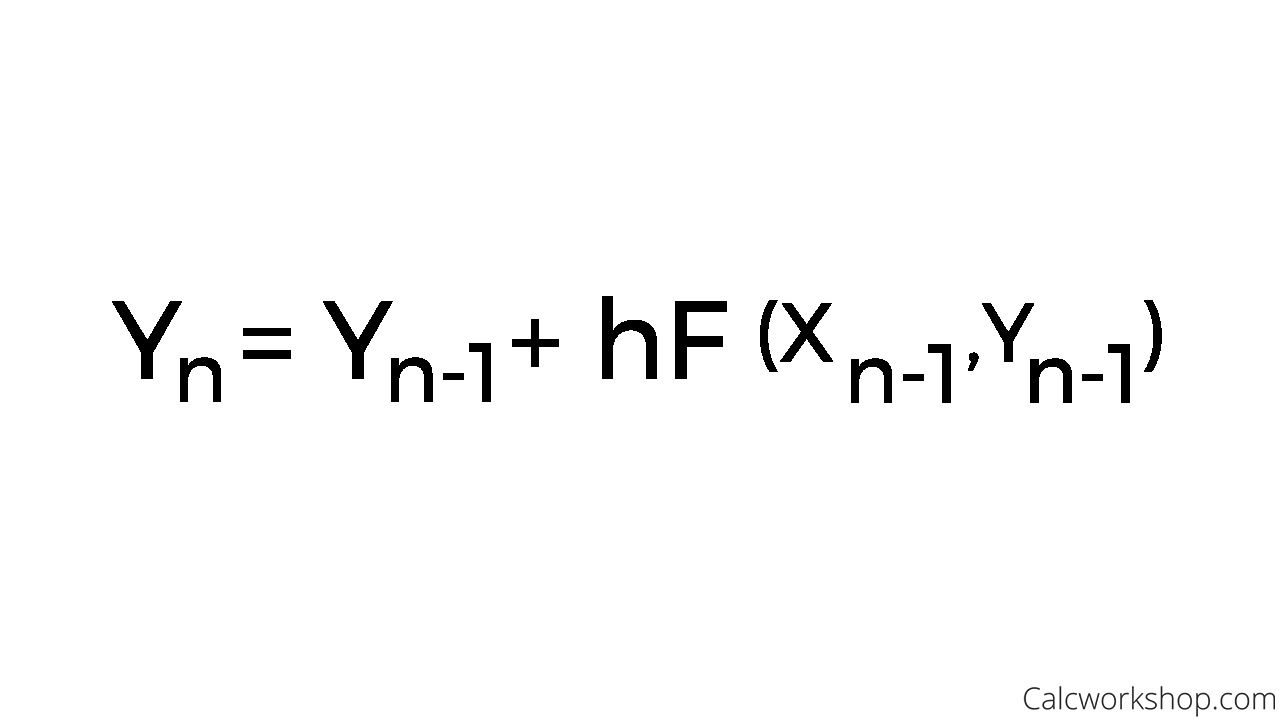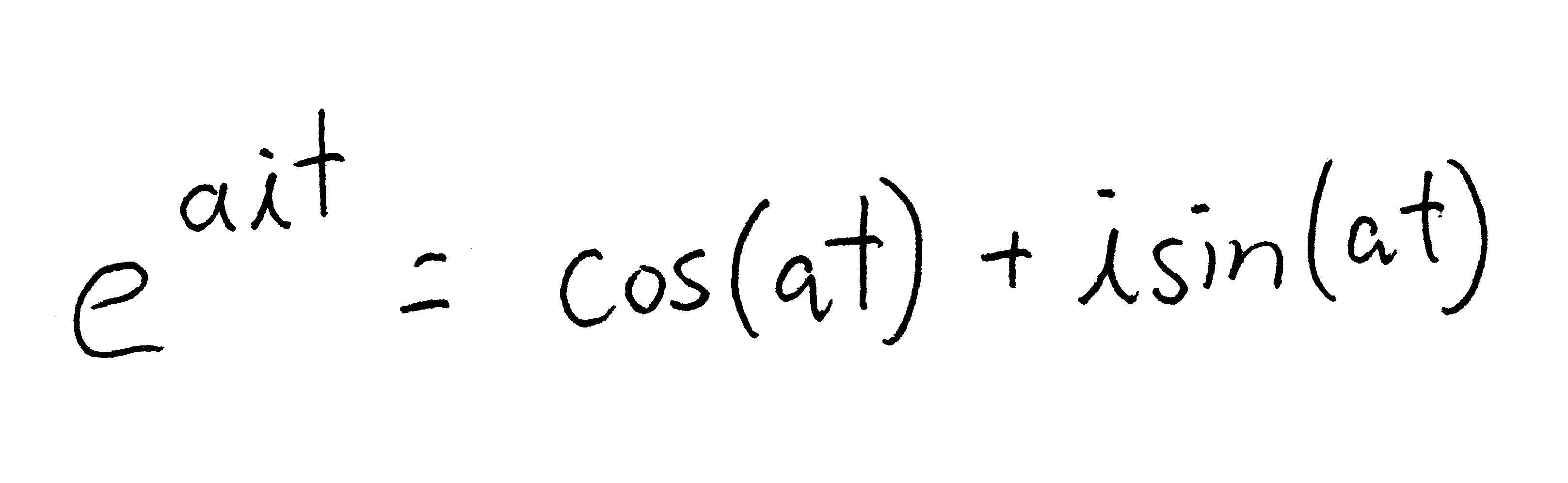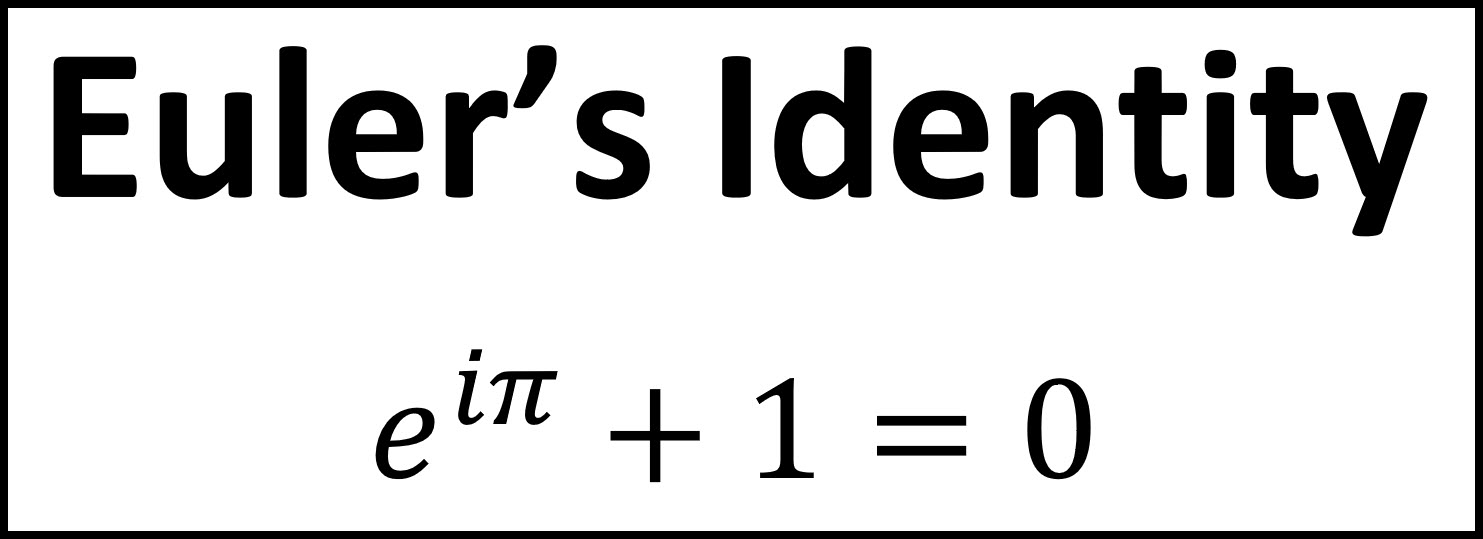Euler Formula Differential Equation - Note that while this does not involve a. They occasionally arise in applications, though not. In this section, we will investigate the solutions of the most simple type of differential equations with regular singular points. Euler equations are important for two or three good reasons: X2y′′ + axy′ + by = 0 x 2. Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)). In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0.
In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. Euler equations are important for two or three good reasons: They occasionally arise in applications, though not. Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)). In this section, we will investigate the solutions of the most simple type of differential equations with regular singular points. X2y′′ + axy′ + by = 0 x 2. Note that while this does not involve a.
X2y′′ + axy′ + by = 0 x 2. Euler equations are important for two or three good reasons: They occasionally arise in applications, though not. In this section, we will investigate the solutions of the most simple type of differential equations with regular singular points. Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)). In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. Note that while this does not involve a.
Euler's Method Explained with Examples
X2y′′ + axy′ + by = 0 x 2. In this section, we will investigate the solutions of the most simple type of differential equations with regular singular points. Note that while this does not involve a. Euler equations are important for two or three good reasons: They occasionally arise in applications, though not.
