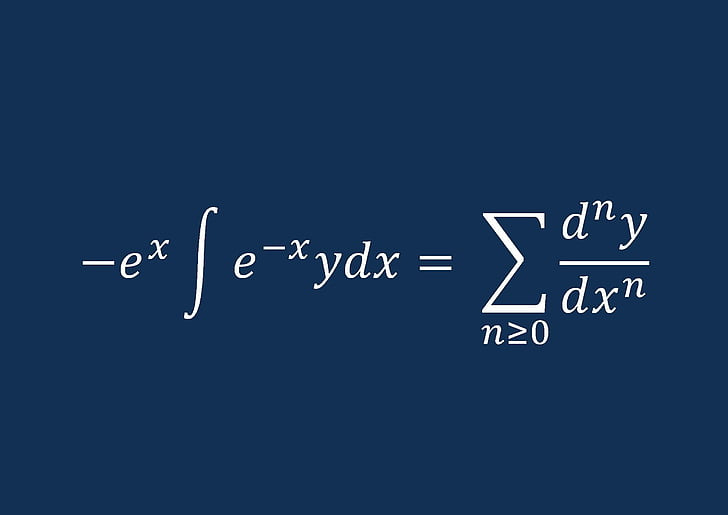Differential Operator - Define the operator as then you get and also where i have used that exp(pt) = p exp(pt) ∂ t exp (p t) = p exp (p t) to convert the action of the operator ∂ t into multiplication by p p, and then i. The differential operator in this question is itself indexed by two variables m and n. For instance the formal taylor expansion of an exponential like eia e i a is generally and incorrect procedure, leading to false results, if a a is an unbounded operator in a hilbert or banach. @carlwoll, i actuallly referred to how to define a differential operator?, but, still, my operator does not give the correct answer. This arises after expressing the laplace operator in spherical coordinates (see the answer by b.gatessucks,. Here is a trick for making a series expansion of a function of a single operator — i.e.
The differential operator in this question is itself indexed by two variables m and n. This arises after expressing the laplace operator in spherical coordinates (see the answer by b.gatessucks,. Define the operator as then you get and also where i have used that exp(pt) = p exp(pt) ∂ t exp (p t) = p exp (p t) to convert the action of the operator ∂ t into multiplication by p p, and then i. For instance the formal taylor expansion of an exponential like eia e i a is generally and incorrect procedure, leading to false results, if a a is an unbounded operator in a hilbert or banach. Here is a trick for making a series expansion of a function of a single operator — i.e. @carlwoll, i actuallly referred to how to define a differential operator?, but, still, my operator does not give the correct answer.
@carlwoll, i actuallly referred to how to define a differential operator?, but, still, my operator does not give the correct answer. Define the operator as then you get and also where i have used that exp(pt) = p exp(pt) ∂ t exp (p t) = p exp (p t) to convert the action of the operator ∂ t into multiplication by p p, and then i. Here is a trick for making a series expansion of a function of a single operator — i.e. For instance the formal taylor expansion of an exponential like eia e i a is generally and incorrect procedure, leading to false results, if a a is an unbounded operator in a hilbert or banach. The differential operator in this question is itself indexed by two variables m and n. This arises after expressing the laplace operator in spherical coordinates (see the answer by b.gatessucks,.
SOLUTION Differential equations differential operator higher order
The differential operator in this question is itself indexed by two variables m and n. Here is a trick for making a series expansion of a function of a single operator — i.e. Define the operator as then you get and also where i have used that exp(pt) = p exp(pt) ∂ t exp (p t) = p exp (p.
HD wallpaper differential, operator, series Wallpaper Flare
Define the operator as then you get and also where i have used that exp(pt) = p exp(pt) ∂ t exp (p t) = p exp (p t) to convert the action of the operator ∂ t into multiplication by p p, and then i. @carlwoll, i actuallly referred to how to define a differential operator?, but, still, my operator.
(PDF) Applications of Vector differential operator del
For instance the formal taylor expansion of an exponential like eia e i a is generally and incorrect procedure, leading to false results, if a a is an unbounded operator in a hilbert or banach. The differential operator in this question is itself indexed by two variables m and n. Define the operator as then you get and also where.
calculus Simplifying to Linear Differential Operator? Mathematics
@carlwoll, i actuallly referred to how to define a differential operator?, but, still, my operator does not give the correct answer. Define the operator as then you get and also where i have used that exp(pt) = p exp(pt) ∂ t exp (p t) = p exp (p t) to convert the action of the operator ∂ t into multiplication.
Differential operator definition by Wong. Mathematics Stack Exchange
Define the operator as then you get and also where i have used that exp(pt) = p exp(pt) ∂ t exp (p t) = p exp (p t) to convert the action of the operator ∂ t into multiplication by p p, and then i. For instance the formal taylor expansion of an exponential like eia e i a is.
calculus and analysis Differential operator in simple equation
Define the operator as then you get and also where i have used that exp(pt) = p exp(pt) ∂ t exp (p t) = p exp (p t) to convert the action of the operator ∂ t into multiplication by p p, and then i. @carlwoll, i actuallly referred to how to define a differential operator?, but, still, my operator.
