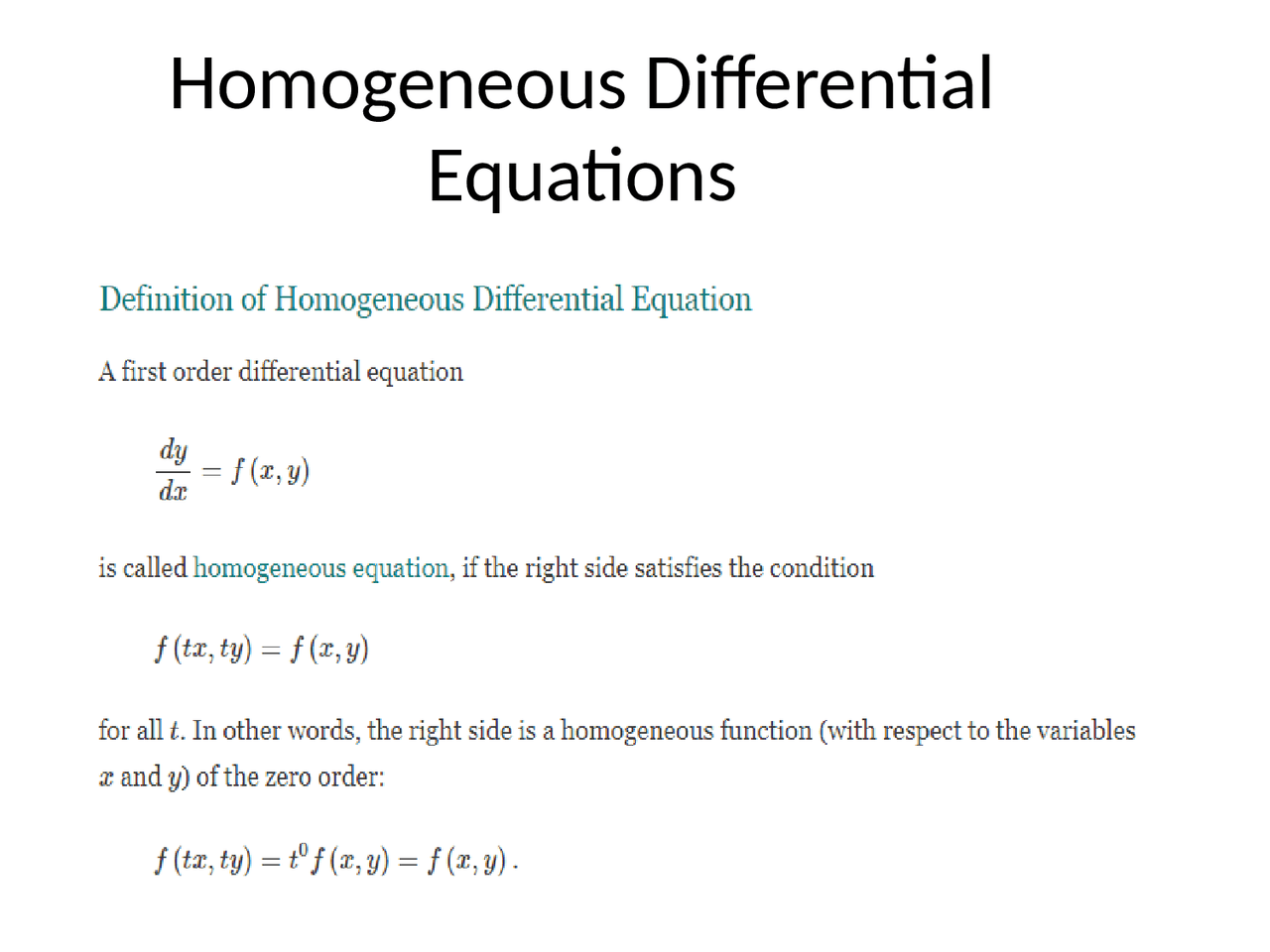
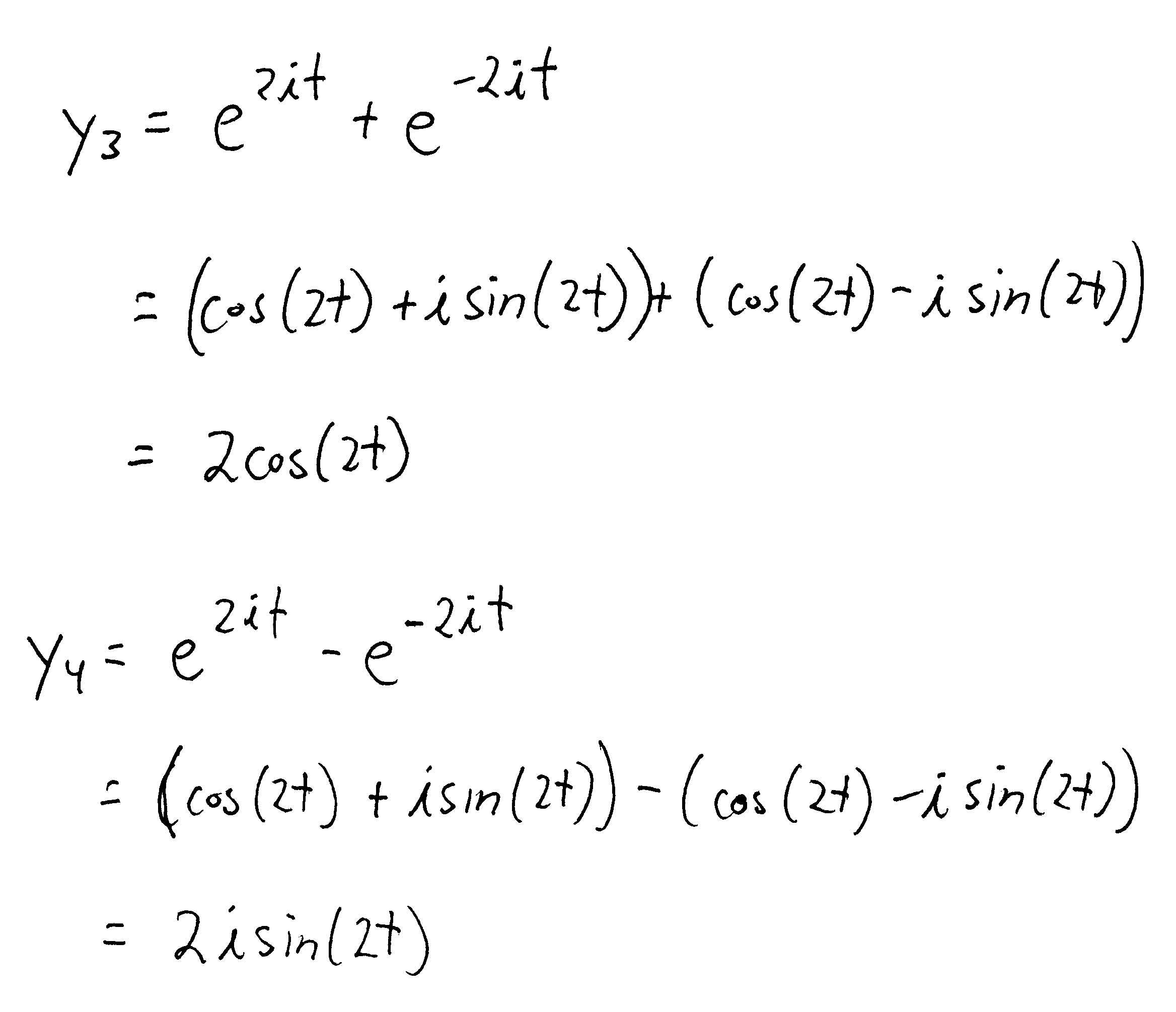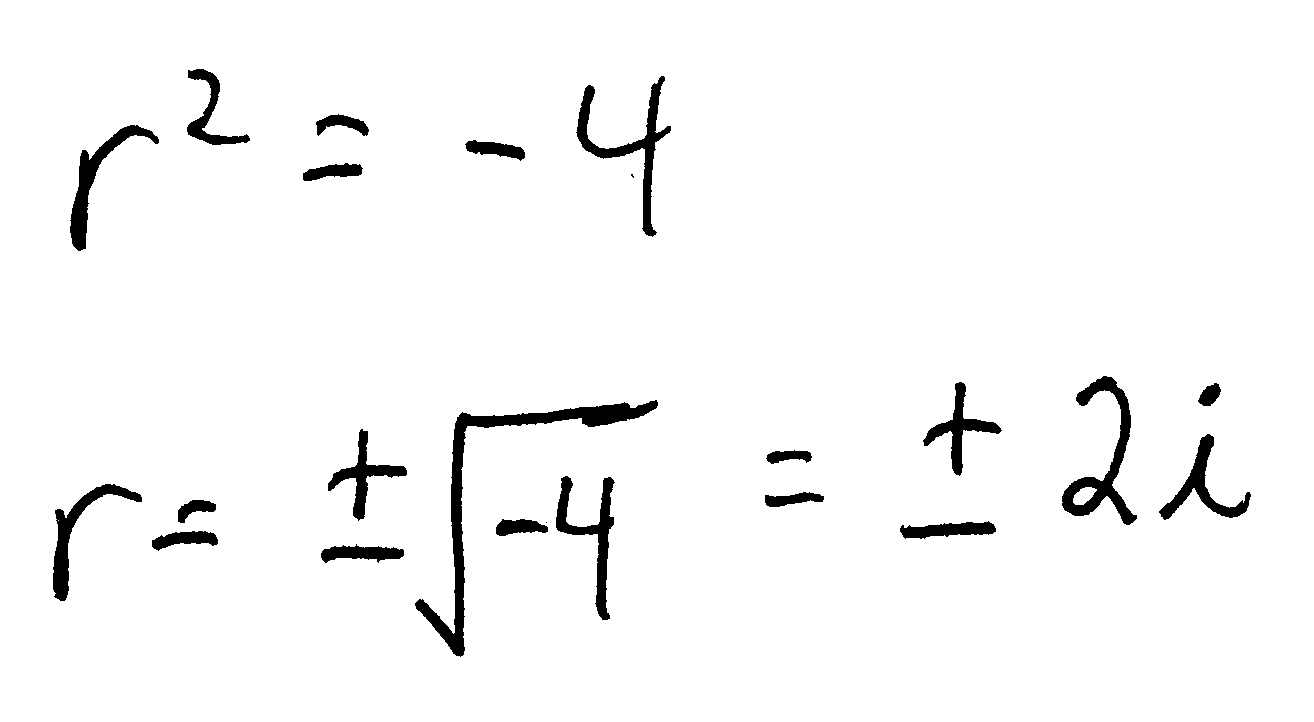Homogeneous Ordinary Differential Equation - A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x, y) is. An example will show how it is all done: In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be.
A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x, y) is. A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be. An example will show how it is all done: Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher.
A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be. An example will show how it is all done: A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x, y) is. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation.
Homogeneous Differential Equation Know types, Steps to solve
Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be. An example will show how it is all done: In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,.
(PDF) Solution of First Order Linear Non Homogeneous Ordinary
