Bradycardia Differential - A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm. Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management. Sinus bradycardia can be defined as a sinus rhythm with a resting heart rate of 60 beats.
Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management. Sinus bradycardia can be defined as a sinus rhythm with a resting heart rate of 60 beats. A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm.
A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm. Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management. Sinus bradycardia can be defined as a sinus rhythm with a resting heart rate of 60 beats.
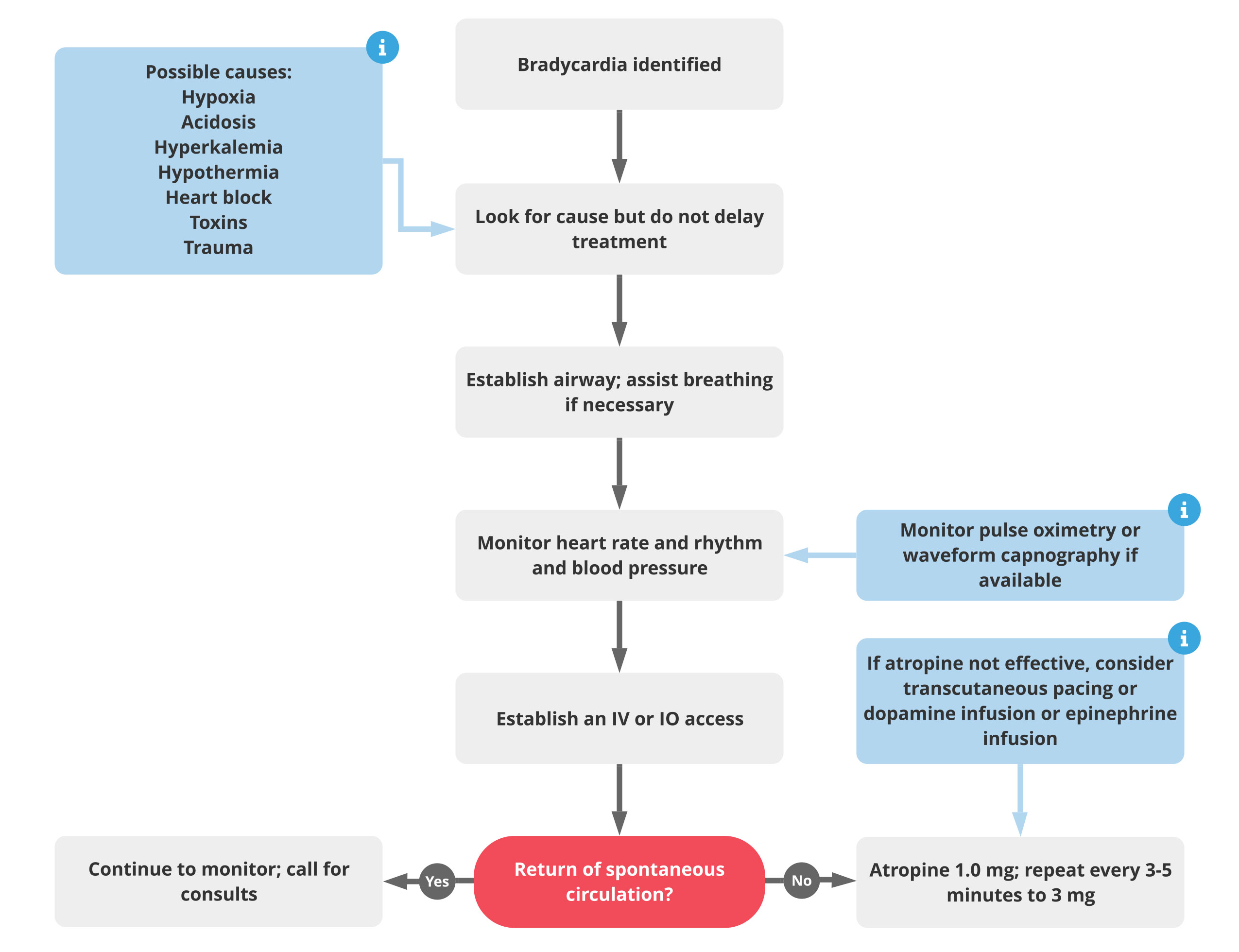
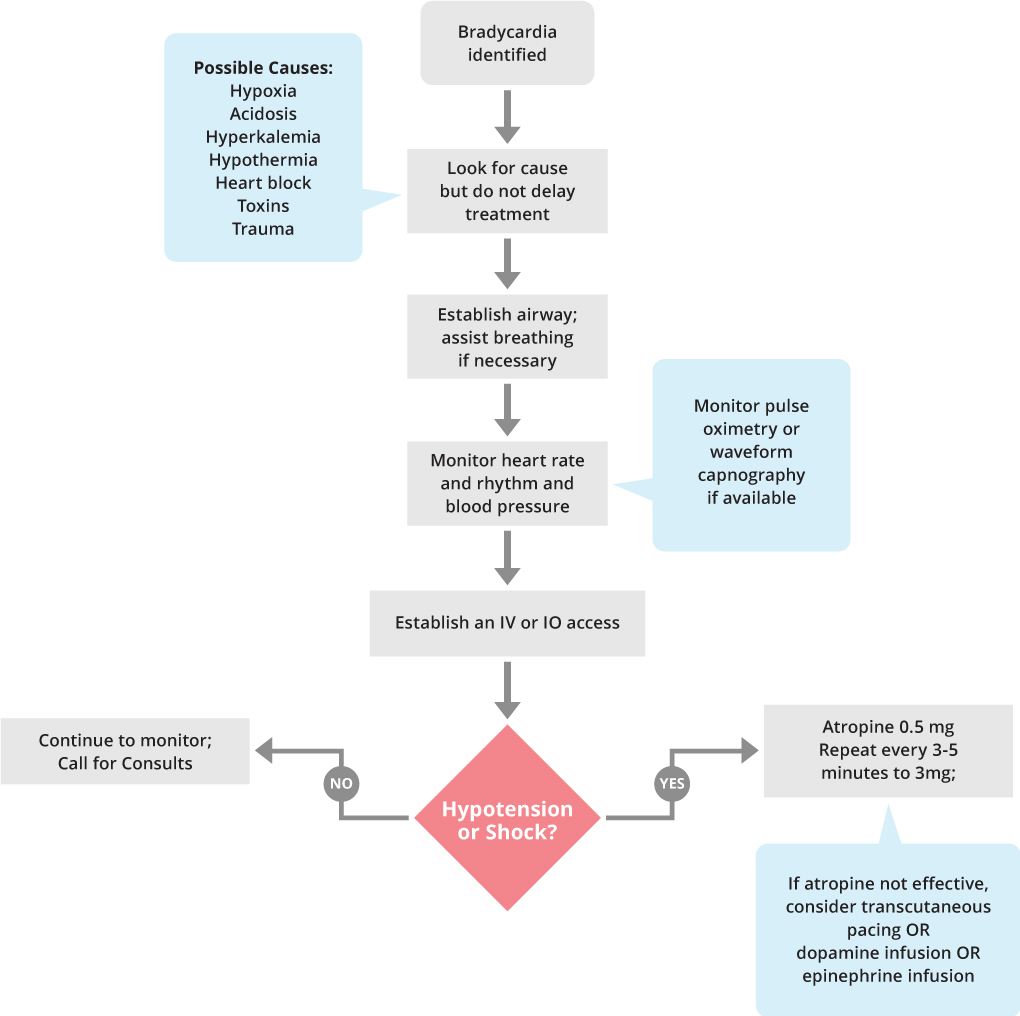
Atropine Dose for Bradycardia ACLS Guidelines
Sinus bradycardia can be defined as a sinus rhythm with a resting heart rate of 60 beats. Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management. A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm.
SOLUTION Main differential diagnosis of tachycardia bradycardia
A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm. Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management. Sinus bradycardia can be defined as a sinus rhythm with a resting heart rate of 60 beats.
Pin by Cindy D Starkey on PALS Pediatrics, Pals algorithm, Algorithm
Sinus bradycardia can be defined as a sinus rhythm with a resting heart rate of 60 beats. Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management. A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm.
Pin on Acls
Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management. Sinus bradycardia can be defined as a sinus rhythm with a resting heart rate of 60 beats. A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm.
Bradycardia
