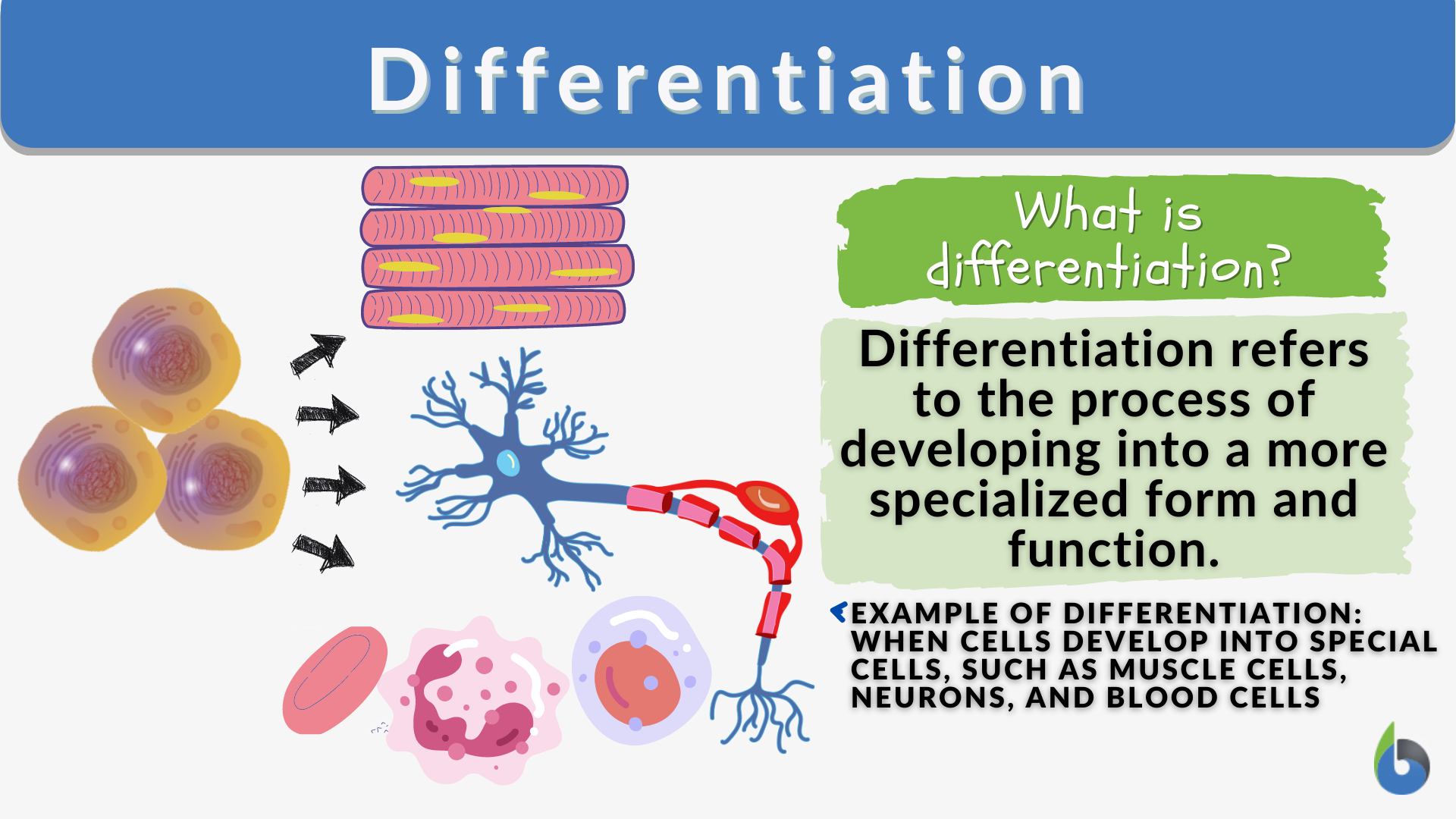
Differentiation In Plants - Differentiation in plants refers to the processes by which distinct cell types arise from precursor cells and become different from each other. Cell walls not only provide strength and mechanical support, but they also play diverse functions in plant growth, development,. In plants, differentiation refers to the mechanisms through which separate cell types emerge from precursor cells by becoming distinct from one. In plants, the living differentiated cells can regain the capacity to divide mitotically under certain conditions. The sum of events, that bestow this. Differentiation occurs in plants when cells from the root apical and shoot apical meristems, as well as the cambium, differentiate and mature.
