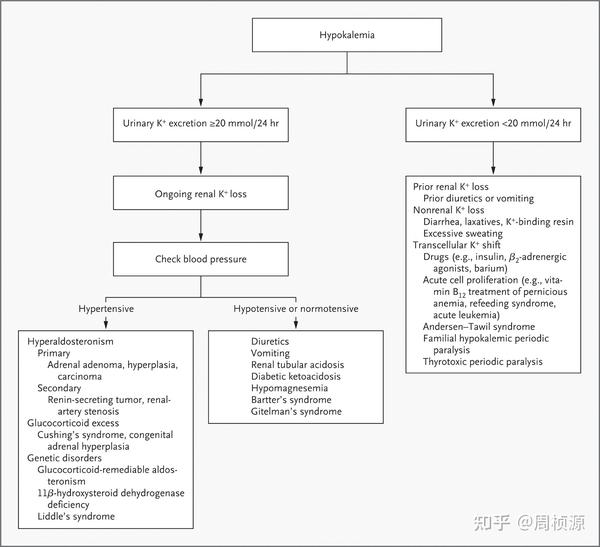
Differential Diagnosis For Hypokalemia - A fall in serum potassium. Hypokalemia is most commonly due to urinary or gi losses. Damage to the renal tubule. There are two major components to the diagnostic evaluation: Characterizing ability of serum potassium (k) and the serum k reference interval to flag. Measurement of urine potassium is essential to establishment of the.
Measurement of urine potassium is essential to establishment of the. There are two major components to the diagnostic evaluation: A fall in serum potassium. Damage to the renal tubule. Hypokalemia is most commonly due to urinary or gi losses. Characterizing ability of serum potassium (k) and the serum k reference interval to flag.
Characterizing ability of serum potassium (k) and the serum k reference interval to flag. A fall in serum potassium. Hypokalemia is most commonly due to urinary or gi losses. Measurement of urine potassium is essential to establishment of the. Damage to the renal tubule. There are two major components to the diagnostic evaluation:
Differential Diagnosis of Hypokalemia Based on Types and Causes of
Measurement of urine potassium is essential to establishment of the. Damage to the renal tubule. A fall in serum potassium. Hypokalemia is most commonly due to urinary or gi losses. There are two major components to the diagnostic evaluation:
Differential Diagnosis of Hypokalemia Based on Types and Causes of
A fall in serum potassium. Measurement of urine potassium is essential to establishment of the. There are two major components to the diagnostic evaluation: Damage to the renal tubule. Characterizing ability of serum potassium (k) and the serum k reference interval to flag.
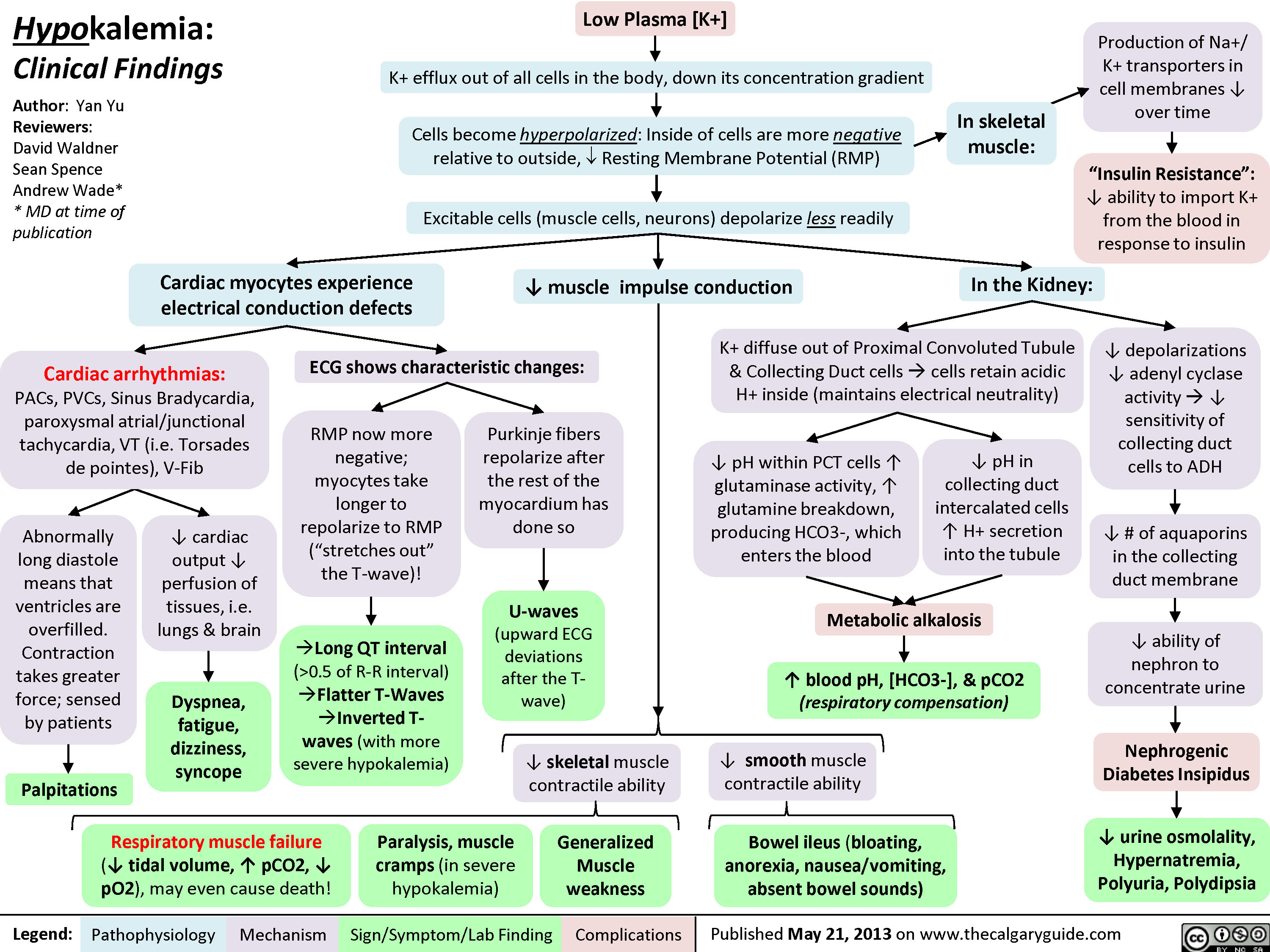
Hypokalemia Clinical Findings Calgary Guide
A fall in serum potassium. Damage to the renal tubule. There are two major components to the diagnostic evaluation: Hypokalemia is most commonly due to urinary or gi losses. Characterizing ability of serum potassium (k) and the serum k reference interval to flag.
Hypokalemia Approach
A fall in serum potassium. Characterizing ability of serum potassium (k) and the serum k reference interval to flag. Hypokalemia is most commonly due to urinary or gi losses. Damage to the renal tubule. Measurement of urine potassium is essential to establishment of the.
