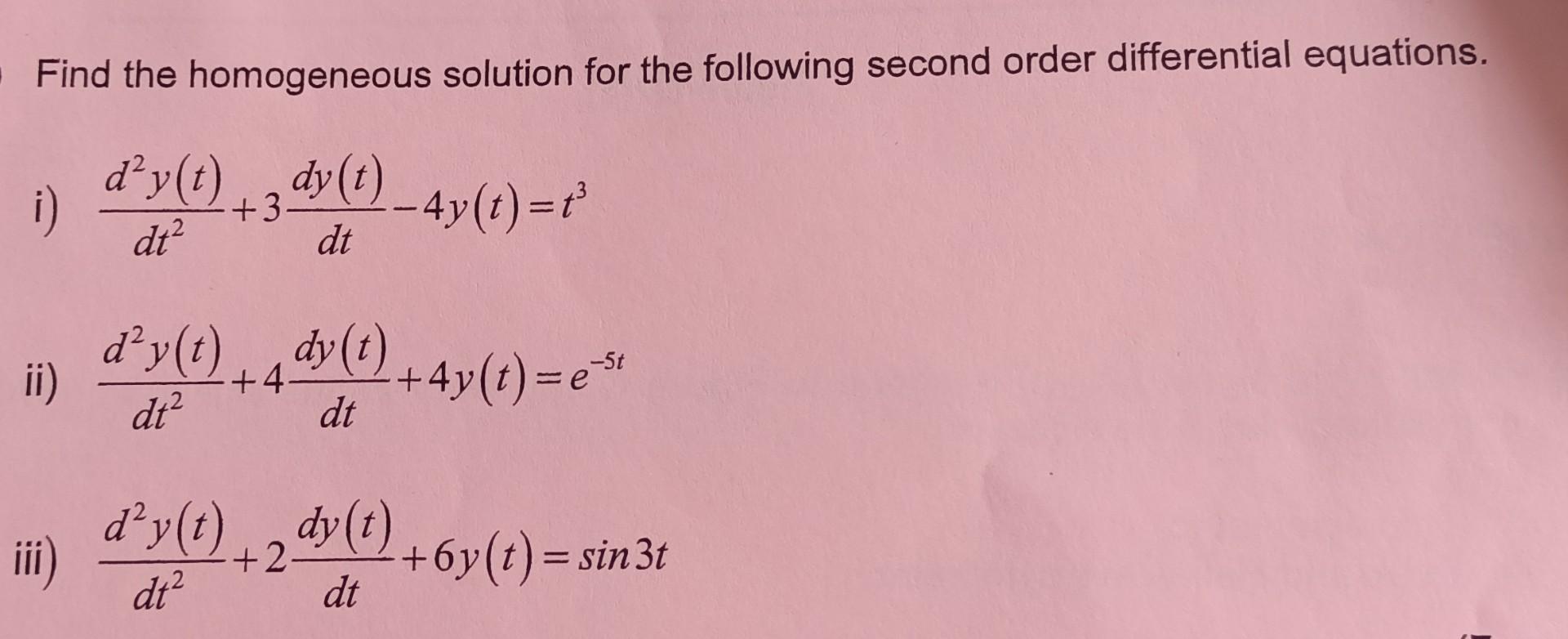Differential Equations Homogeneous Solution - Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. Homogeneous differential equations are differential equations where each term will be of the form,. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. It is easy to see that the polynomials and respectively, at and are homogeneous functions.
Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. Homogeneous differential equations are differential equations where each term will be of the form,. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. It is easy to see that the polynomials and respectively, at and are homogeneous functions.
In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the. Homogeneous differential equations are differential equations where each term will be of the form,. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. It is easy to see that the polynomials and respectively, at and are homogeneous functions.
[Solved] Find the general solution to the homogeneous differential
Homogeneous differential equations are differential equations where each term will be of the form,. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. It is easy to see that the polynomials and respectively, at and are homogeneous functions. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the. Homogeneous.
Solved Find the homogeneous solution for the following
It is easy to see that the polynomials and respectively, at and are homogeneous functions. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. Homogeneous differential equations are differential equations where each term will be of the form,. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the. Homogeneous.
[Solved] Solve the HOMOGENEOUS differential equation in step by step
It is easy to see that the polynomials and respectively, at and are homogeneous functions. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. Homogeneous differential equations.
Homogeneous Differential Equations Docsity
It is easy to see that the polynomials and respectively, at and are homogeneous functions. Homogeneous differential equations are differential equations where each term will be of the form,. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. Homogeneous.
Homogeneous Linear Differential Equations KZHU.ai 🚀
It is easy to see that the polynomials and respectively, at and are homogeneous functions. Homogeneous differential equations are differential equations where each term will be of the form,. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the. In this.
[Solved] Solve the HOMOGENEOUS differential equation in step by step
Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. Homogeneous differential equations are differential equations where each term will be of the form,. It is easy to.
Solution of Homogeneous Linear Differential equation Yawin
Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the. It is easy to see that the polynomials and respectively, at and are homogeneous functions. Homogeneous differential equations are differential equations where each term will be of the form,. In this.
Particular Solution of NonHomogeneous Differential Equations Mr
It is easy to see that the polynomials and respectively, at and are homogeneous functions. Homogeneous differential equations are differential equations where each term will be of the form,. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the. In this.
2nd Order Homogeneous Equations
Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. Homogeneous differential equations are differential equations where each term will be of the form,. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. It is easy to.
[Solved] Determine whether the given differential equations are
It is easy to see that the polynomials and respectively, at and are homogeneous functions. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the. Homogeneous differential equations are differential equations where each term will be of the form,. Homogeneous.
Homogeneous Differential Equation Are The Equations Having Functions Of The Same Degree.
Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the. Homogeneous differential equations are differential equations where each term will be of the form,. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,. It is easy to see that the polynomials and respectively, at and are homogeneous functions.