Differentiate Between Variation And Heritability - Heritability estimates the relative contribution of genetic factors to the phenotypic variability observed in a population. Heritability is addressing the population level correlation between phenotypic variation and genotypic variation. Heritability, amount of phenotypic (observable) variation in a population that is attributable to individual genetic differences. There are two different types of heritability: Heritability is a concept that summarizes how much of the variation in a trait is due to variation in genetic factors. Often, this term is used in.
Heritability is a concept that summarizes how much of the variation in a trait is due to variation in genetic factors. There are two different types of heritability: Heritability is addressing the population level correlation between phenotypic variation and genotypic variation. Often, this term is used in. Heritability estimates the relative contribution of genetic factors to the phenotypic variability observed in a population. Heritability, amount of phenotypic (observable) variation in a population that is attributable to individual genetic differences.
Heritability, amount of phenotypic (observable) variation in a population that is attributable to individual genetic differences. Heritability is a concept that summarizes how much of the variation in a trait is due to variation in genetic factors. Heritability is addressing the population level correlation between phenotypic variation and genotypic variation. Often, this term is used in. There are two different types of heritability: Heritability estimates the relative contribution of genetic factors to the phenotypic variability observed in a population.
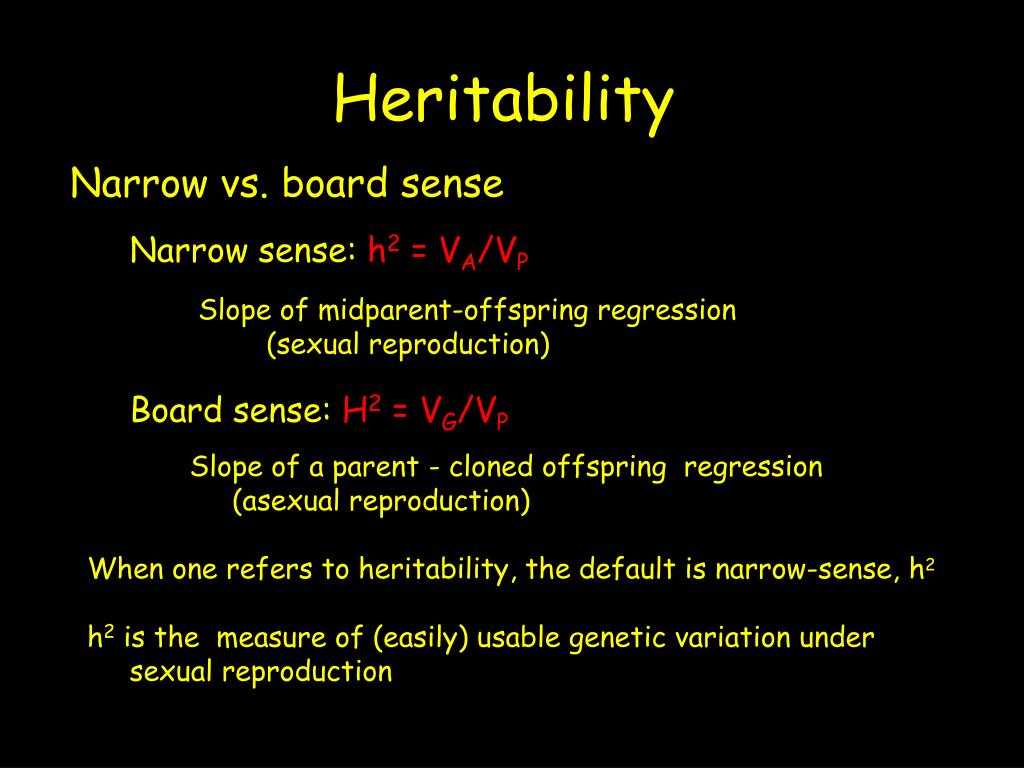
Coefficient of variation, heritability (broad sense) and
Heritability is a concept that summarizes how much of the variation in a trait is due to variation in genetic factors. There are two different types of heritability: Heritability is addressing the population level correlation between phenotypic variation and genotypic variation. Heritability, amount of phenotypic (observable) variation in a population that is attributable to individual genetic differences. Heritability estimates the.
Variation of heritability values for plant traits (a), physiological
Often, this term is used in. There are two different types of heritability: Heritability, amount of phenotypic (observable) variation in a population that is attributable to individual genetic differences. Heritability is a concept that summarizes how much of the variation in a trait is due to variation in genetic factors. Heritability is addressing the population level correlation between phenotypic variation.
variation and heritability estimates of quality traits in by
There are two different types of heritability: Heritability, amount of phenotypic (observable) variation in a population that is attributable to individual genetic differences. Heritability is a concept that summarizes how much of the variation in a trait is due to variation in genetic factors. Often, this term is used in. Heritability estimates the relative contribution of genetic factors to the.
