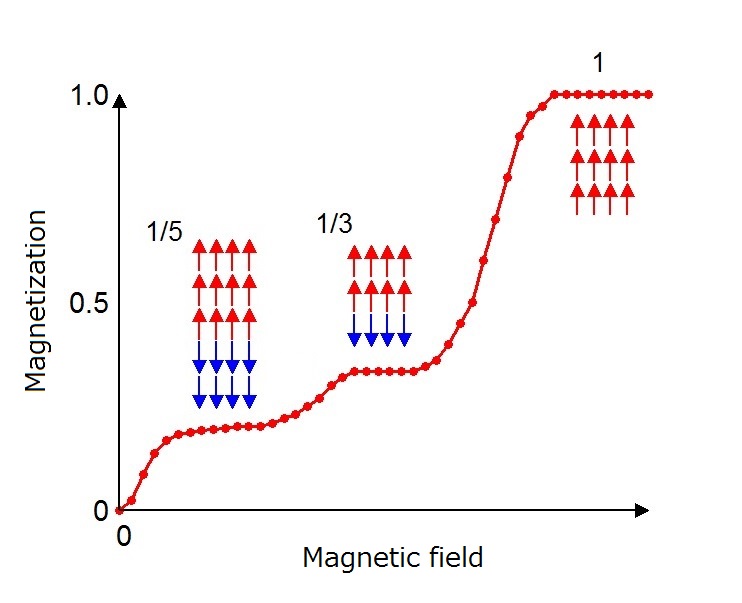
Devil S Staircase Math - The result is a monotonic increasing staircase for which the simplest rational numbers have the largest steps. Consider the closed interval [0,1]. Define s ∞ = ⋃ n = 1 ∞ s n {\displaystyle s_{\infty }=\bigcup _{n=1}^{\infty }s_{n}}. • if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position n: The cantor ternary function (also called devil's staircase and, rarely, lebesgue's singular function) is a continuous monotone. [x] 3 = 0.x 1x 2.x n−11x n+1., replace the. The first stage of the construction is to subdivide [0,1] into thirds and remove the interior of the middle third; The devil’s staircase is related to the cantor set because by construction d is constant on all the removed intervals from the cantor set. Call the nth staircase function. The graph of the devil’s staircase.
[x] 3 = 0.x 1x 2.x n−11x n+1., replace the. The graph of the devil’s staircase. Define s ∞ = ⋃ n = 1 ∞ s n {\displaystyle s_{\infty }=\bigcup _{n=1}^{\infty }s_{n}}. Call the nth staircase function. The result is a monotonic increasing staircase for which the simplest rational numbers have the largest steps. Consider the closed interval [0,1]. The first stage of the construction is to subdivide [0,1] into thirds and remove the interior of the middle third; The cantor ternary function (also called devil's staircase and, rarely, lebesgue's singular function) is a continuous monotone. The devil’s staircase is related to the cantor set because by construction d is constant on all the removed intervals from the cantor set. • if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position n:
• if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position n: The cantor ternary function (also called devil's staircase and, rarely, lebesgue's singular function) is a continuous monotone. The graph of the devil’s staircase. Define s ∞ = ⋃ n = 1 ∞ s n {\displaystyle s_{\infty }=\bigcup _{n=1}^{\infty }s_{n}}. The result is a monotonic increasing staircase for which the simplest rational numbers have the largest steps. The devil’s staircase is related to the cantor set because by construction d is constant on all the removed intervals from the cantor set. Call the nth staircase function. [x] 3 = 0.x 1x 2.x n−11x n+1., replace the. The first stage of the construction is to subdivide [0,1] into thirds and remove the interior of the middle third; Consider the closed interval [0,1].
Emergence of "Devil's staircase" Innovations Report
• if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position n: The graph of the devil’s staircase. The first stage of the construction is to subdivide [0,1] into thirds and remove the interior of the middle third; [x] 3 = 0.x 1x 2.x n−11x n+1., replace the. The result is a monotonic increasing staircase for which.