Differential Diagnosis of Hypokalemia Based on Types and Causes of
A fall in serum potassium. There are two major components to the diagnostic evaluation: Damage to the renal tubule. Measurement of urine potassium is essential to establishment of the. Characterizing ability of serum potassium (k) and the serum k reference interval to flag.
Hypokalemia Differential Diagnosis Algorithm Hypertensive Grepmed The
There are two major components to the diagnostic evaluation: Measurement of urine potassium is essential to establishment of the. Damage to the renal tubule. A fall in serum potassium. Characterizing ability of serum potassium (k) and the serum k reference interval to flag.
Differential diagnosis of hyperkalemia is shown [15]. Hyperkalemia is
Damage to the renal tubule. There are two major components to the diagnostic evaluation: Measurement of urine potassium is essential to establishment of the. Hypokalemia is most commonly due to urinary or gi losses. Characterizing ability of serum potassium (k) and the serum k reference interval to flag.
Nejm 2012 Case 4 知乎
Characterizing ability of serum potassium (k) and the serum k reference interval to flag. There are two major components to the diagnostic evaluation: Damage to the renal tubule. A fall in serum potassium. Measurement of urine potassium is essential to establishment of the.
Case 42012 — A 37YearOld Man with Muscle Pain, Weakness, and Weight
Characterizing ability of serum potassium (k) and the serum k reference interval to flag. A fall in serum potassium. Hypokalemia is most commonly due to urinary or gi losses. There are two major components to the diagnostic evaluation: Damage to the renal tubule.
Hypokalemia Is Most Commonly Due To Urinary Or Gi Losses.
Damage to the renal tubule. Measurement of urine potassium is essential to establishment of the. Characterizing ability of serum potassium (k) and the serum k reference interval to flag. There are two major components to the diagnostic evaluation:




![Differential diagnosis of hyperkalemia is shown [15]. Hyperkalemia is](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/276340616/figure/fig3/AS:294543414054923@1447236030646/Differential-diagnosis-of-hyperkalemia-is-shown-15-Hyperkalemia-is-defined-as-a-serum.png)