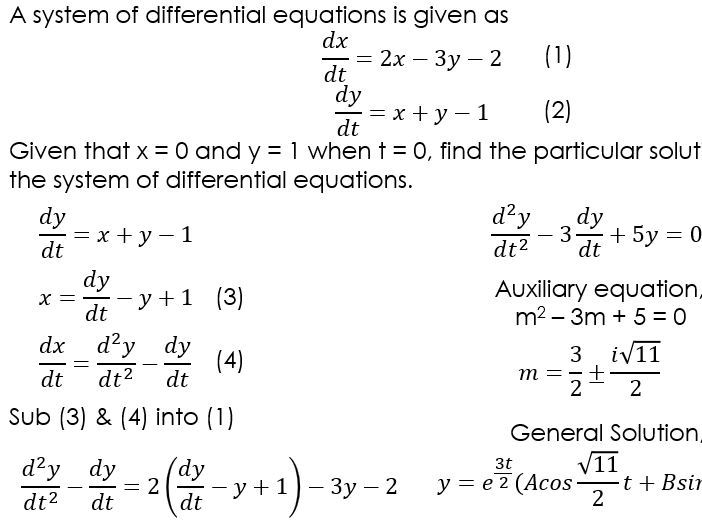Eigenvectors Differential Equations - Here is the eigenvalue and x is the eigenvector. This chapter ends by solving linear differential equations du/dt = au. The pieces of the solution are u(t) = eλtx instead of un =. Note that it is always true that a0 = 0 for any. The usefulness of these facts will become apparent when we get back into differential equations since in that work we will. This section introduces eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a matrix, and discusses the role of the eigenvalues in determining the behavior of. Understanding eigenvalues and eigenvectors is essential for solving systems of differential equations, particularly in finding solutions to. This is why we make the. Let \(a\) be an \(n\times n\) matrix, \(\vec{x}\) a nonzero \(n\times 1\) column.
This section introduces eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a matrix, and discusses the role of the eigenvalues in determining the behavior of. This chapter ends by solving linear differential equations du/dt = au. The pieces of the solution are u(t) = eλtx instead of un =. Note that it is always true that a0 = 0 for any. This is why we make the. The usefulness of these facts will become apparent when we get back into differential equations since in that work we will. Here is the eigenvalue and x is the eigenvector. Understanding eigenvalues and eigenvectors is essential for solving systems of differential equations, particularly in finding solutions to. Let \(a\) be an \(n\times n\) matrix, \(\vec{x}\) a nonzero \(n\times 1\) column.
Let \(a\) be an \(n\times n\) matrix, \(\vec{x}\) a nonzero \(n\times 1\) column. This section introduces eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a matrix, and discusses the role of the eigenvalues in determining the behavior of. This chapter ends by solving linear differential equations du/dt = au. Understanding eigenvalues and eigenvectors is essential for solving systems of differential equations, particularly in finding solutions to. This is why we make the. The pieces of the solution are u(t) = eλtx instead of un =. Here is the eigenvalue and x is the eigenvector. The usefulness of these facts will become apparent when we get back into differential equations since in that work we will. Note that it is always true that a0 = 0 for any.
(PDF) Differential Equations Review _ Eigenvalues & Eigenvectors
Let \(a\) be an \(n\times n\) matrix, \(\vec{x}\) a nonzero \(n\times 1\) column. This chapter ends by solving linear differential equations du/dt = au. Note that it is always true that a0 = 0 for any. Here is the eigenvalue and x is the eigenvector. The usefulness of these facts will become apparent when we get back into differential equations.
On Derivatives of Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors of The Download Free
This is why we make the. This section introduces eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a matrix, and discusses the role of the eigenvalues in determining the behavior of. The usefulness of these facts will become apparent when we get back into differential equations since in that work we will. Understanding eigenvalues and eigenvectors is essential for solving systems of differential equations,.
Solved Solve the given system of differential equations
Note that it is always true that a0 = 0 for any. The usefulness of these facts will become apparent when we get back into differential equations since in that work we will. This chapter ends by solving linear differential equations du/dt = au. Understanding eigenvalues and eigenvectors is essential for solving systems of differential equations, particularly in finding solutions.
Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors, Linear Differential Equations CSE 494
The usefulness of these facts will become apparent when we get back into differential equations since in that work we will. This chapter ends by solving linear differential equations du/dt = au. This is why we make the. Understanding eigenvalues and eigenvectors is essential for solving systems of differential equations, particularly in finding solutions to. The pieces of the solution.
linear algebra Using eigenvectors and values to get systems of
Note that it is always true that a0 = 0 for any. The pieces of the solution are u(t) = eλtx instead of un =. This chapter ends by solving linear differential equations du/dt = au. Understanding eigenvalues and eigenvectors is essential for solving systems of differential equations, particularly in finding solutions to. This is why we make the.
finite element method Finding eigenvectors of a differential operator
Understanding eigenvalues and eigenvectors is essential for solving systems of differential equations, particularly in finding solutions to. Here is the eigenvalue and x is the eigenvector. This section introduces eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a matrix, and discusses the role of the eigenvalues in determining the behavior of. Note that it is always true that a0 = 0 for any. This.
Modelling with differential equations Teaching Resources
This section introduces eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a matrix, and discusses the role of the eigenvalues in determining the behavior of. Here is the eigenvalue and x is the eigenvector. This is why we make the. This chapter ends by solving linear differential equations du/dt = au. The usefulness of these facts will become apparent when we get back into.
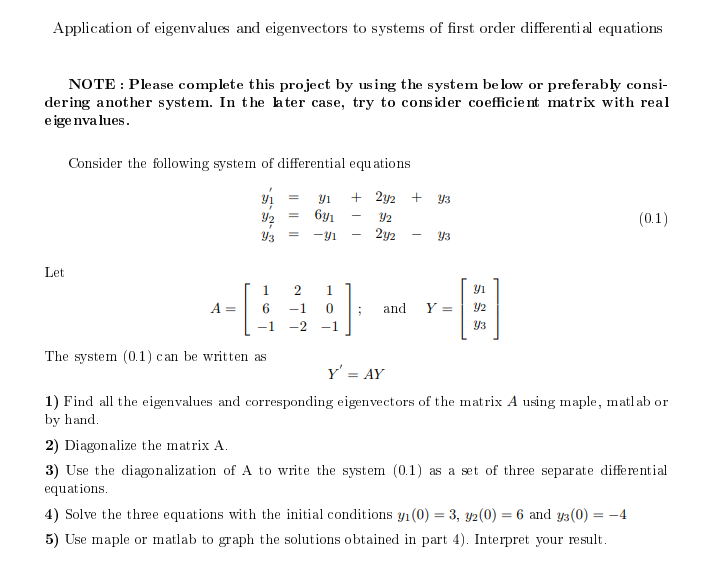
Solved Application of eigenvalues and eigenvectors to
This section introduces eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a matrix, and discusses the role of the eigenvalues in determining the behavior of. Let \(a\) be an \(n\times n\) matrix, \(\vec{x}\) a nonzero \(n\times 1\) column. The pieces of the solution are u(t) = eλtx instead of un =. The usefulness of these facts will become apparent when we get back into.
