Differential Bias - In this paper, we compile and characterize 7 exceptions to this rule and encourage analysts to. The differential bias (δ bias) is induced when a model differentially under or over. When a bias unequally affects comparison groups. Differential misclassification causes a bias in the risk ratio, rate ratio, or odds ratio either towards or. Those biases affecting a study’s internal validity (selection bias that pertains more to one group.
When a bias unequally affects comparison groups. Differential misclassification causes a bias in the risk ratio, rate ratio, or odds ratio either towards or. The differential bias (δ bias) is induced when a model differentially under or over. In this paper, we compile and characterize 7 exceptions to this rule and encourage analysts to. Those biases affecting a study’s internal validity (selection bias that pertains more to one group.
Differential misclassification causes a bias in the risk ratio, rate ratio, or odds ratio either towards or. The differential bias (δ bias) is induced when a model differentially under or over. When a bias unequally affects comparison groups. Those biases affecting a study’s internal validity (selection bias that pertains more to one group. In this paper, we compile and characterize 7 exceptions to this rule and encourage analysts to.
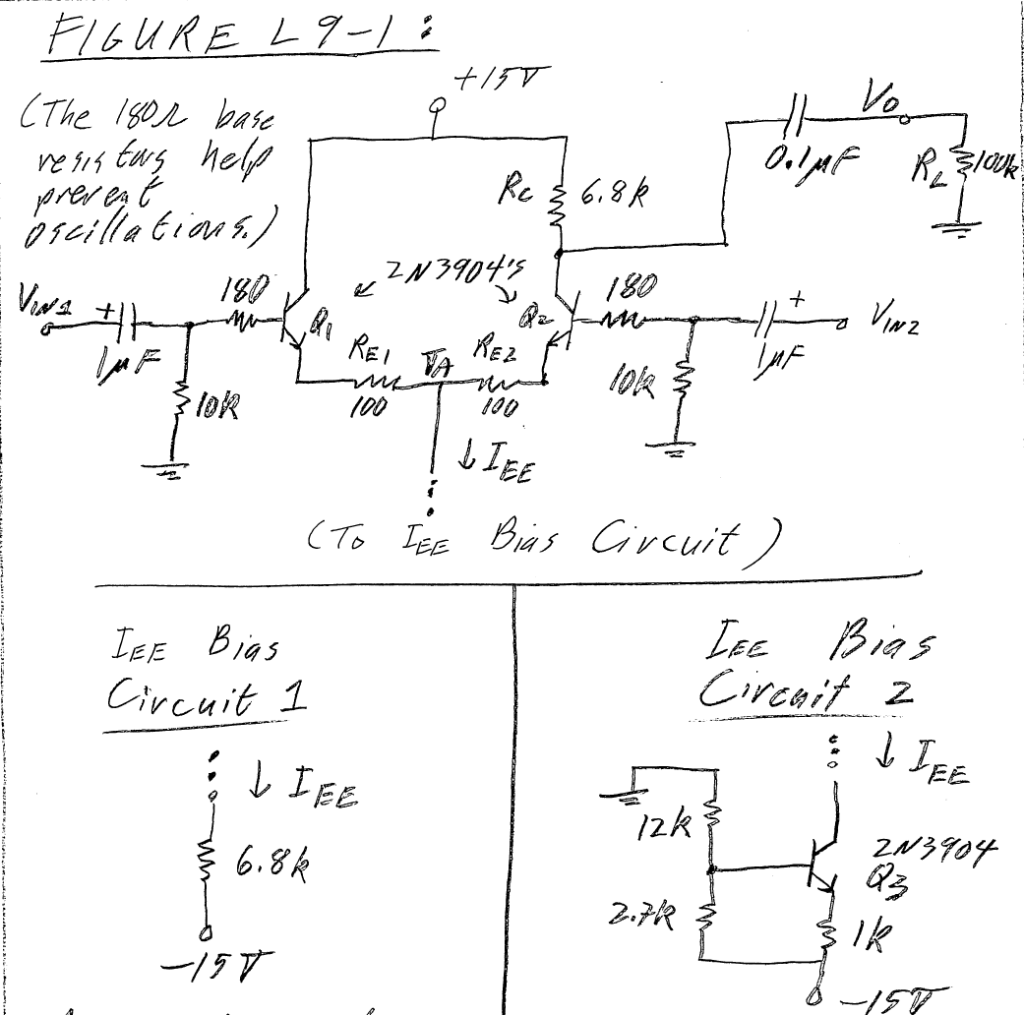
Bias current differential amplifier design
When a bias unequally affects comparison groups. In this paper, we compile and characterize 7 exceptions to this rule and encourage analysts to. Differential misclassification causes a bias in the risk ratio, rate ratio, or odds ratio either towards or. The differential bias (δ bias) is induced when a model differentially under or over. Those biases affecting a study’s internal.
Dual bias current differential characteristic. Download Scientific
Differential misclassification causes a bias in the risk ratio, rate ratio, or odds ratio either towards or. When a bias unequally affects comparison groups. The differential bias (δ bias) is induced when a model differentially under or over. Those biases affecting a study’s internal validity (selection bias that pertains more to one group. In this paper, we compile and characterize.
op amp OP07 Input Bias Current vs. Differential Input Voltage
Differential misclassification causes a bias in the risk ratio, rate ratio, or odds ratio either towards or. The differential bias (δ bias) is induced when a model differentially under or over. In this paper, we compile and characterize 7 exceptions to this rule and encourage analysts to. Those biases affecting a study’s internal validity (selection bias that pertains more to.
Differential characteristics or bias characteristics implemented in
When a bias unequally affects comparison groups. The differential bias (δ bias) is induced when a model differentially under or over. In this paper, we compile and characterize 7 exceptions to this rule and encourage analysts to. Those biases affecting a study’s internal validity (selection bias that pertains more to one group. Differential misclassification causes a bias in the risk.