A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm. Sinus bradycardia can be defined as a sinus rhythm with a resting heart rate of 60 beats. Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management.
SOLUTION Main differential diagnosis of tachycardia bradycardia
Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management. Sinus bradycardia can be defined as a sinus rhythm with a resting heart rate of 60 beats. A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm.
ACLS Bradycardia Algorithm ACLS Medical Training
A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm. Sinus bradycardia can be defined as a sinus rhythm with a resting heart rate of 60 beats. Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management.
SOLUTION Main differential diagnosis of tachycardia bradycardia
A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm. Sinus bradycardia can be defined as a sinus rhythm with a resting heart rate of 60 beats. Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management.
BRASH Syndrome (Bradycardia, renal failure, AV block, shock
Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management. Sinus bradycardia can be defined as a sinus rhythm with a resting heart rate of 60 beats. A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm.
SOLUTION Main differential diagnosis of tachycardia bradycardia
A pulse of < 60 bpm is considered bradycardia in adults, whereas in newborns a pulse < 60 bpm. Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management. Sinus bradycardia can be defined as a sinus rhythm with a resting heart rate of 60 beats.
A Pulse Of < 60 Bpm Is Considered Bradycardia In Adults, Whereas In Newborns A Pulse < 60 Bpm.
Case presentation of bradycardia with a review of the common causes and management. Sinus bradycardia can be defined as a sinus rhythm with a resting heart rate of 60 beats.