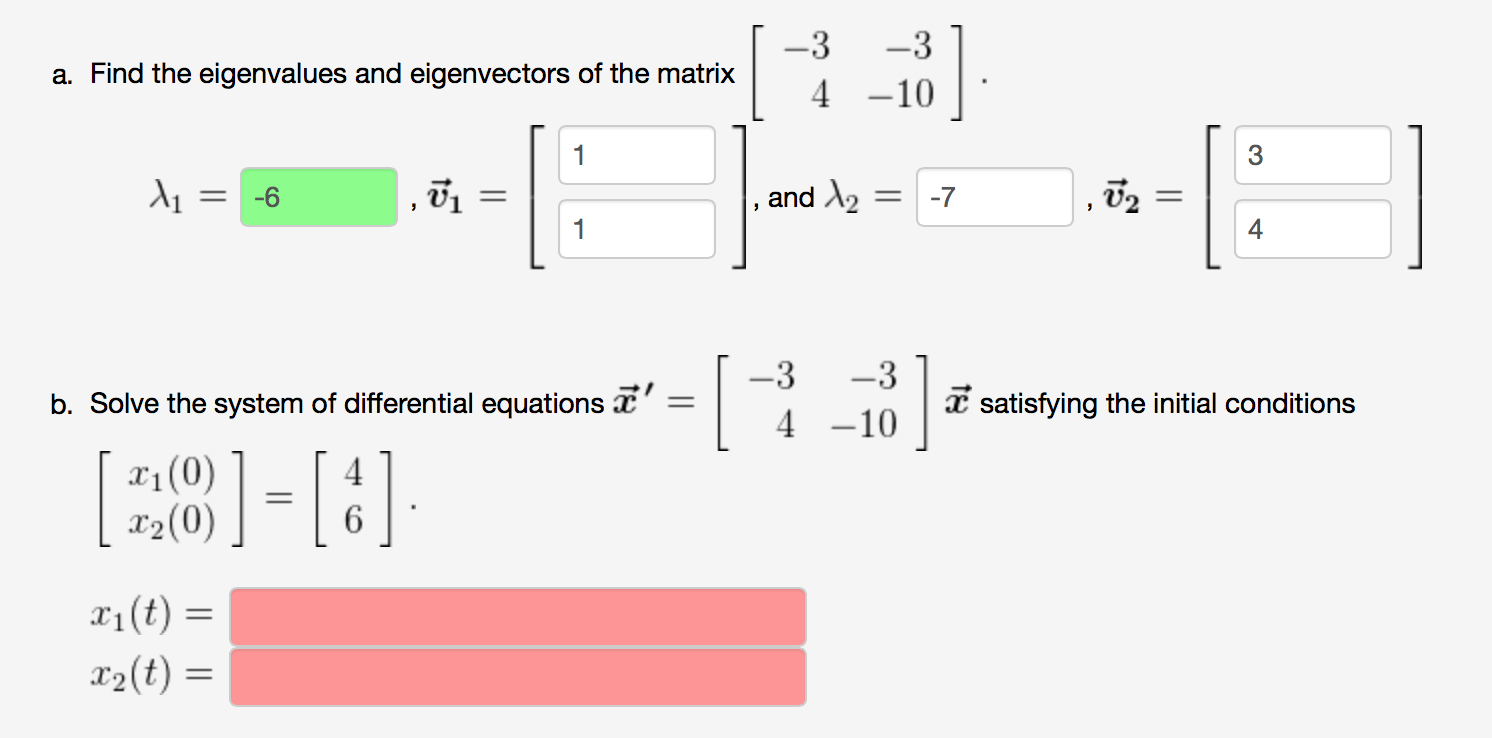
Solved a. Find the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the
Understanding eigenvalues and eigenvectors is essential for solving systems of differential equations, particularly in finding solutions to. This section introduces eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a matrix, and discusses the role of the eigenvalues in determining the behavior of. The pieces of the solution are u(t) = eλtx instead of un =. Let \(a\) be an \(n\times n\) matrix, \(\vec{x}\) a.
eigenvalues eigenvectors Differential Equations Direction Field
This chapter ends by solving linear differential equations du/dt = au. Let \(a\) be an \(n\times n\) matrix, \(\vec{x}\) a nonzero \(n\times 1\) column. Understanding eigenvalues and eigenvectors is essential for solving systems of differential equations, particularly in finding solutions to. This section introduces eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a matrix, and discusses the role of the eigenvalues in determining the.
Note That It Is Always True That A0 = 0 For Any.
This chapter ends by solving linear differential equations du/dt = au. The usefulness of these facts will become apparent when we get back into differential equations since in that work we will. This is why we make the. Let \(a\) be an \(n\times n\) matrix, \(\vec{x}\) a nonzero \(n\times 1\) column.
This Section Introduces Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors Of A Matrix, And Discusses The Role Of The Eigenvalues In Determining The Behavior Of.
Understanding eigenvalues and eigenvectors is essential for solving systems of differential equations, particularly in finding solutions to. The pieces of the solution are u(t) = eλtx instead of un =. Here is the eigenvalue and x is the eigenvector.