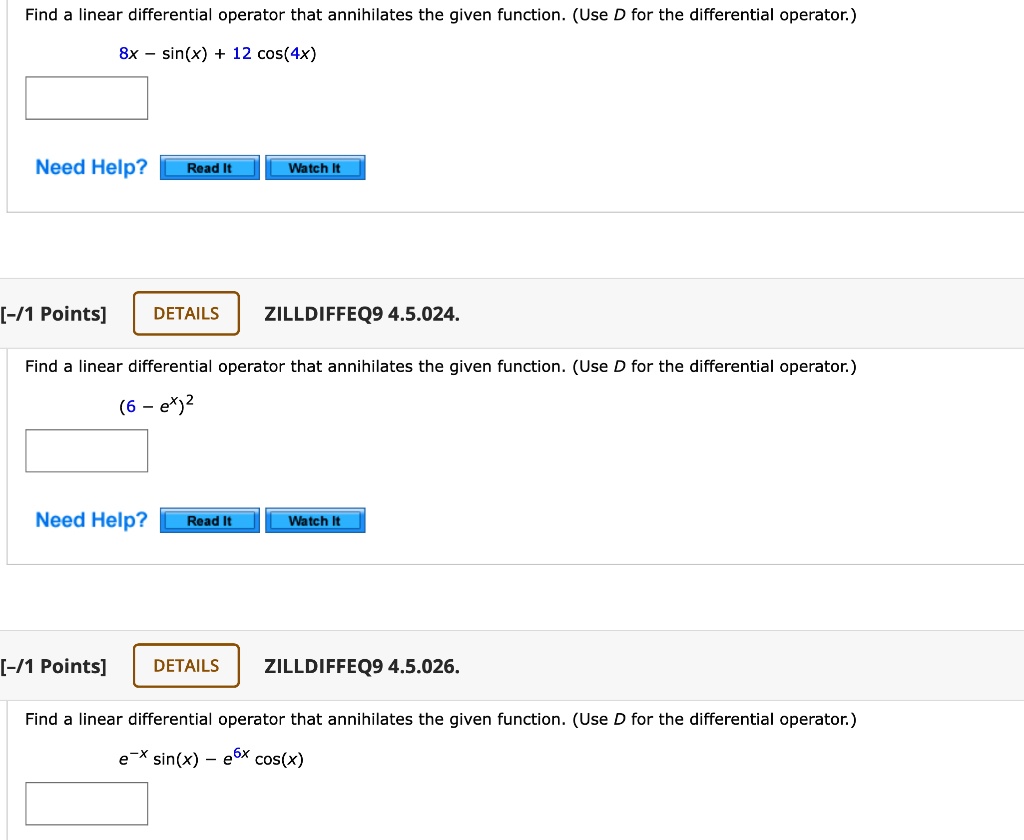
SOLVED Find a linear differential operator that annihilates the given
Define the operator as then you get and also where i have used that exp(pt) = p exp(pt) ∂ t exp (p t) = p exp (p t) to convert the action of the operator ∂ t into multiplication by p p, and then i. This arises after expressing the laplace operator in spherical coordinates (see the answer by b.gatessucks,..
[Solved] In the following cases, determine the linear differential
The differential operator in this question is itself indexed by two variables m and n. Here is a trick for making a series expansion of a function of a single operator — i.e. @carlwoll, i actuallly referred to how to define a differential operator?, but, still, my operator does not give the correct answer. Define the operator as then you.
nabla differential operator symbol Math TShirt TeePublic
The differential operator in this question is itself indexed by two variables m and n. Here is a trick for making a series expansion of a function of a single operator — i.e. For instance the formal taylor expansion of an exponential like eia e i a is generally and incorrect procedure, leading to false results, if a a is.
Inverse Differential Operator And Particular Integral
This arises after expressing the laplace operator in spherical coordinates (see the answer by b.gatessucks,. Define the operator as then you get and also where i have used that exp(pt) = p exp(pt) ∂ t exp (p t) = p exp (p t) to convert the action of the operator ∂ t into multiplication by p p, and then i..
The Differential Operator In This Question Is Itself Indexed By Two Variables M And N.
Here is a trick for making a series expansion of a function of a single operator — i.e. For instance the formal taylor expansion of an exponential like eia e i a is generally and incorrect procedure, leading to false results, if a a is an unbounded operator in a hilbert or banach. This arises after expressing the laplace operator in spherical coordinates (see the answer by b.gatessucks,. Define the operator as then you get and also where i have used that exp(pt) = p exp(pt) ∂ t exp (p t) = p exp (p t) to convert the action of the operator ∂ t into multiplication by p p, and then i.