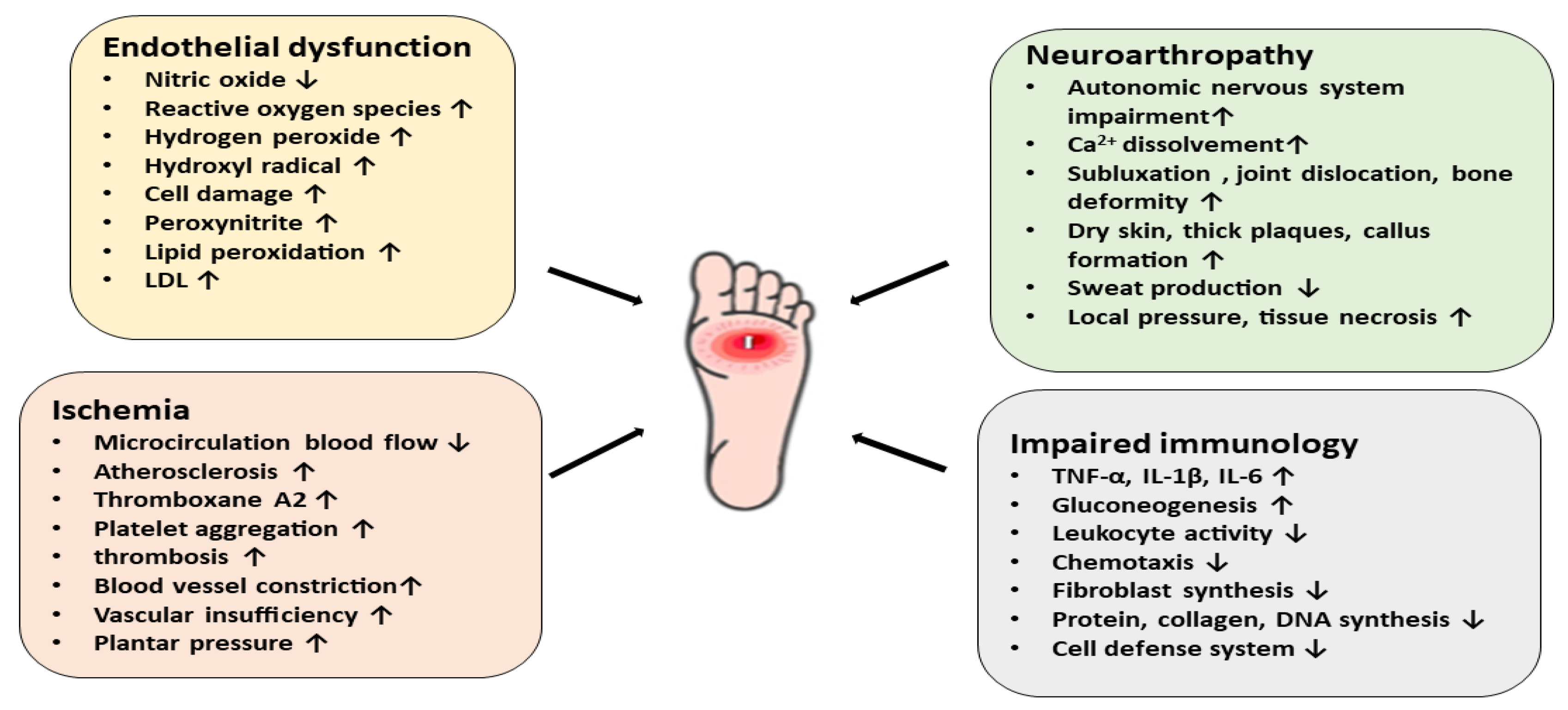
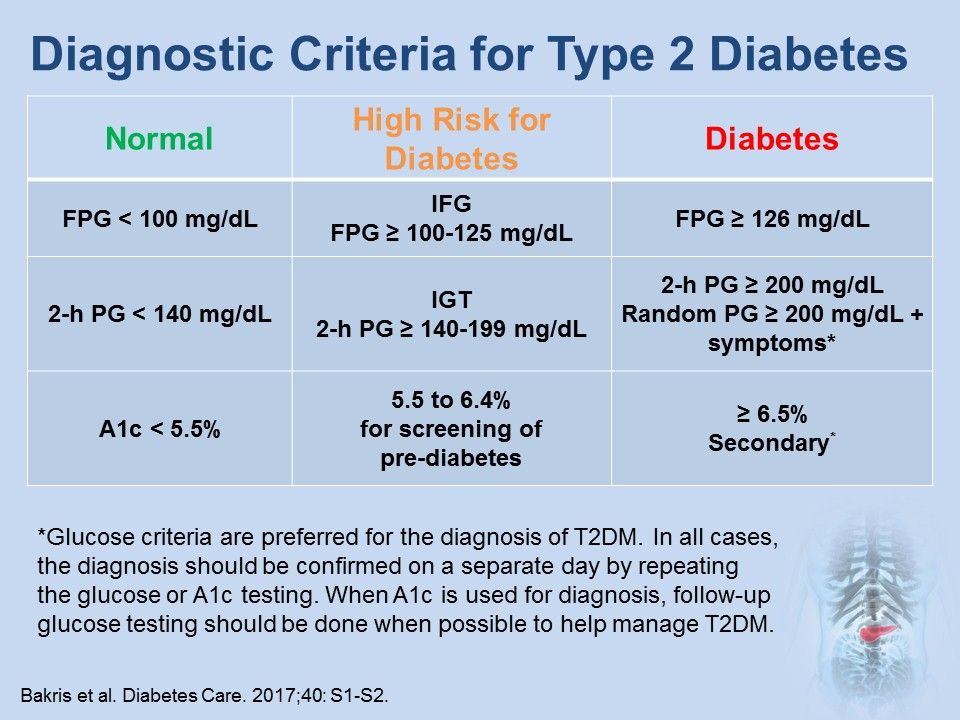
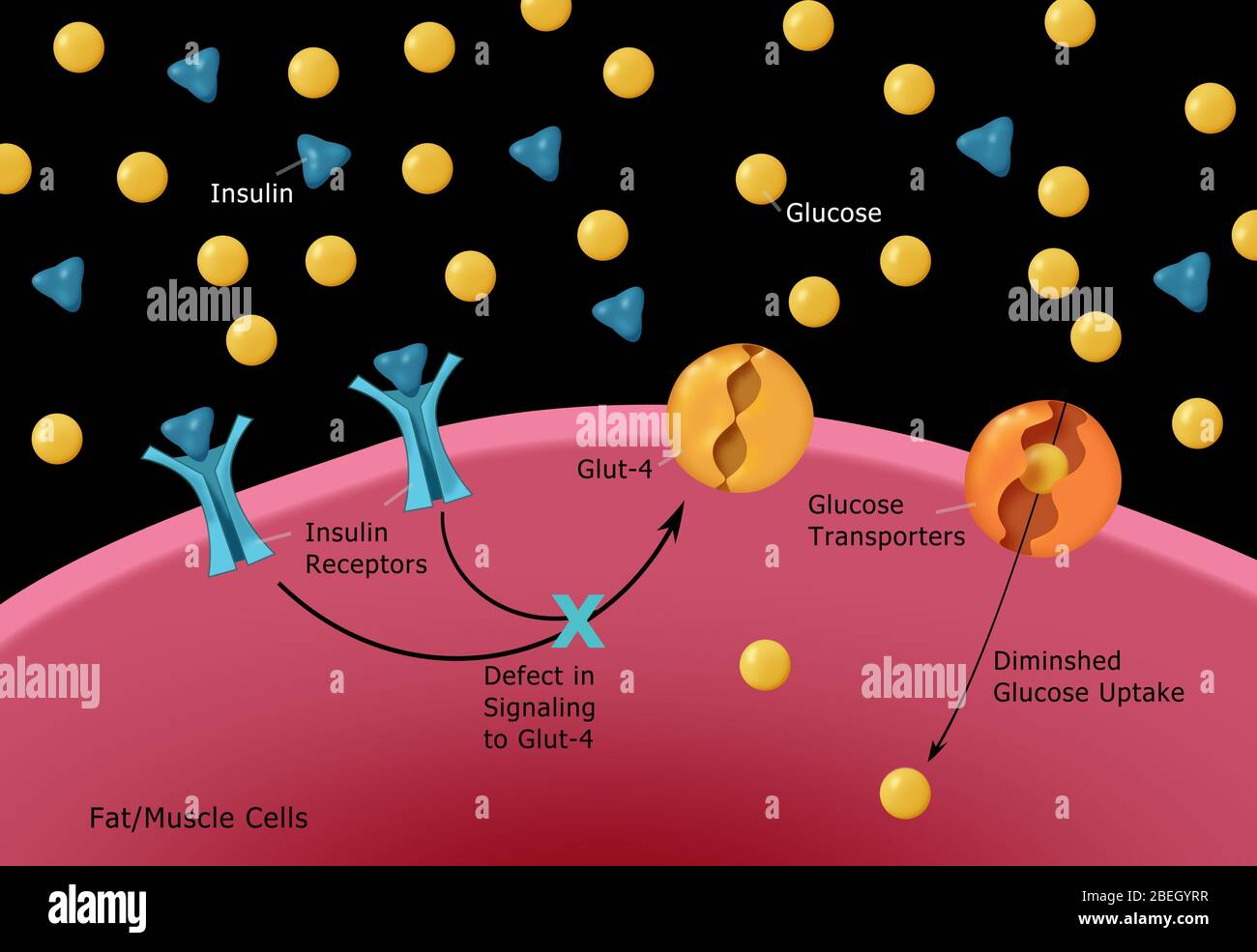
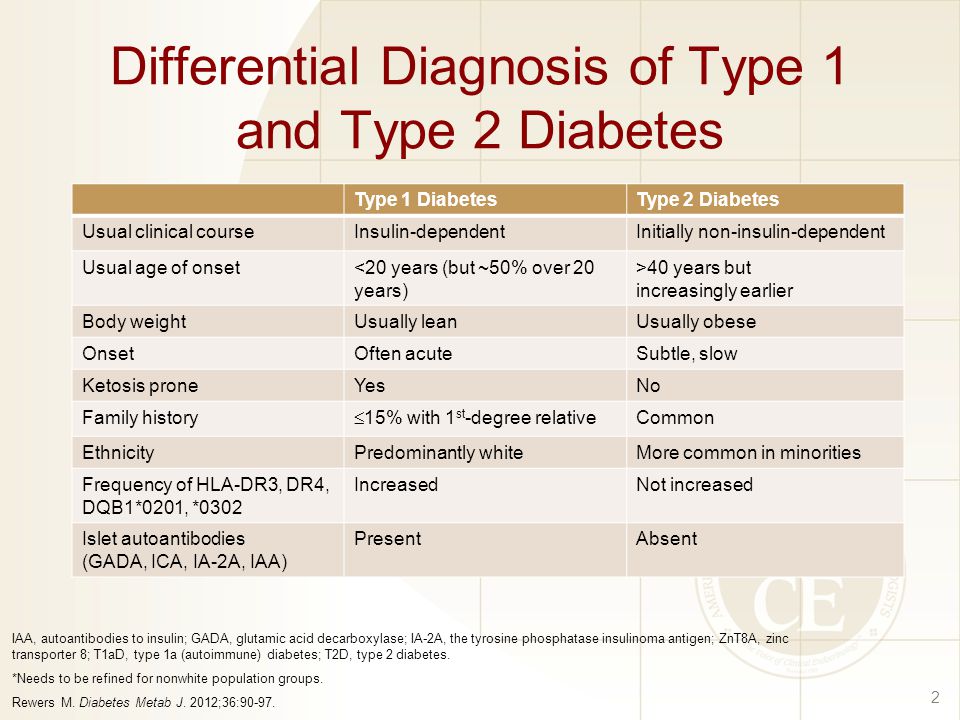
Differential Diagnosis For Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 - Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%];
Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be.
Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications:
Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific.
Differential Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus PDF Diabetes Autoimmunity
Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be.
PPT Role of the Laboratory in Differential Diagnosis of Diabetes
Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%];
Diagnosis Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 in the Medical Form Stock Image
Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include:
Diabetes Mellitus Differential Diagnosis Hot Sex Picture
As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include:
Type 2 Diabetes Clinical Suspicion and Diagnosis Patient Care Online
Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%];
(PDF) Feline Diabetes Mellitus and Differential Diagnosis We Need to
In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus hires stock photography and images Alamy
In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be.
Diabetes mellitus (Type 2) Clinical sciences Osmosis Video Library
In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications:
Differential Diagnosis For Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 DiabetesWalls
Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include:
As Previously Stated, Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Can Usually Be.
Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific. Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: In this review, we provide an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical.