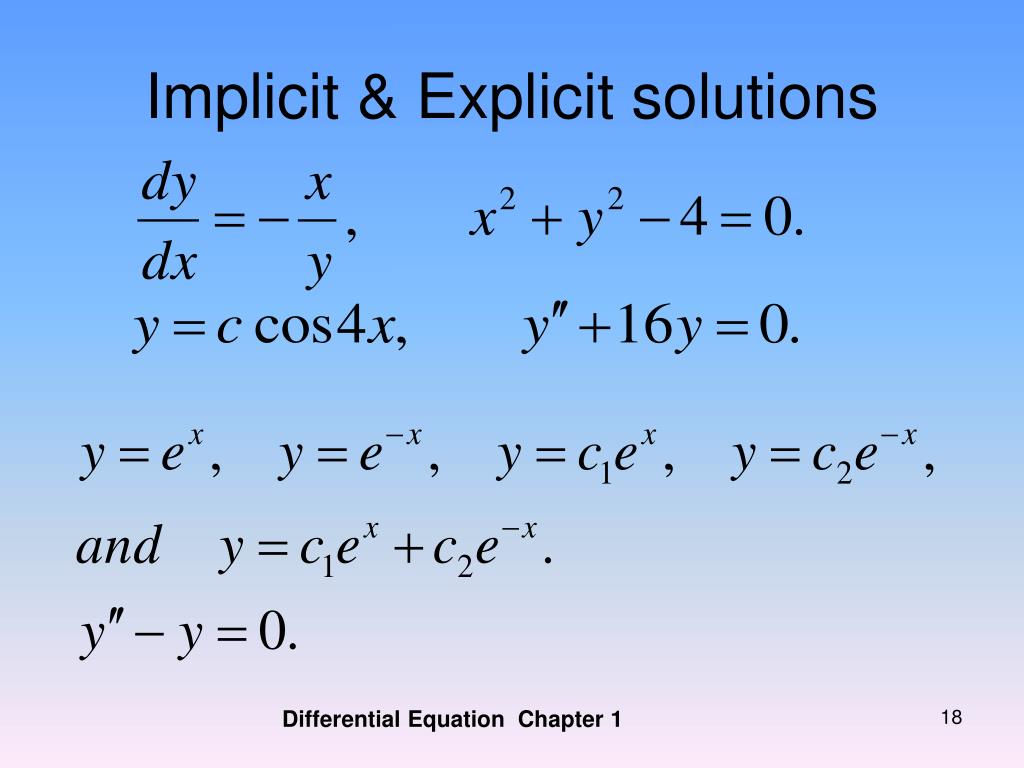
Explicit Form Differential Equations - Differential equations (des) are mathematical equations that describe the relationship between a function and its derivatives, either ordinary. Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an implicit differential equation. If it is of the form. Implicit differentiation allow us to find the derivative (s) of y with respect to x without making the function (s) explicit. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n) is. The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y ′ ′. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$;
Implicit differentiation allow us to find the derivative (s) of y with respect to x without making the function (s) explicit. Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n) is. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an implicit differential equation. Differential equations (des) are mathematical equations that describe the relationship between a function and its derivatives, either ordinary. The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y ′ ′. If it is of the form. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$;
Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n) is. If it is of the form. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Differential equations (des) are mathematical equations that describe the relationship between a function and its derivatives, either ordinary. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y ′ ′. Implicit differentiation allow us to find the derivative (s) of y with respect to x without making the function (s) explicit. Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an implicit differential equation.
Find the explicit particular solution of the differenti... Math
Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n) is. Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an implicit differential equation. If it is of the form. The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y.
[Solved] Find the solution of the given initial value problem in
Implicit differentiation allow us to find the derivative (s) of y with respect to x without making the function (s) explicit. Differential equations (des) are mathematical equations that describe the relationship between a function and its derivatives, either ordinary. Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called.
Solved A) Determine the implicit and explicit form of
Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y ′ ′. Differential equations (des) are mathematical equations that describe the relationship between a function and its derivatives, either ordinary. Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative.
PPT Ordinary Differential Equations PowerPoint Presentation, free
Differential equations (des) are mathematical equations that describe the relationship between a function and its derivatives, either ordinary. Implicit differentiation allow us to find the derivative (s) of y with respect to x without making the function (s) explicit. Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n) is. Thus, if a differential equation of order n has.
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y ′ ′. Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n) is. Differential equations (des) are mathematical equations that describe the relationship between a function and its derivatives, either ordinary. Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form.
Exact differential equations Yawin
If it is of the form. Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n) is. The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y ′ ′. Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an implicit.
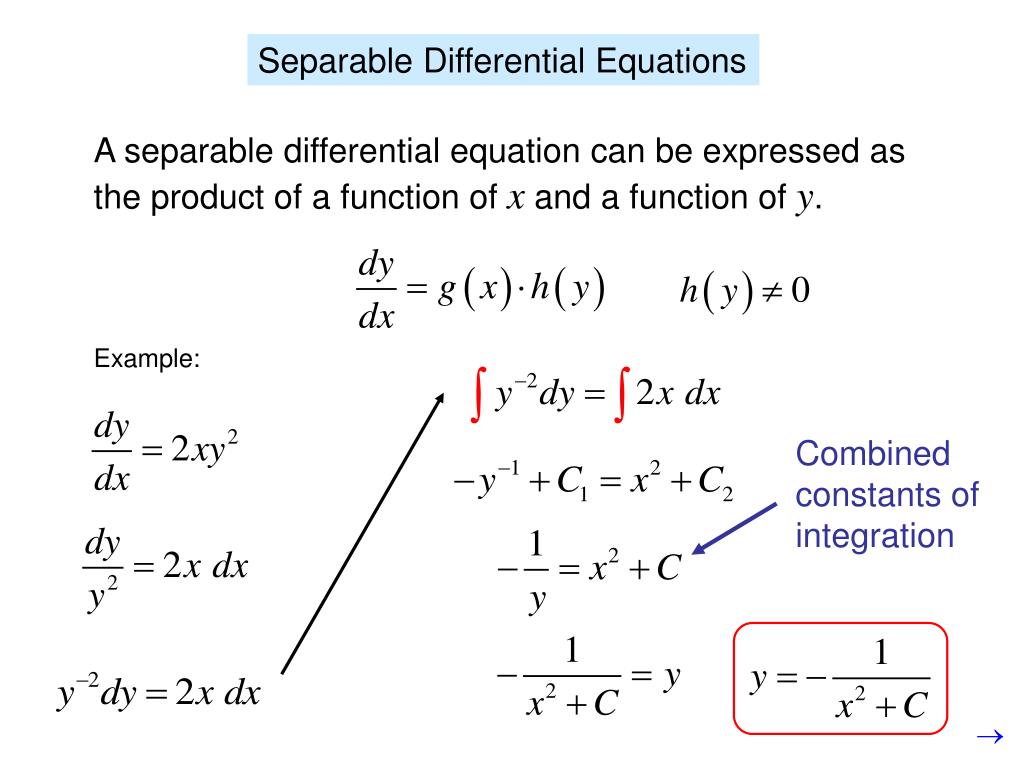
PPT Separable Differential Equations PowerPoint Presentation, free
The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Differential equations (des) are mathematical equations that describe the relationship between a function and its derivatives, either ordinary. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y ′ ′. Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative.
Ordinary Differential Equations (A Comprehensive Resource)
Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n) is. Implicit differentiation allow us to find the derivative (s) of y with respect to x without making the function (s) explicit. The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y ′ ′. Thus, if a differential equation of order n.
Particular Solution of NonHomogeneous Differential Equations Mr
Differential equations (des) are mathematical equations that describe the relationship between a function and its derivatives, either ordinary. If it is of the form. Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n) is. The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y ′ ′. Implicit differentiation allow us to.
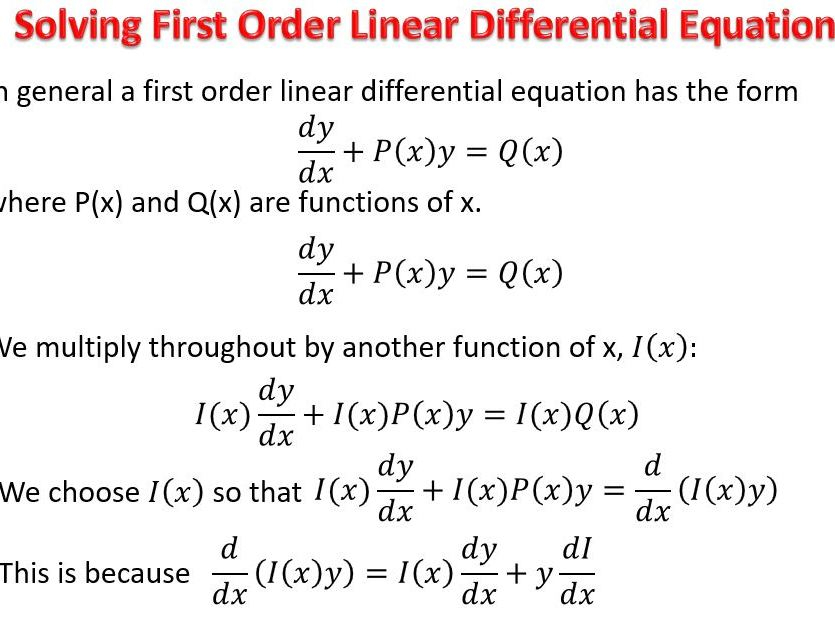
First Order Differential Equation Worksheet Equations Worksheets
Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. Implicit differentiation allow us to find the derivative (s) of y with respect to x without making the function (s) explicit. If it is of the form. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it.
If It Is Of The Form.
Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. Differential equations (des) are mathematical equations that describe the relationship between a function and its derivatives, either ordinary. The de can be structured to look like y (n) = f (x, y, y ′, y ′ ′. Y (n − 1)), where the highest order derivative y (n) is.
Implicit Differentiation Allow Us To Find The Derivative (S) Of Y With Respect To X Without Making The Function (S) Explicit.
The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Thus, if a differential equation of order n has the form f(x, y', y'',.y (n)) = 0, then it is called an implicit differential equation.