Heritability and phenotype variation Download Table
Heritability is addressing the population level correlation between phenotypic variation and genotypic variation. Heritability, amount of phenotypic (observable) variation in a population that is attributable to individual genetic differences. Often, this term is used in. Heritability estimates the relative contribution of genetic factors to the phenotypic variability observed in a population. There are two different types of heritability:
PPT Lecture 4 Heritability PowerPoint Presentation ID518331
Often, this term is used in. Heritability estimates the relative contribution of genetic factors to the phenotypic variability observed in a population. Heritability is addressing the population level correlation between phenotypic variation and genotypic variation. There are two different types of heritability: Heritability, amount of phenotypic (observable) variation in a population that is attributable to individual genetic differences.
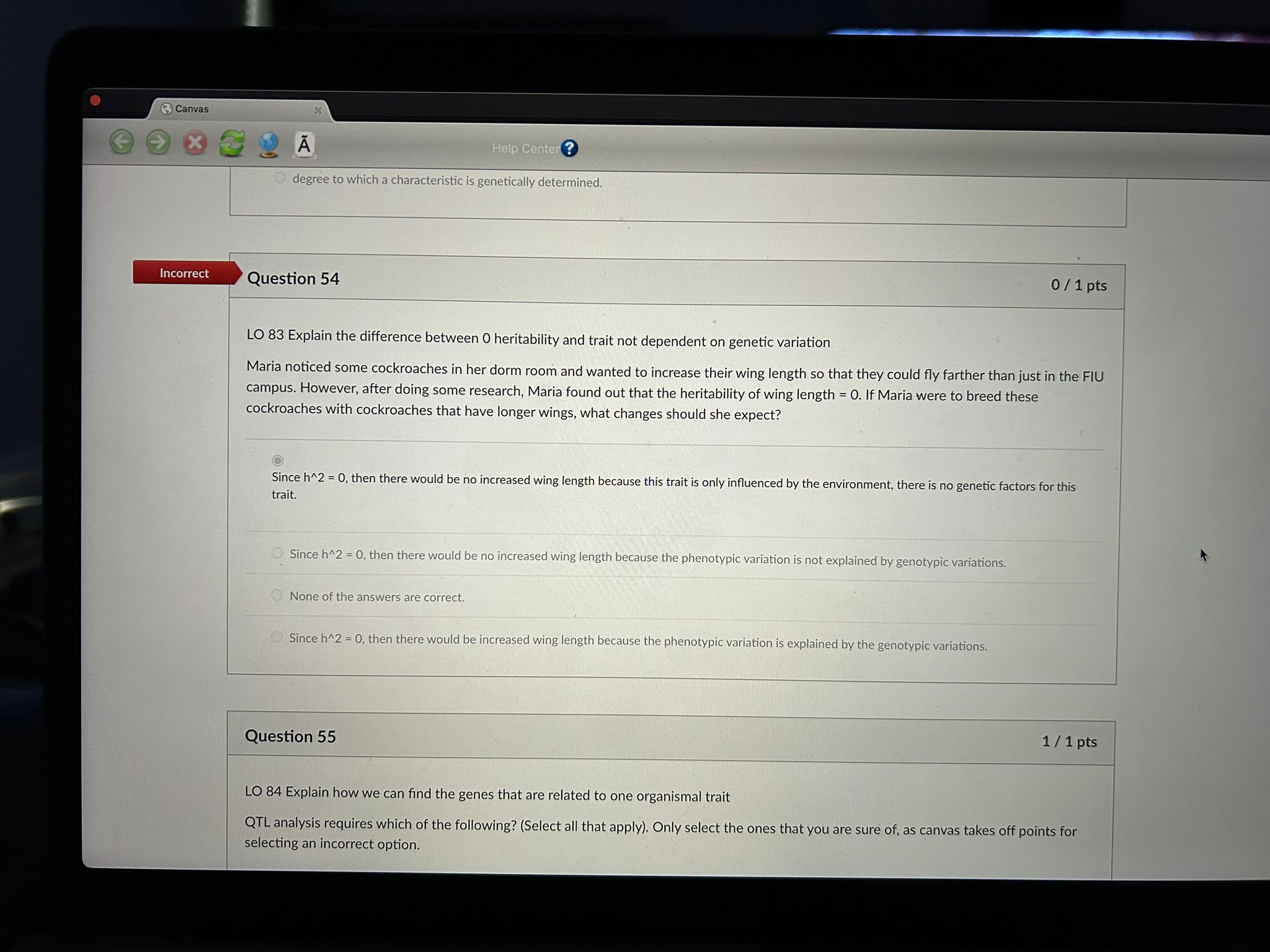
Solved LO 83 Explain the difference between 0 heritability
Often, this term is used in. There are two different types of heritability: Heritability is addressing the population level correlation between phenotypic variation and genotypic variation. Heritability estimates the relative contribution of genetic factors to the phenotypic variability observed in a population. Heritability, amount of phenotypic (observable) variation in a population that is attributable to individual genetic differences.
