Differential Equations Frq - Dy y = 3 −. Consider the differential equation 1, dy y dx x + = where 0.x ≠ (a) on the axes provided, sketch a. (b) find the values of the constants m, b, and rfor which is a solution to the differential equation. The function f is defined for all real numbers. Differential equation with the initial condition f ( 1 ) = 2. T = 1 hour, there are 2.5 milligrams of the medication.
Dy y = 3 −. (b) find the values of the constants m, b, and rfor which is a solution to the differential equation. T = 1 hour, there are 2.5 milligrams of the medication. Consider the differential equation 1, dy y dx x + = where 0.x ≠ (a) on the axes provided, sketch a. The function f is defined for all real numbers. Differential equation with the initial condition f ( 1 ) = 2.
Consider the differential equation 1, dy y dx x + = where 0.x ≠ (a) on the axes provided, sketch a. (b) find the values of the constants m, b, and rfor which is a solution to the differential equation. The function f is defined for all real numbers. Dy y = 3 −. T = 1 hour, there are 2.5 milligrams of the medication. Differential equation with the initial condition f ( 1 ) = 2.
AP CALCULUS BC FRQ Differential Equations
Differential equation with the initial condition f ( 1 ) = 2. Dy y = 3 −. Consider the differential equation 1, dy y dx x + = where 0.x ≠ (a) on the axes provided, sketch a. (b) find the values of the constants m, b, and rfor which is a solution to the differential equation. T = 1.
Slope fields and differential equations
The function f is defined for all real numbers. Consider the differential equation 1, dy y dx x + = where 0.x ≠ (a) on the axes provided, sketch a. T = 1 hour, there are 2.5 milligrams of the medication. Dy y = 3 −. Differential equation with the initial condition f ( 1 ) = 2.
Modelling Motion with Differential Equations
Consider the differential equation 1, dy y dx x + = where 0.x ≠ (a) on the axes provided, sketch a. T = 1 hour, there are 2.5 milligrams of the medication. The function f is defined for all real numbers. Differential equation with the initial condition f ( 1 ) = 2. (b) find the values of the constants.
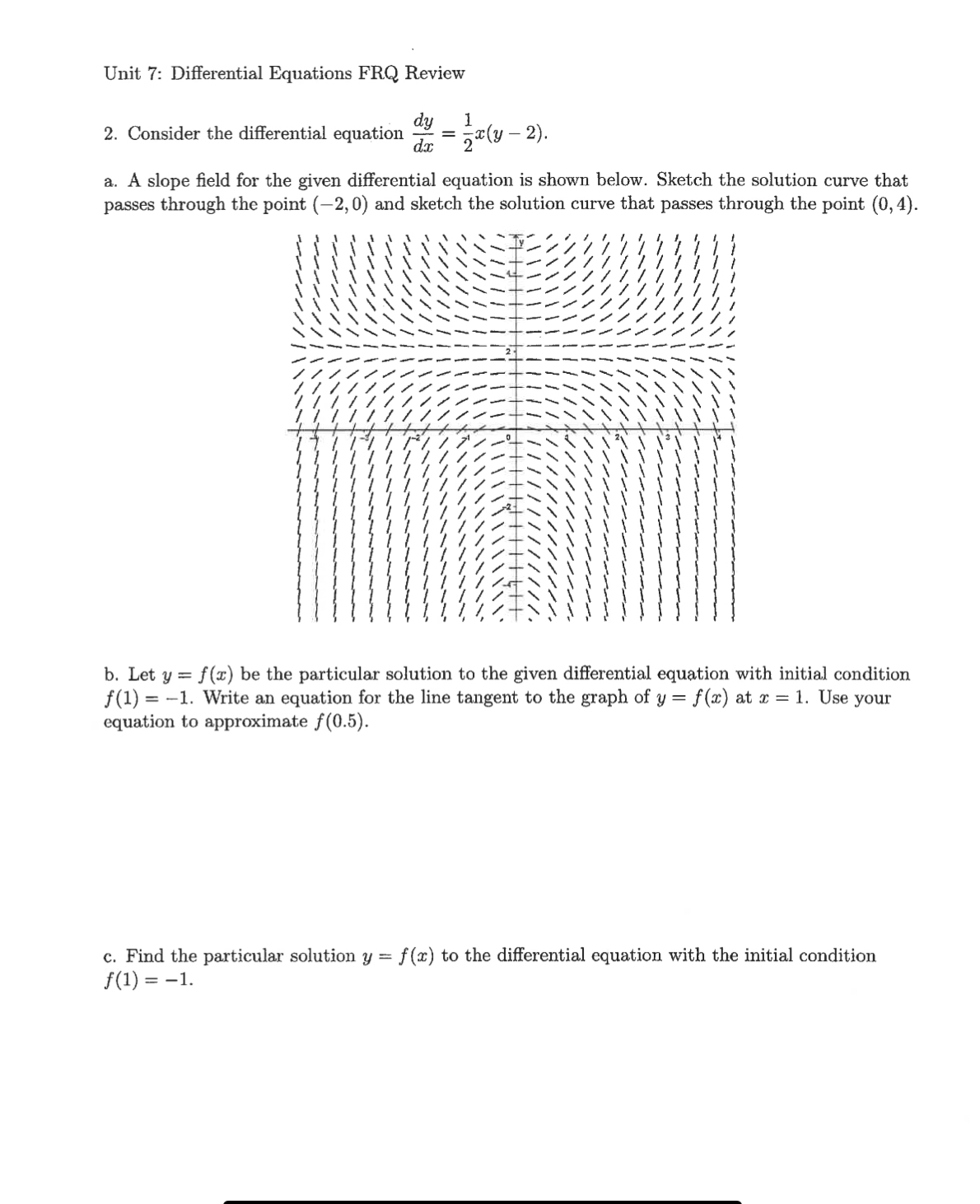
Solved Unit 7 Differential Equations FRQ ReviewConsider the
T = 1 hour, there are 2.5 milligrams of the medication. Differential equation with the initial condition f ( 1 ) = 2. Dy y = 3 −. Consider the differential equation 1, dy y dx x + = where 0.x ≠ (a) on the axes provided, sketch a. (b) find the values of the constants m, b, and rfor.
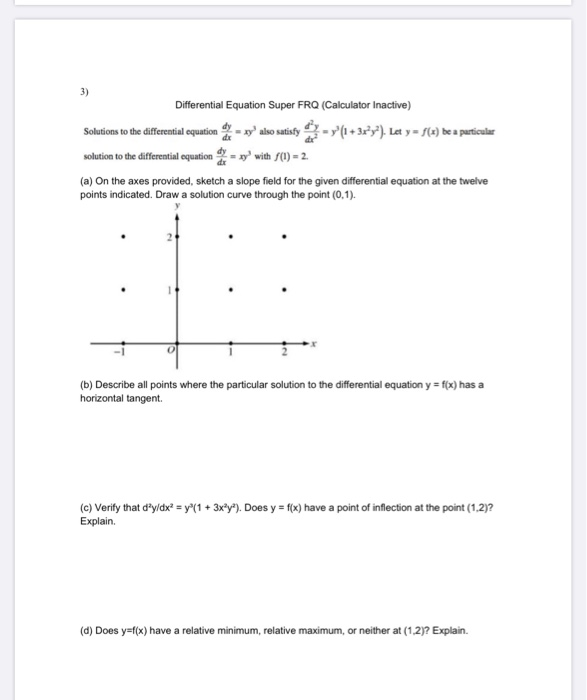
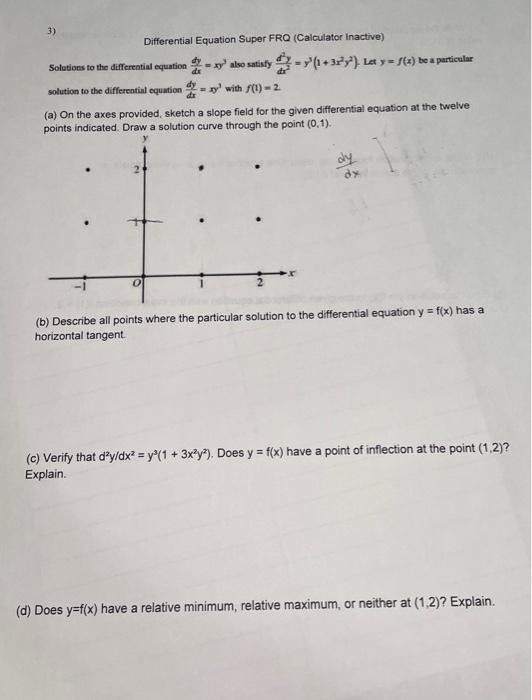
Solved Differential Equation Super FRQ (Calculator Inactive)
Differential equation with the initial condition f ( 1 ) = 2. (b) find the values of the constants m, b, and rfor which is a solution to the differential equation. T = 1 hour, there are 2.5 milligrams of the medication. Dy y = 3 −. The function f is defined for all real numbers.
Solved Unit 7 Differential Equations FRQ Review2. Consider
T = 1 hour, there are 2.5 milligrams of the medication. Dy y = 3 −. Consider the differential equation 1, dy y dx x + = where 0.x ≠ (a) on the axes provided, sketch a. (b) find the values of the constants m, b, and rfor which is a solution to the differential equation. The function f is.
Solved 3) Differential Equation Super FRQ (Calculator
T = 1 hour, there are 2.5 milligrams of the medication. Differential equation with the initial condition f ( 1 ) = 2. Dy y = 3 −. Consider the differential equation 1, dy y dx x + = where 0.x ≠ (a) on the axes provided, sketch a. The function f is defined for all real numbers.
Solved 3) Differential Equation Super FRQ (Calculator
T = 1 hour, there are 2.5 milligrams of the medication. Differential equation with the initial condition f ( 1 ) = 2. The function f is defined for all real numbers. Consider the differential equation 1, dy y dx x + = where 0.x ≠ (a) on the axes provided, sketch a. Dy y = 3 −.
Maxwell's Equations in Integral and Differential form YouTube
Dy y = 3 −. T = 1 hour, there are 2.5 milligrams of the medication. (b) find the values of the constants m, b, and rfor which is a solution to the differential equation. Differential equation with the initial condition f ( 1 ) = 2. Consider the differential equation 1, dy y dx x + = where 0.x.
Solved Unit 7 Differential Equations FRQ Review3. The
Consider the differential equation 1, dy y dx x + = where 0.x ≠ (a) on the axes provided, sketch a. (b) find the values of the constants m, b, and rfor which is a solution to the differential equation. The function f is defined for all real numbers. Differential equation with the initial condition f ( 1 ) =.
T = 1 Hour, There Are 2.5 Milligrams Of The Medication.
Dy y = 3 −. Consider the differential equation 1, dy y dx x + = where 0.x ≠ (a) on the axes provided, sketch a. The function f is defined for all real numbers. (b) find the values of the constants m, b, and rfor which is a solution to the differential equation.