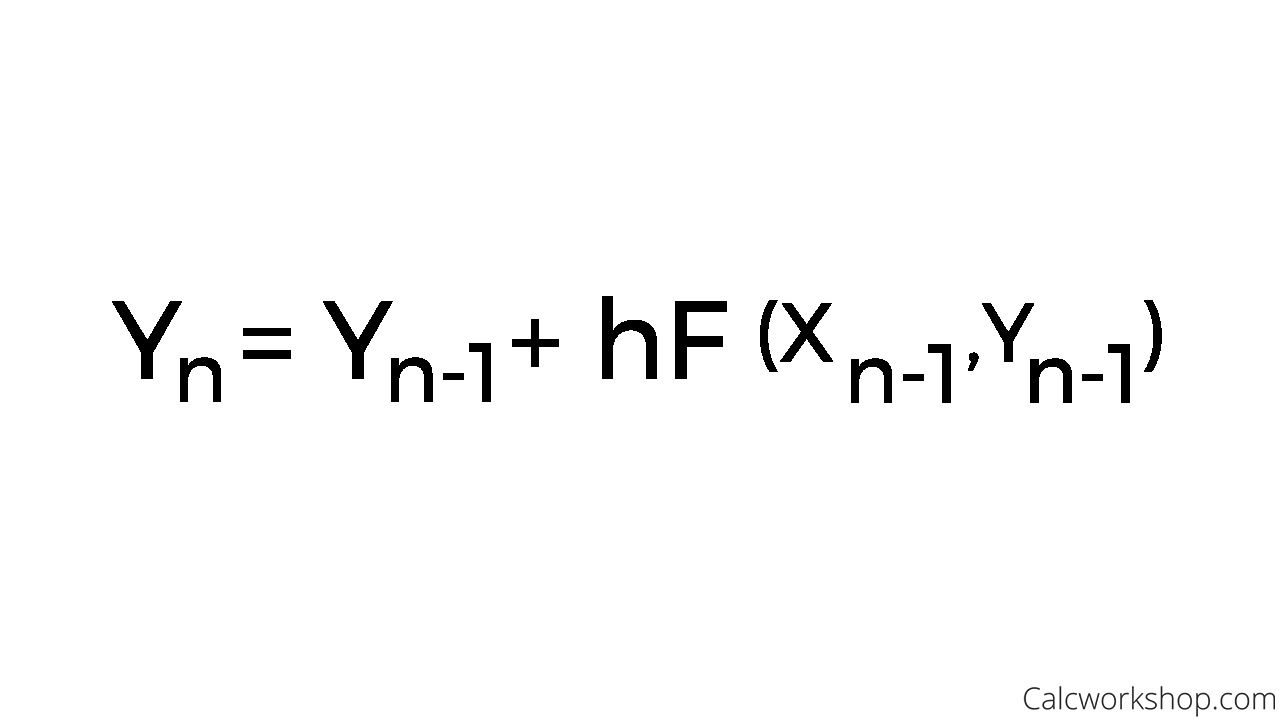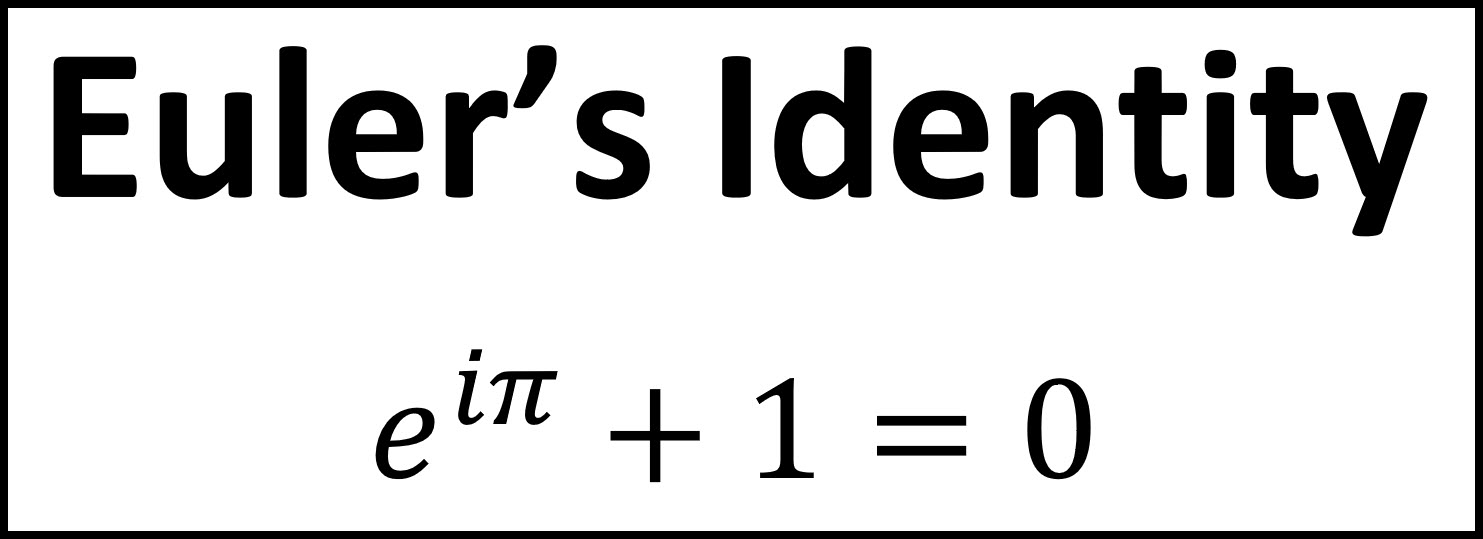Euler's Formula Differential Equations - In general, euler’s method starts with the known value y(x0) = y0 and computes y1, y2,., yn successively by with the formula. Note that while this does not involve a. Euler’s formula, polar representation 1. The complex plane complex numbers are represented geometrically by points in the plane: A differential equation is called an euler equation if it can be written in the form $a_nx^ny^{(n)}(x)+\cdots+a_1xy'+a_0y=f(x)$. In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0.