The difference between heritability and inheritance Heritability
Heritability, amount of phenotypic (observable) variation in a population that is attributable to individual genetic differences. Often, this term is used in. Heritability is addressing the population level correlation between phenotypic variation and genotypic variation. There are two different types of heritability: Heritability is a concept that summarizes how much of the variation in a trait is due to variation.
The difference between heritability and inheritance Heritability
Heritability estimates the relative contribution of genetic factors to the phenotypic variability observed in a population. Heritability, amount of phenotypic (observable) variation in a population that is attributable to individual genetic differences. Often, this term is used in. There are two different types of heritability: Heritability is addressing the population level correlation between phenotypic variation and genotypic variation.
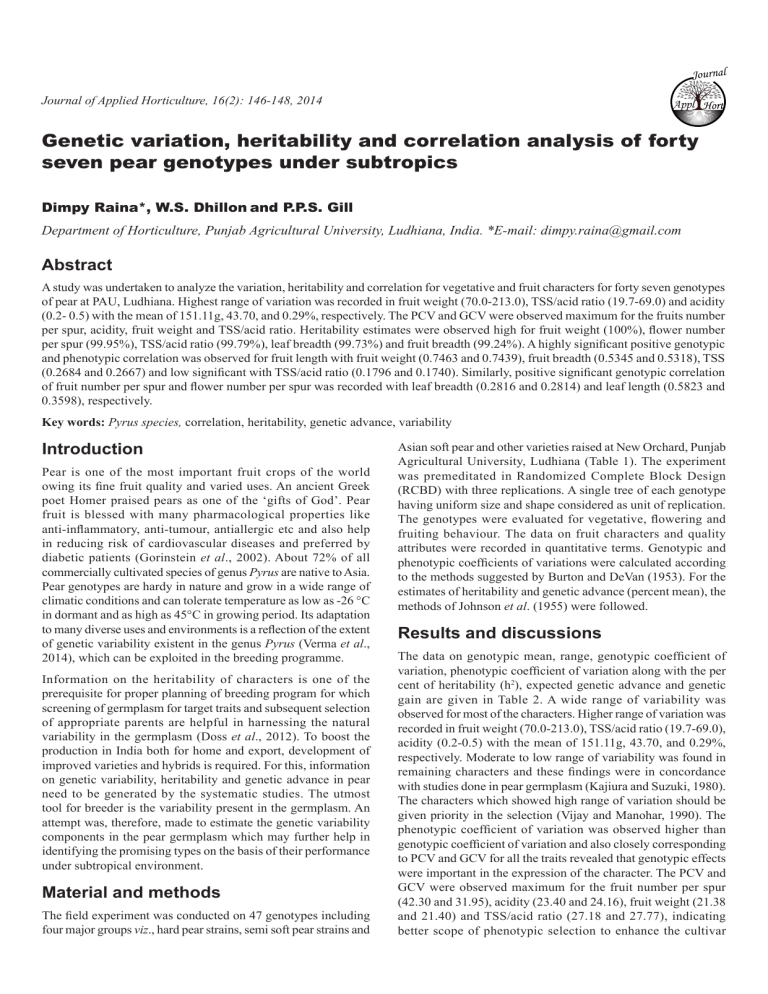
variation, heritability and correlation analysis of forty
Heritability, amount of phenotypic (observable) variation in a population that is attributable to individual genetic differences. There are two different types of heritability: Often, this term is used in. Heritability is a concept that summarizes how much of the variation in a trait is due to variation in genetic factors. Heritability is addressing the population level correlation between phenotypic variation.
Solved LO 83 Explain the difference between 0 heritability
Often, this term is used in. Heritability, amount of phenotypic (observable) variation in a population that is attributable to individual genetic differences. There are two different types of heritability: Heritability is addressing the population level correlation between phenotypic variation and genotypic variation. Heritability is a concept that summarizes how much of the variation in a trait is due to variation.
There Are Two Different Types Of Heritability:
Heritability is a concept that summarizes how much of the variation in a trait is due to variation in genetic factors. Heritability, amount of phenotypic (observable) variation in a population that is attributable to individual genetic differences. Heritability is addressing the population level correlation between phenotypic variation and genotypic variation. Heritability estimates the relative contribution of genetic factors to the phenotypic variability observed in a population.