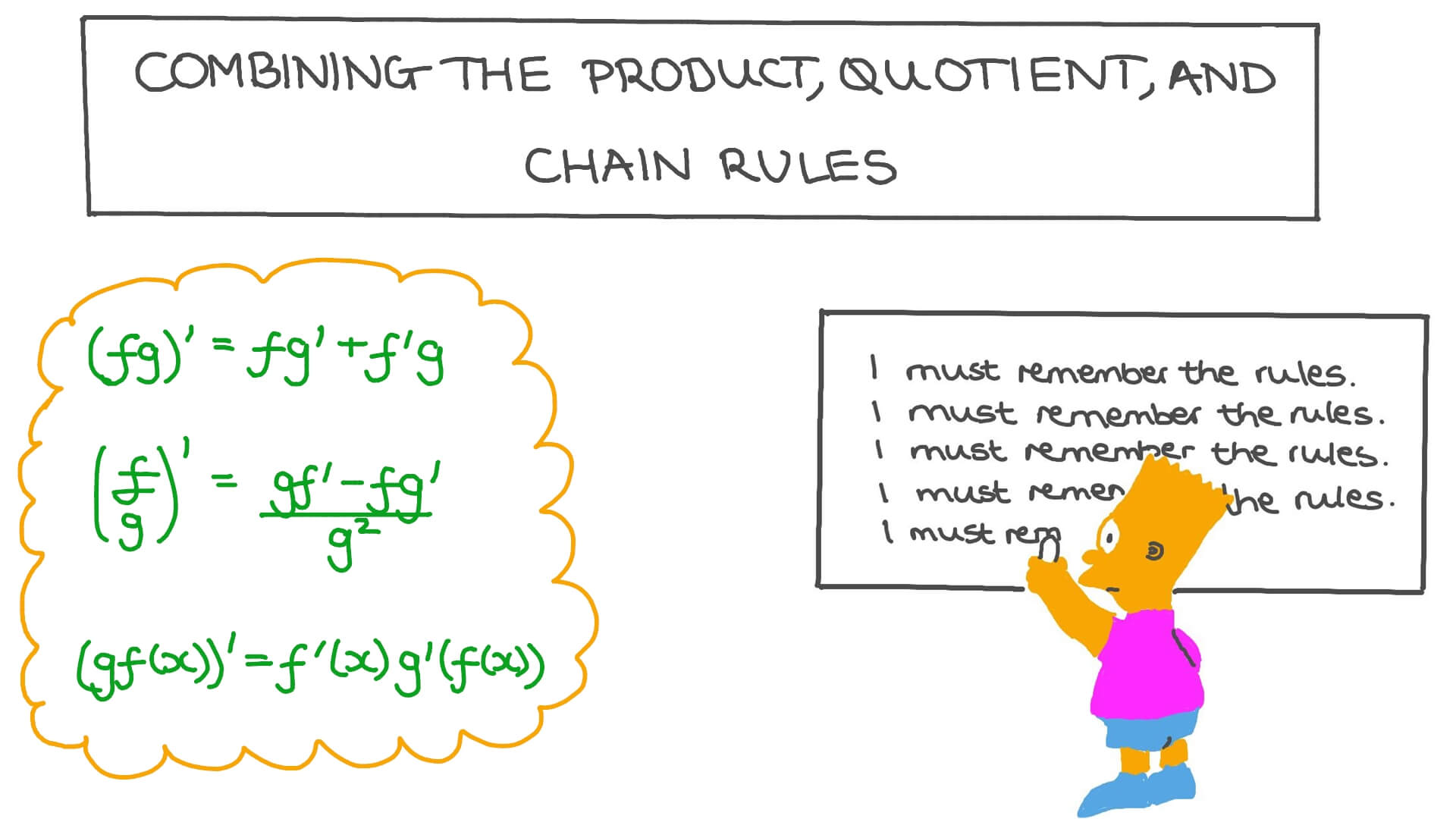
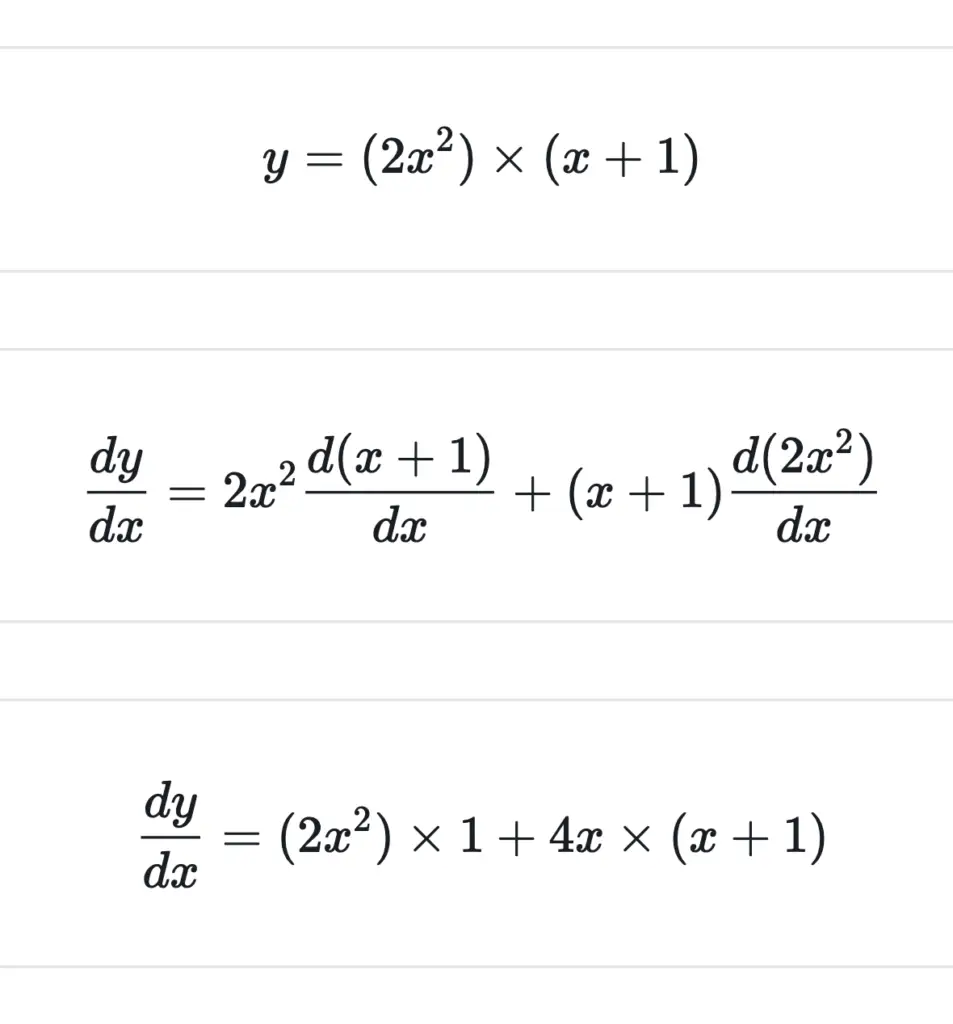
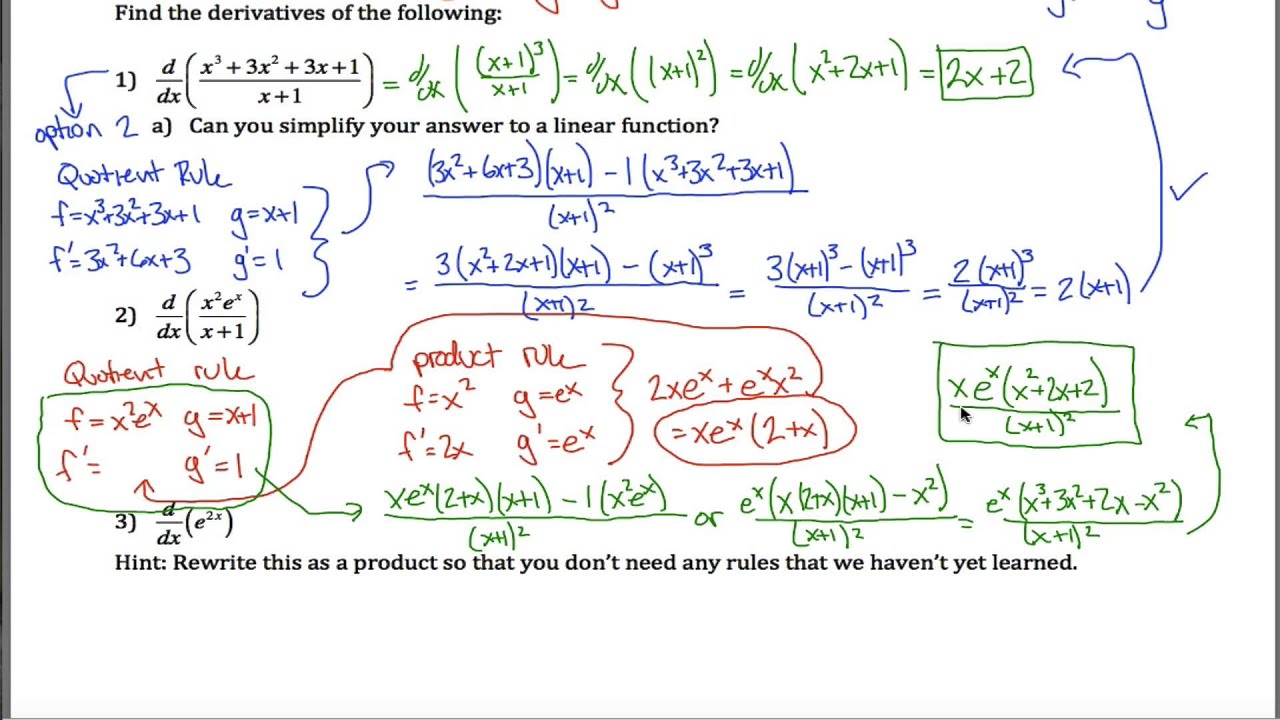
Differentiation Product And Quotient Rule - If the two functions \ (f\left ( x. The sum/difference, constant multiple, power, product and quotient rules show us how to find the derivatives of certain. D dx(f ⋅ g) = f ′ ⋅ g + f ⋅ g ′. The product and quotient rules are covered in this section. If a function is a sum, product, or quotient of simpler functions, then we can use the sum, product, or quotient rules to differentiate it. In this chapter we introduce derivatives. We cover the standard derivatives formulas including the product rule, quotient rule and chain rule as well. The derivative of the first factor times the. In what follows, f and g are differentiable functions of x. D (uv) = vdu + udv dx dx dx.
In what follows, f and g are differentiable functions of x. If the two functions \ (f\left ( x. In this chapter we introduce derivatives. This is another very useful formula: D dx(f ⋅ g) = f ′ ⋅ g + f ⋅ g ′. D (uv) = vdu + udv dx dx dx. Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the product and quotient rule section of the derivatives chapter of the notes. The derivative of the first factor times the. To differentiate products and quotients we have the product rule and the quotient rule. If a function is a sum, product, or quotient of simpler functions, then we can use the sum, product, or quotient rules to differentiate it.
In what follows, f and g are differentiable functions of x. In this chapter we introduce derivatives. If the two functions \ (f\left ( x. We cover the standard derivatives formulas including the product rule, quotient rule and chain rule as well. This is another very useful formula: To differentiate products and quotients we have the product rule and the quotient rule. The product and quotient rules are covered in this section. D (uv) = vdu + udv dx dx dx. If a function is a sum, product, or quotient of simpler functions, then we can use the sum, product, or quotient rules to differentiate it. D dx(f ⋅ g) = f ′ ⋅ g + f ⋅ g ′.