SOLUTION Cauchy euler s differential equations Studypool
X2y′′ + axy′ + by = 0 x 2. They occasionally arise in applications, though not. In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. Note that while this does not involve a. In this section, we will investigate the solutions of the most simple type of differential equations with regular.
How to do Euler's Method? (Simply Explained in 4 Powerful Examples)
They occasionally arise in applications, though not. In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. Euler equations are important for two or three good reasons: Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)). X2y′′ + axy′ +.
Solved The Euler formula for the differential equation
In this section, we will investigate the solutions of the most simple type of differential equations with regular singular points. Note that while this does not involve a. X2y′′ + axy′ + by = 0 x 2. Euler equations are important for two or three good reasons: In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y''.
Euler's Formula Definition Facts Britannica, 47 OFF
In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)). They occasionally arise in applications, though not. In this section, we will investigate the solutions of the most simple type of.
Eulers Equation
They occasionally arise in applications, though not. X2y′′ + axy′ + by = 0 x 2. In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)). Euler equations are important for.
Euler's Method Explained With Examples, 40 OFF
Euler equations are important for two or three good reasons: They occasionally arise in applications, though not. Note that while this does not involve a. In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. X2y′′ + axy′ + by = 0 x 2.
Euler's Formula
X2y′′ + axy′ + by = 0 x 2. In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. They occasionally arise in applications, though not. Euler equations are important for two or three good reasons: Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of.
Solved Euler's Method Today you will use Euler's method to
In this section, we will investigate the solutions of the most simple type of differential equations with regular singular points. Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)). They occasionally arise in applications, though not. X2y′′ + axy′ + by = 0 x 2. Euler equations are.
Euler's Method on differential equation Mathematics Stack Exchange
Note that while this does not involve a. X2y′′ + axy′ + by = 0 x 2. Euler equations are important for two or three good reasons: Euler’s method is based on the assumption that the tangent line to the integral curve of equation 3.1.1 at (xi, y(xi)). In this section, we will investigate the solutions of the most simple.
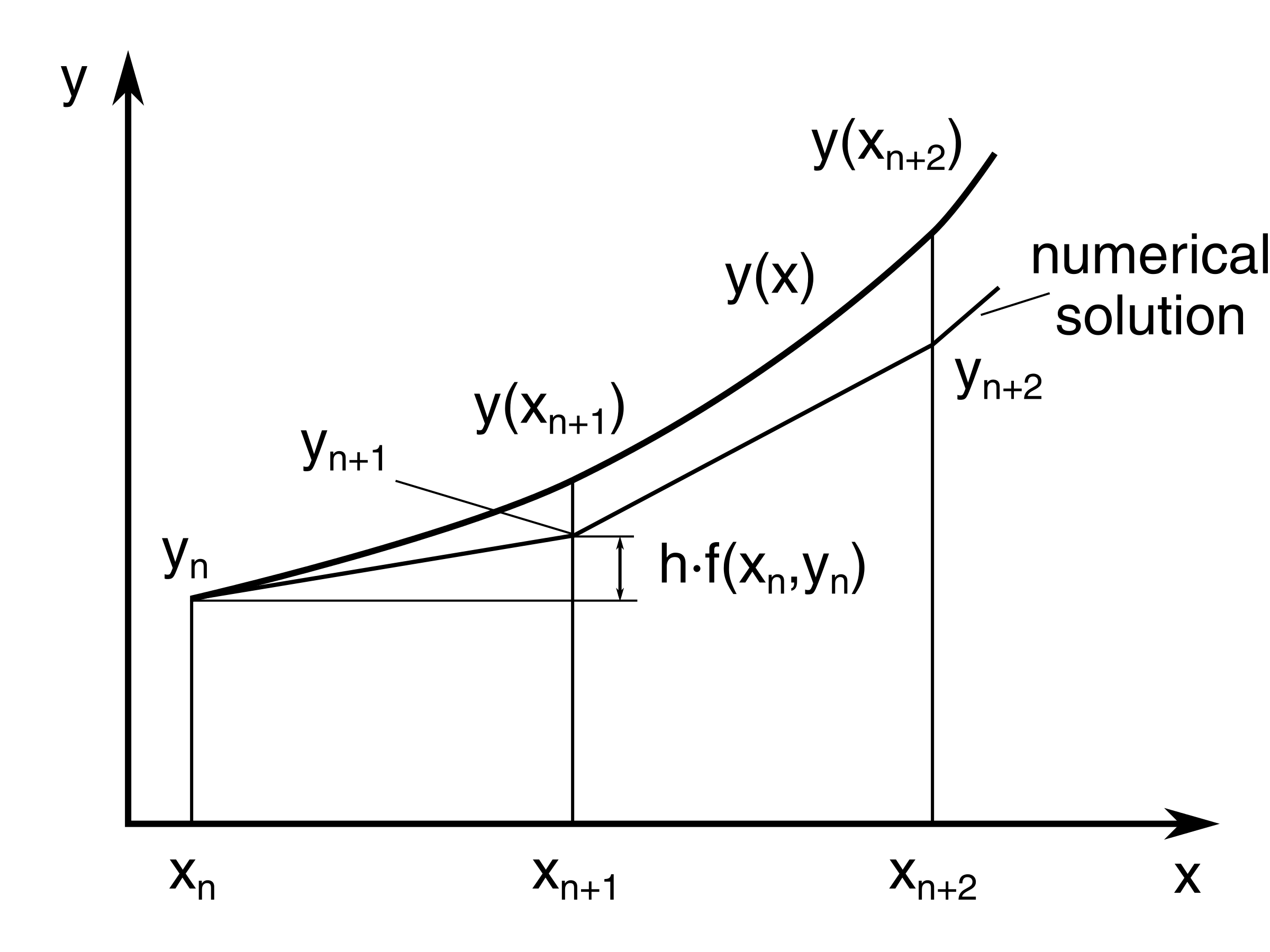
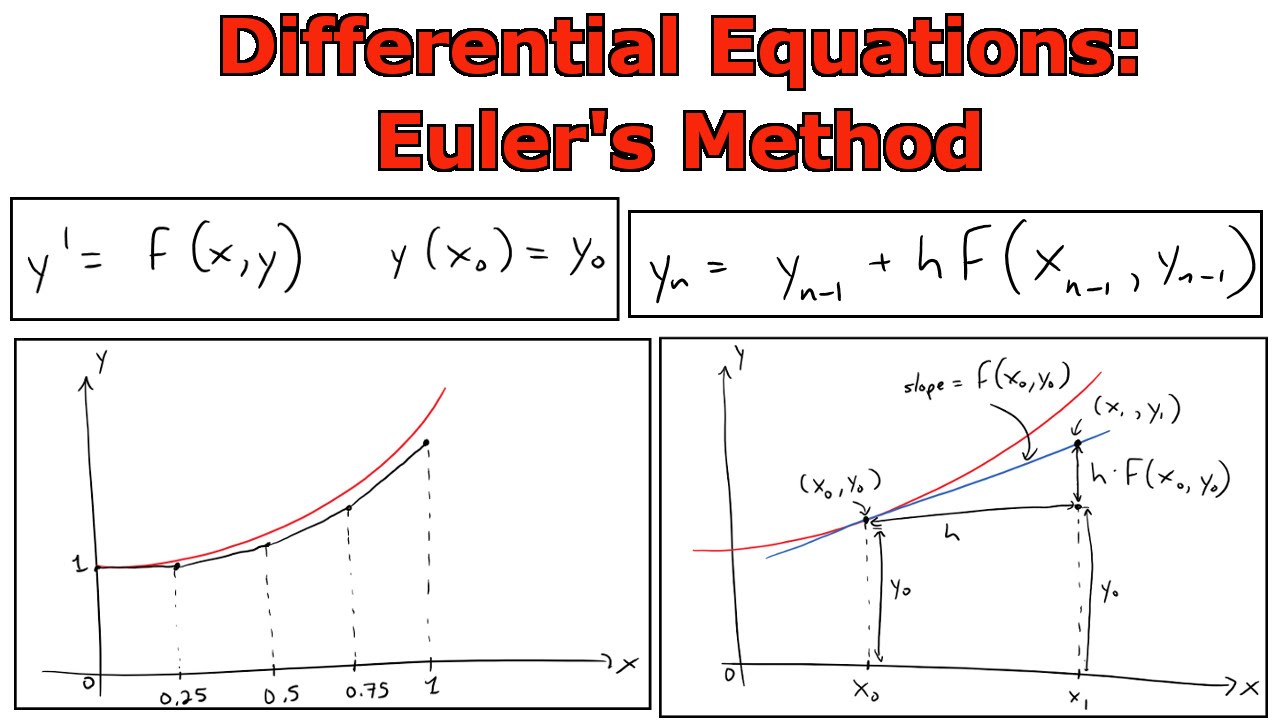
Euler’s Method Is Based On The Assumption That The Tangent Line To The Integral Curve Of Equation 3.1.1 At (Xi, Y(Xi)).
They occasionally arise in applications, though not. Note that while this does not involve a. In this section, we will investigate the solutions of the most simple type of differential equations with regular singular points. Euler equations are important for two or three good reasons:
X2Y′′ + Axy′ + By = 0 X 2.
In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0.