Differential characteristics or bias characteristics implemented in
Differential misclassification causes a bias in the risk ratio, rate ratio, or odds ratio either towards or. Those biases affecting a study’s internal validity (selection bias that pertains more to one group. The differential bias (δ bias) is induced when a model differentially under or over. When a bias unequally affects comparison groups. In this paper, we compile and characterize.
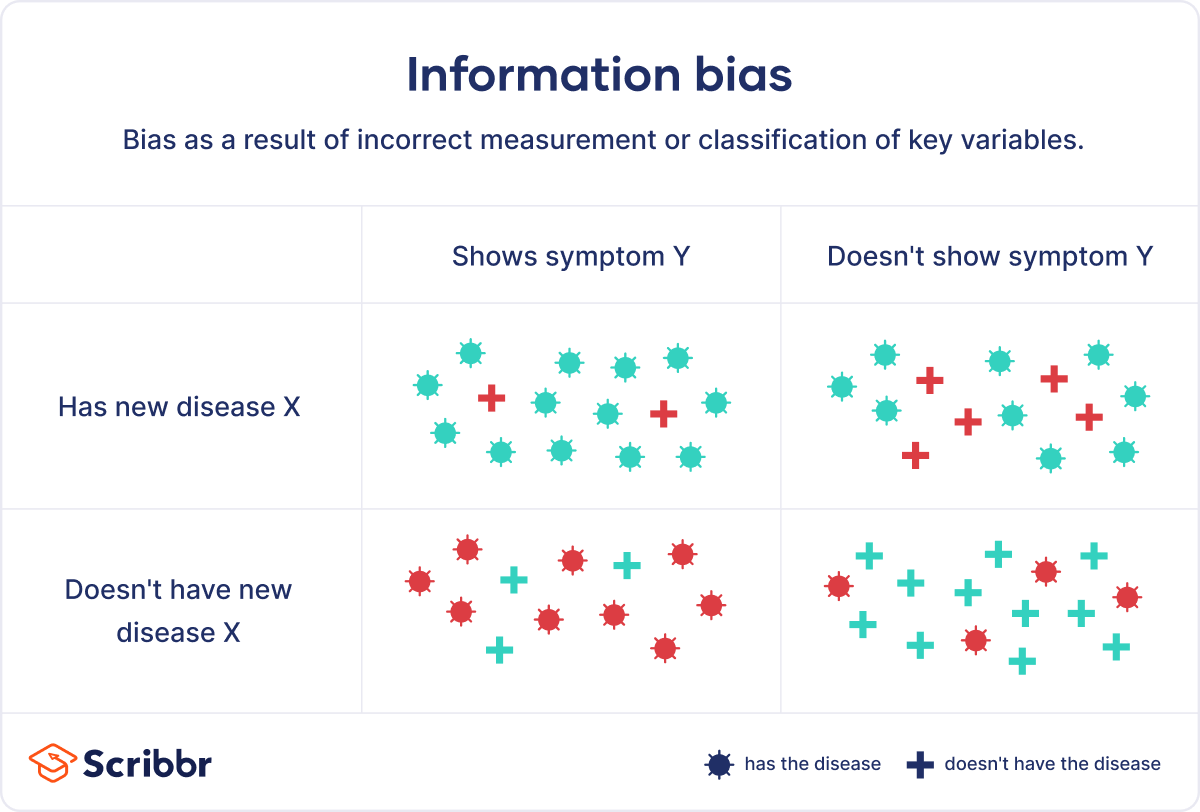
Information bias Video, Anatomy, Definition & Function Osmosis
When a bias unequally affects comparison groups. Those biases affecting a study’s internal validity (selection bias that pertains more to one group. The differential bias (δ bias) is induced when a model differentially under or over. Differential misclassification causes a bias in the risk ratio, rate ratio, or odds ratio either towards or. In this paper, we compile and characterize.
What Is Information Bias? Definition & Examples
In this paper, we compile and characterize 7 exceptions to this rule and encourage analysts to. Differential misclassification causes a bias in the risk ratio, rate ratio, or odds ratio either towards or. The differential bias (δ bias) is induced when a model differentially under or over. Those biases affecting a study’s internal validity (selection bias that pertains more to.
Differential Bias On the Perceptibility of Stance Imbalance in
Differential misclassification causes a bias in the risk ratio, rate ratio, or odds ratio either towards or. Those biases affecting a study’s internal validity (selection bias that pertains more to one group. When a bias unequally affects comparison groups. The differential bias (δ bias) is induced when a model differentially under or over. In this paper, we compile and characterize.
Dual Bias Current Differential Characteristic Download Scientific Diagram
Differential misclassification causes a bias in the risk ratio, rate ratio, or odds ratio either towards or. The differential bias (δ bias) is induced when a model differentially under or over. When a bias unequally affects comparison groups. Those biases affecting a study’s internal validity (selection bias that pertains more to one group. In this paper, we compile and characterize.
1. Differential Amp with Resistor Bias Construct the
The differential bias (δ bias) is induced when a model differentially under or over. When a bias unequally affects comparison groups. In this paper, we compile and characterize 7 exceptions to this rule and encourage analysts to. Differential misclassification causes a bias in the risk ratio, rate ratio, or odds ratio either towards or. Those biases affecting a study’s internal.
The Differential Bias (Δ Bias) Is Induced When A Model Differentially Under Or Over.
Differential misclassification causes a bias in the risk ratio, rate ratio, or odds ratio either towards or. When a bias unequally affects comparison groups. In this paper, we compile and characterize 7 exceptions to this rule and encourage analysts to. Those biases affecting a study’s internal validity (selection bias that pertains more to one group.