneous Differential Equations Mr
A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. Second order (the highest derivative is of. In this tutorial, we will.
(PDF) Second Order Differential Equations
A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: Second order (the highest derivative is of. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form: A d2y dx2.
Solving secondorder homogeneous differential equations — Krista King
In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form: A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. Second.
secondorder linear homogeneous differential equations
We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. Second order (the highest derivative is of. A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0. A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: In this tutorial, we will.
We Define Fundamental Sets Of Solutions And Discuss How They Can Be Used To Get A General Solution To A Homogeneous Second.
In this tutorial, we will practise solving equations of the form: A linear homogeneous second order ode with constant coefficients is an ordinary differential equation in the form: Second order (the highest derivative is of. A d2y dx2 +b dy dx +cy = 0.