A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be. Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. An example will show.
Solved The homogeneous secondorder ordinary differential
Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x, y) is. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations.
Differential Equation Calculator
In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x, y) is. A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said.
College Park Tutors Blog Differential Equations Solving a second
A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be. An example will show how it is all done: Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be.
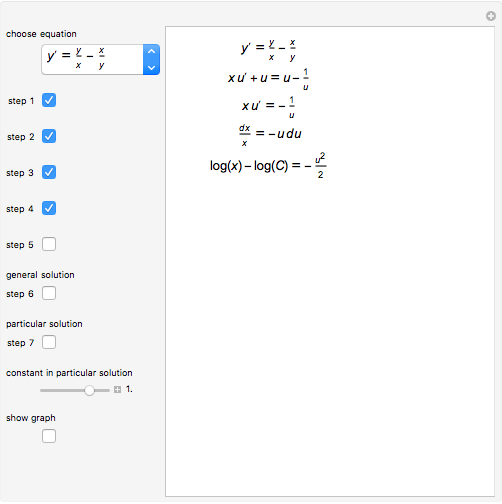
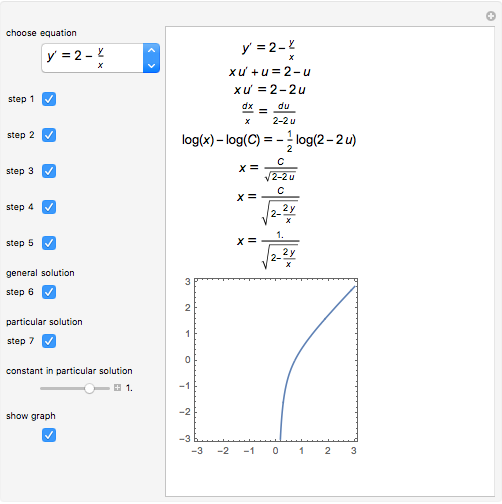
Some Homogeneous Ordinary Differential Equations Wolfram
An example will show how it is all done: Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x, y) is. In this section we will extend the.
College Park Tutors Blog Differential Equations Solving a second
An example will show how it is all done: A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x, y) is. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. Using y = vx and dy dx =.
Differential Equations Ordinary differential equation ODE Partial
In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. An example will show how it is all done: A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x, y) is. A first order differential equation of the form.
Some Homogeneous Ordinary Differential Equations Wolfram
A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be. A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x, y) is. Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve.
Homogeneous Differential Equations Docsity
An example will show how it is all done: In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be. A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous.
Using Y = Vx And Dy Dx = V + X Dv Dx We Can Solve The Differential Equation.
In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. An example will show how it is all done: A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be. A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x, y) is.