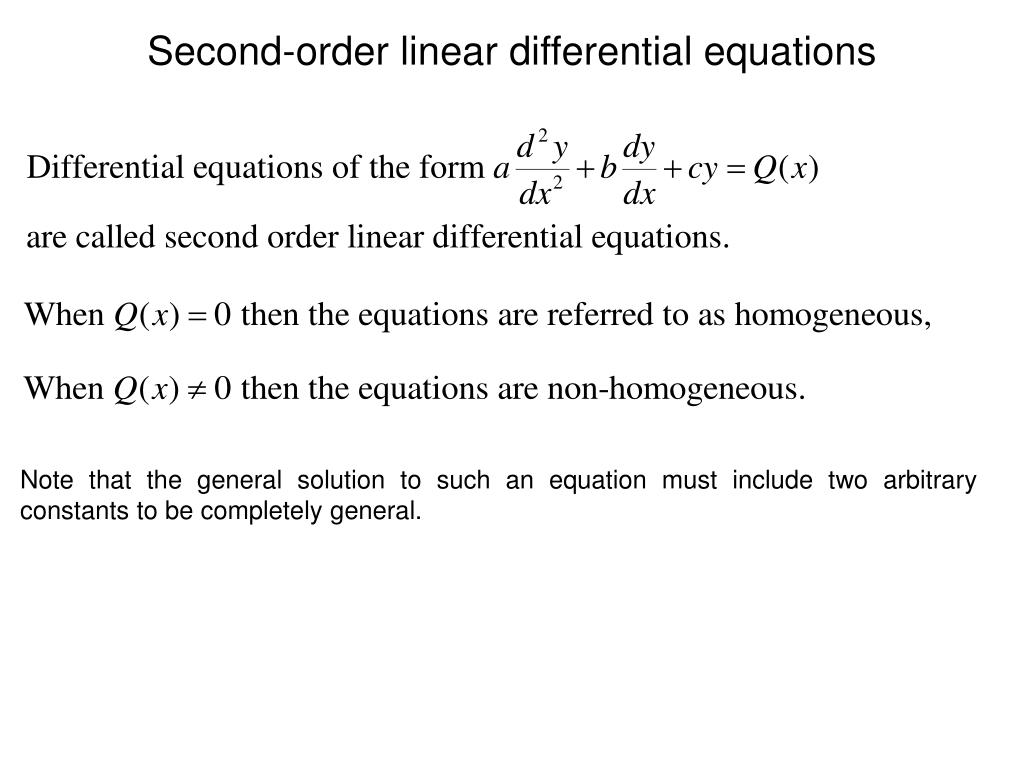
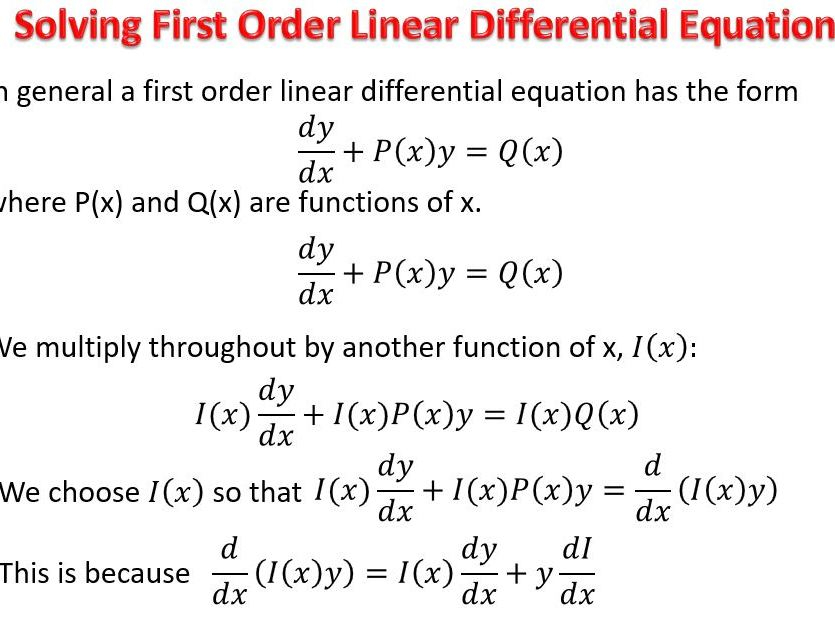
First Order Nonhomogeneous Differential Equation - A differential equation of type \[y' + a\left( x \right)y = f\left( x \right),\] where a ( x ) and f ( x ) are continuous functions of x , is called a linear. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation. →x ′ (t) = a→x(t) + →f(t), where a is a constant matrix. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation \begin{equation*} {\vec{x}}'(t) = a\vec{x}(t) + \vec{f}(t) , \end{equation*} where. We define the complimentary and. In this section we will discuss the basics of solving nonhomogeneous differential equations.