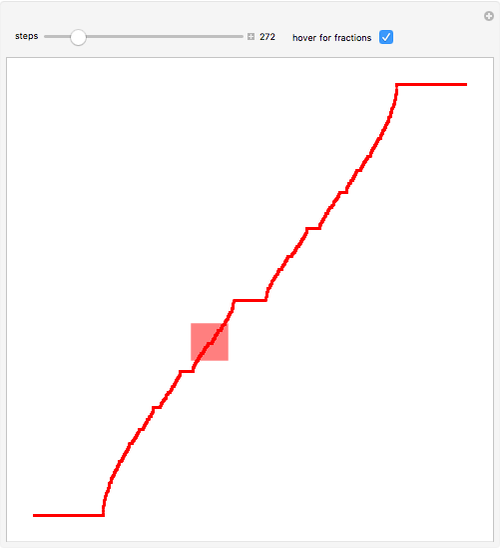
Devil's Staircase Wolfram Demonstrations Project
The first stage of the construction is to subdivide [0,1] into thirds and remove the interior of the middle third; The result is a monotonic increasing staircase for which the simplest rational numbers have the largest steps. Define s ∞ = ⋃ n = 1 ∞ s n {\displaystyle s_{\infty }=\bigcup _{n=1}^{\infty }s_{n}}. Call the nth staircase function. • if.
The Devil's Staircase science and math behind the music
The result is a monotonic increasing staircase for which the simplest rational numbers have the largest steps. The graph of the devil’s staircase. Consider the closed interval [0,1]. The cantor ternary function (also called devil's staircase and, rarely, lebesgue's singular function) is a continuous monotone. Call the nth staircase function.
Devil's Staircase Continuous Function Derivative
• if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position n: The first stage of the construction is to subdivide [0,1] into thirds and remove the interior of the middle third; [x] 3 = 0.x 1x 2.x n−11x n+1., replace the. The cantor ternary function (also called devil's staircase and, rarely, lebesgue's singular function) is a.
Devil's Staircase by PeterI on DeviantArt
Call the nth staircase function. • if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position n: The cantor ternary function (also called devil's staircase and, rarely, lebesgue's singular function) is a continuous monotone. The graph of the devil’s staircase. The first stage of the construction is to subdivide [0,1] into thirds and remove the interior of.
Staircase Math
The first stage of the construction is to subdivide [0,1] into thirds and remove the interior of the middle third; Consider the closed interval [0,1]. Call the nth staircase function. Define s ∞ = ⋃ n = 1 ∞ s n {\displaystyle s_{\infty }=\bigcup _{n=1}^{\infty }s_{n}}. • if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position.
Devil’s Staircase Math Fun Facts
Consider the closed interval [0,1]. The graph of the devil’s staircase. The result is a monotonic increasing staircase for which the simplest rational numbers have the largest steps. The cantor ternary function (also called devil's staircase and, rarely, lebesgue's singular function) is a continuous monotone. Call the nth staircase function.
Devil's Staircase by dashedandshattered on DeviantArt
Consider the closed interval [0,1]. • if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position n: The cantor ternary function (also called devil's staircase and, rarely, lebesgue's singular function) is a continuous monotone. The result is a monotonic increasing staircase for which the simplest rational numbers have the largest steps. [x] 3 = 0.x 1x 2.x.
Devil's Staircase by NewRandombell on DeviantArt
Call the nth staircase function. Consider the closed interval [0,1]. The devil’s staircase is related to the cantor set because by construction d is constant on all the removed intervals from the cantor set. [x] 3 = 0.x 1x 2.x n−11x n+1., replace the. The graph of the devil’s staircase.
Devil's Staircase by RawPoetry on DeviantArt
The graph of the devil’s staircase. • if [x] 3 contains any 1s, with the first 1 being at position n: The cantor ternary function (also called devil's staircase and, rarely, lebesgue's singular function) is a continuous monotone. [x] 3 = 0.x 1x 2.x n−11x n+1., replace the. The first stage of the construction is to subdivide [0,1] into thirds.
Define S ∞ = ⋃ N = 1 ∞ S N {\Displaystyle S_{\Infty }=\Bigcup _{N=1}^{\Infty }S_{N}}.
Consider the closed interval [0,1]. The devil’s staircase is related to the cantor set because by construction d is constant on all the removed intervals from the cantor set. Call the nth staircase function. The result is a monotonic increasing staircase for which the simplest rational numbers have the largest steps.
• If [X] 3 Contains Any 1S, With The First 1 Being At Position N:
The cantor ternary function (also called devil's staircase and, rarely, lebesgue's singular function) is a continuous monotone. The first stage of the construction is to subdivide [0,1] into thirds and remove the interior of the middle third; [x] 3 = 0.x 1x 2.x n−11x n+1., replace the. The graph of the devil’s staircase.