In plants, differentiation refers to the mechanisms through which separate cell types emerge from precursor cells by becoming distinct from one. In plants, the living differentiated cells can regain the capacity to divide mitotically under certain conditions. The sum of events, that bestow this. Cell walls not only provide strength and mechanical support, but they also play diverse functions in plant growth, development,. Differentiation in plants refers to the processes by which distinct cell types arise from precursor cells and become different from each other. Differentiation occurs in plants when cells from the root apical and shoot apical meristems, as well as the cambium, differentiate and mature.
Cell walls not only provide strength and mechanical support, but they also play diverse functions in plant growth, development,. The sum of events, that bestow this. Differentiation occurs in plants when cells from the root apical and shoot apical meristems, as well as the cambium, differentiate and mature. Differentiation in plants refers to the processes by which distinct cell types arise from precursor cells and become different from each other. In plants, the living differentiated cells can regain the capacity to divide mitotically under certain conditions. In plants, differentiation refers to the mechanisms through which separate cell types emerge from precursor cells by becoming distinct from one.
Differentiation Strategy The Marketing Eggspert Blog
Cell walls not only provide strength and mechanical support, but they also play diverse functions in plant growth, development,. In plants, the living differentiated cells can regain the capacity to divide mitotically under certain conditions. In plants, differentiation refers to the mechanisms through which separate cell types emerge from precursor cells by becoming distinct from one. The sum of events,.
Plant Cell Differentiation
In plants, differentiation refers to the mechanisms through which separate cell types emerge from precursor cells by becoming distinct from one. Cell walls not only provide strength and mechanical support, but they also play diverse functions in plant growth, development,. Differentiation in plants refers to the processes by which distinct cell types arise from precursor cells and become different from.
AoBP special issue Population differentiation in plants
Differentiation in plants refers to the processes by which distinct cell types arise from precursor cells and become different from each other. Cell walls not only provide strength and mechanical support, but they also play diverse functions in plant growth, development,. Differentiation occurs in plants when cells from the root apical and shoot apical meristems, as well as the cambium,.
Differentiation An Important Marketing Strategy Technique Career Parts
Cell walls not only provide strength and mechanical support, but they also play diverse functions in plant growth, development,. Differentiation occurs in plants when cells from the root apical and shoot apical meristems, as well as the cambium, differentiate and mature. In plants, the living differentiated cells can regain the capacity to divide mitotically under certain conditions. Differentiation in plants.
(PDF) Development and differentiation in plants
In plants, the living differentiated cells can regain the capacity to divide mitotically under certain conditions. Differentiation occurs in plants when cells from the root apical and shoot apical meristems, as well as the cambium, differentiate and mature. The sum of events, that bestow this. Differentiation in plants refers to the processes by which distinct cell types arise from precursor.
Differentiation Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
Cell walls not only provide strength and mechanical support, but they also play diverse functions in plant growth, development,. The sum of events, that bestow this. In plants, differentiation refers to the mechanisms through which separate cell types emerge from precursor cells by becoming distinct from one. Differentiation in plants refers to the processes by which distinct cell types arise.
PPT Differentiation in Seed Plants PowerPoint Presentation, free
In plants, the living differentiated cells can regain the capacity to divide mitotically under certain conditions. Differentiation in plants refers to the processes by which distinct cell types arise from precursor cells and become different from each other. The sum of events, that bestow this. Differentiation occurs in plants when cells from the root apical and shoot apical meristems, as.
(PDF) Differentiation patterns in higher plants DOKUMEN.TIPS
Differentiation in plants refers to the processes by which distinct cell types arise from precursor cells and become different from each other. In plants, differentiation refers to the mechanisms through which separate cell types emerge from precursor cells by becoming distinct from one. In plants, the living differentiated cells can regain the capacity to divide mitotically under certain conditions. Differentiation.
EB1911 Plants examples of cell differentiation (2 Stock Photo Alamy
Differentiation occurs in plants when cells from the root apical and shoot apical meristems, as well as the cambium, differentiate and mature. The sum of events, that bestow this. Differentiation in plants refers to the processes by which distinct cell types arise from precursor cells and become different from each other. Cell walls not only provide strength and mechanical support,.
Plant Cell Differentiation
The sum of events, that bestow this. Cell walls not only provide strength and mechanical support, but they also play diverse functions in plant growth, development,. In plants, differentiation refers to the mechanisms through which separate cell types emerge from precursor cells by becoming distinct from one. Differentiation in plants refers to the processes by which distinct cell types arise.
In Plants, The Living Differentiated Cells Can Regain The Capacity To Divide Mitotically Under Certain Conditions.
The sum of events, that bestow this. Differentiation occurs in plants when cells from the root apical and shoot apical meristems, as well as the cambium, differentiate and mature. Cell walls not only provide strength and mechanical support, but they also play diverse functions in plant growth, development,. In plants, differentiation refers to the mechanisms through which separate cell types emerge from precursor cells by becoming distinct from one.