Differentiation Product & Quotient Rule Kappa Maths Resources for A
If a function is a sum, product, or quotient of simpler functions, then we can use the sum, product, or quotient rules to differentiate it. The product and quotient rules are covered in this section. In this chapter we introduce derivatives. This is another very useful formula: The sum/difference, constant multiple, power, product and quotient rules show us how to.
Differentiation Product & Quotient Rule Kappa Maths Resources for A
The sum/difference, constant multiple, power, product and quotient rules show us how to find the derivatives of certain. In this chapter we introduce derivatives. The derivative of the first factor times the. The product and quotient rules are covered in this section. D dx(f ⋅ g) = f ′ ⋅ g + f ⋅ g ′.
A2 Differentiation Quotient Rule Part 1 alevelmathematicsnotes
This is another very useful formula: Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the product and quotient rule section of the derivatives chapter of the notes. If a function is a sum, product, or quotient of simpler functions, then we can use the sum, product, or quotient rules to differentiate it. In this chapter we introduce derivatives. In.
Product And Quotient Rule Worksheet Zip Worksheet
In what follows, f and g are differentiable functions of x. The sum/difference, constant multiple, power, product and quotient rules show us how to find the derivatives of certain. This is another very useful formula: If the two functions \ (f\left ( x. The derivative of the first factor times the.
Products, Quotients, and Chains Simple Rules for Calculus
The derivative of the first factor times the. D dx(f ⋅ g) = f ′ ⋅ g + f ⋅ g ′. D (uv) = vdu + udv dx dx dx. To differentiate products and quotients we have the product rule and the quotient rule. If a function is a sum, product, or quotient of simpler functions, then we can.
Product And Quotient Rule Worksheet Zip Worksheet
The sum/difference, constant multiple, power, product and quotient rules show us how to find the derivatives of certain. We cover the standard derivatives formulas including the product rule, quotient rule and chain rule as well. Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the product and quotient rule section of the derivatives chapter of the notes. The derivative of.
Product And Quotient Rule Worksheet Zip Worksheet
Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the product and quotient rule section of the derivatives chapter of the notes. We cover the standard derivatives formulas including the product rule, quotient rule and chain rule as well. The product and quotient rules are covered in this section. D dx(f ⋅ g) = f ′ ⋅ g + f.
Differentiation Product & Quotient Rule Kappa Maths Resources for A
If a function is a sum, product, or quotient of simpler functions, then we can use the sum, product, or quotient rules to differentiate it. Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the product and quotient rule section of the derivatives chapter of the notes. This is another very useful formula: In this chapter we introduce derivatives. To.
A2 Differentiation Quotient Rule Part 1 alevelmathematicsnotes
In this chapter we introduce derivatives. D (uv) = vdu + udv dx dx dx. The product and quotient rules are covered in this section. D dx(f ⋅ g) = f ′ ⋅ g + f ⋅ g ′. The sum/difference, constant multiple, power, product and quotient rules show us how to find the derivatives of certain.
Differentiation Product & Quotient Rule Kappa Maths Resources for A
To differentiate products and quotients we have the product rule and the quotient rule. Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the product and quotient rule section of the derivatives chapter of the notes. In what follows, f and g are differentiable functions of x. The derivative of the first factor times the. The product and quotient rules.
D (Uv) = Vdu + Udv Dx Dx Dx.
If the two functions \ (f\left ( x. We cover the standard derivatives formulas including the product rule, quotient rule and chain rule as well. In what follows, f and g are differentiable functions of x. If a function is a sum, product, or quotient of simpler functions, then we can use the sum, product, or quotient rules to differentiate it.
To Differentiate Products And Quotients We Have The Product Rule And The Quotient Rule.
The product and quotient rules are covered in this section. This is another very useful formula: D dx(f ⋅ g) = f ′ ⋅ g + f ⋅ g ′. In this chapter we introduce derivatives.
The Sum/Difference, Constant Multiple, Power, Product And Quotient Rules Show Us How To Find The Derivatives Of Certain.
Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the product and quotient rule section of the derivatives chapter of the notes. The derivative of the first factor times the.