In this section we will discuss the basics of solving nonhomogeneous differential equations. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation. A differential equation of type \[y' + a\left( x \right)y = f\left( x \right),\] where a ( x ) and f ( x ) are continuous functions of x , is called a linear. We define the complimentary and. →x ′ (t) = a→x(t) + →f(t), where a is a constant matrix. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation \begin{equation*} {\vec{x}}'(t) = a\vec{x}(t) + \vec{f}(t) , \end{equation*} where.
→x ′ (t) = a→x(t) + →f(t), where a is a constant matrix. We define the complimentary and. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation. A differential equation of type \[y' + a\left( x \right)y = f\left( x \right),\] where a ( x ) and f ( x ) are continuous functions of x , is called a linear. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation \begin{equation*} {\vec{x}}'(t) = a\vec{x}(t) + \vec{f}(t) , \end{equation*} where. In this section we will discuss the basics of solving nonhomogeneous differential equations.
Solved Consider the first order nonhomogeneous differential
We define the complimentary and. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation \begin{equation*} {\vec{x}}'(t) = a\vec{x}(t) + \vec{f}(t) , \end{equation*} where. A differential equation of type \[y' + a\left( x \right)y = f\left( x \right),\] where a ( x ) and f ( x ) are continuous functions of x , is called a linear. In this.
[Solved] Problem 1. A firstorder nonhomogeneous linear d
In this section we will discuss the basics of solving nonhomogeneous differential equations. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation \begin{equation*} {\vec{x}}'(t) = a\vec{x}(t) + \vec{f}(t) , \end{equation*} where. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation. We define the complimentary and. A differential equation of type \[y' + a\left( x \right)y = f\left( x.
Second Order Differential Equation Solved Find The Second Order
Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation \begin{equation*} {\vec{x}}'(t) = a\vec{x}(t) + \vec{f}(t) , \end{equation*} where. In this section we will discuss the basics of solving nonhomogeneous differential equations. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation. A differential equation of type \[y' + a\left( x \right)y = f\left( x \right),\] where a ( x.
To solve differential equations First order differential equation
We define the complimentary and. A differential equation of type \[y' + a\left( x \right)y = f\left( x \right),\] where a ( x ) and f ( x ) are continuous functions of x , is called a linear. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation. In this section we will discuss the basics of solving nonhomogeneous.
solve the initial value problem first order differential equation
→x ′ (t) = a→x(t) + →f(t), where a is a constant matrix. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation \begin{equation*} {\vec{x}}'(t) = a\vec{x}(t) + \vec{f}(t) , \end{equation*} where. A differential equation of type \[y' + a\left( x \right)y = f\left( x \right),\] where a ( x ) and f ( x ) are continuous functions of.
First Order Differential Equation Worksheet Equations Worksheets
A differential equation of type \[y' + a\left( x \right)y = f\left( x \right),\] where a ( x ) and f ( x ) are continuous functions of x , is called a linear. We define the complimentary and. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation \begin{equation*} {\vec{x}}'(t) = a\vec{x}(t) + \vec{f}(t) , \end{equation*} where. Let us.
SOLVED The equation is linear homogeneous differential equation of
We define the complimentary and. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation. A differential equation of type \[y' + a\left( x \right)y = f\left( x \right),\] where a ( x ) and f ( x ) are continuous functions of x , is called a linear. In this section we will discuss the basics of solving nonhomogeneous.
Differential Equation Calculator
Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation \begin{equation*} {\vec{x}}'(t) = a\vec{x}(t) + \vec{f}(t) , \end{equation*} where. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation. A differential equation of type \[y' + a\left( x \right)y = f\left( x \right),\] where a ( x ) and f ( x ) are continuous functions of x , is.
[Free Solution] In Chapter 6, you solved the firstorder linear
A differential equation of type \[y' + a\left( x \right)y = f\left( x \right),\] where a ( x ) and f ( x ) are continuous functions of x , is called a linear. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation. We define the complimentary and. →x ′ (t) = a→x(t) + →f(t), where a is a.
(PDF) Solution of First Order Linear Non Homogeneous Ordinary
We define the complimentary and. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation. →x ′ (t) = a→x(t) + →f(t), where a is a constant matrix. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation \begin{equation*} {\vec{x}}'(t) = a\vec{x}(t) + \vec{f}(t) , \end{equation*} where. A differential equation of type \[y' + a\left( x \right)y = f\left( x.
→X ′ (T) = A→X(T) + →F(T), Where A Is A Constant Matrix.
A differential equation of type \[y' + a\left( x \right)y = f\left( x \right),\] where a ( x ) and f ( x ) are continuous functions of x , is called a linear. In this section we will discuss the basics of solving nonhomogeneous differential equations. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation. Let us first focus on the nonhomogeneous first order equation \begin{equation*} {\vec{x}}'(t) = a\vec{x}(t) + \vec{f}(t) , \end{equation*} where.

![[Solved] Problem 1. A firstorder nonhomogeneous linear d](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/98a/98ac0020-b00d-4c29-910b-be67d8ef24fc/php2sMFQN)