Euler’s formula, polar representation 1. A differential equation is called an euler equation if it can be written in the form $a_nx^ny^{(n)}(x)+\cdots+a_1xy'+a_0y=f(x)$. Note that while this does not involve a. In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. In general, euler’s method starts with the known value y(x0) = y0 and computes y1, y2,., yn successively by with the formula. The complex plane complex numbers are represented geometrically by points in the plane:
Note that while this does not involve a. In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. In general, euler’s method starts with the known value y(x0) = y0 and computes y1, y2,., yn successively by with the formula. A differential equation is called an euler equation if it can be written in the form $a_nx^ny^{(n)}(x)+\cdots+a_1xy'+a_0y=f(x)$. The complex plane complex numbers are represented geometrically by points in the plane: Euler’s formula, polar representation 1.
SOLUTION Cauchy euler s differential equations Studypool
Note that while this does not involve a. A differential equation is called an euler equation if it can be written in the form $a_nx^ny^{(n)}(x)+\cdots+a_1xy'+a_0y=f(x)$. In general, euler’s method starts with the known value y(x0) = y0 and computes y1, y2,., yn successively by with the formula. The complex plane complex numbers are represented geometrically by points in the plane:.
Mathematical Designing of Euler's Formula. Vector Illustration. Stock
Euler’s formula, polar representation 1. The complex plane complex numbers are represented geometrically by points in the plane: A differential equation is called an euler equation if it can be written in the form $a_nx^ny^{(n)}(x)+\cdots+a_1xy'+a_0y=f(x)$. In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. In general, euler’s method starts with the.
Differential Equations
A differential equation is called an euler equation if it can be written in the form $a_nx^ny^{(n)}(x)+\cdots+a_1xy'+a_0y=f(x)$. Euler’s formula, polar representation 1. In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. The complex plane complex numbers are represented geometrically by points in the plane: Note that while this does not involve.
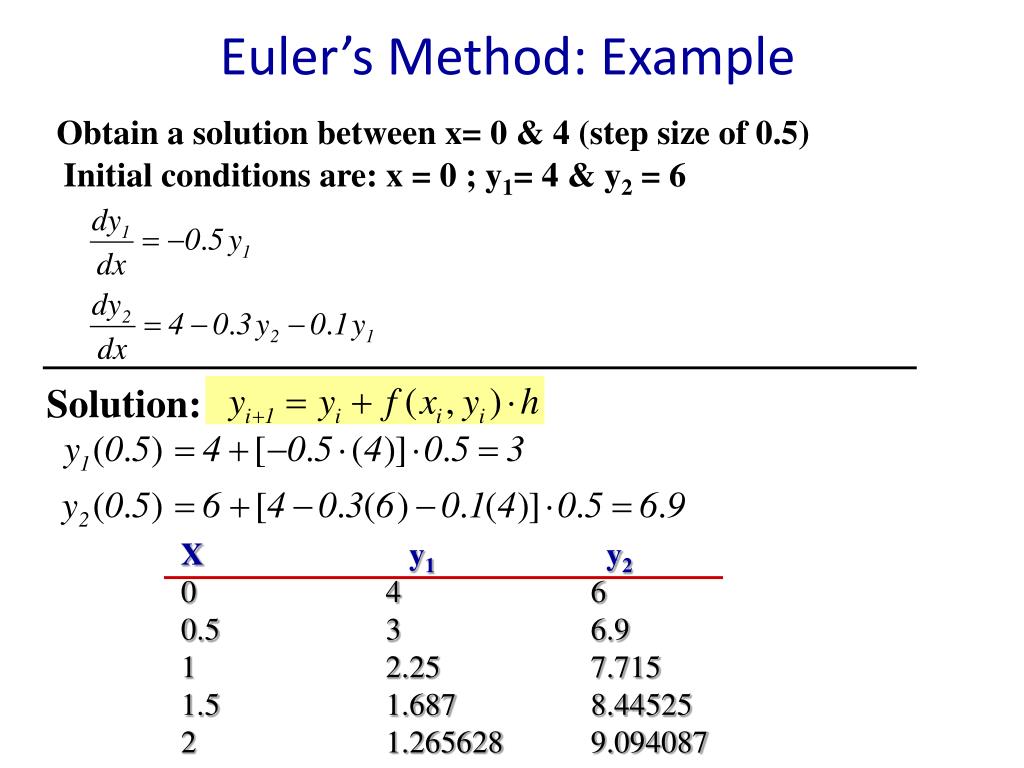
Euler's Method Explained with Examples
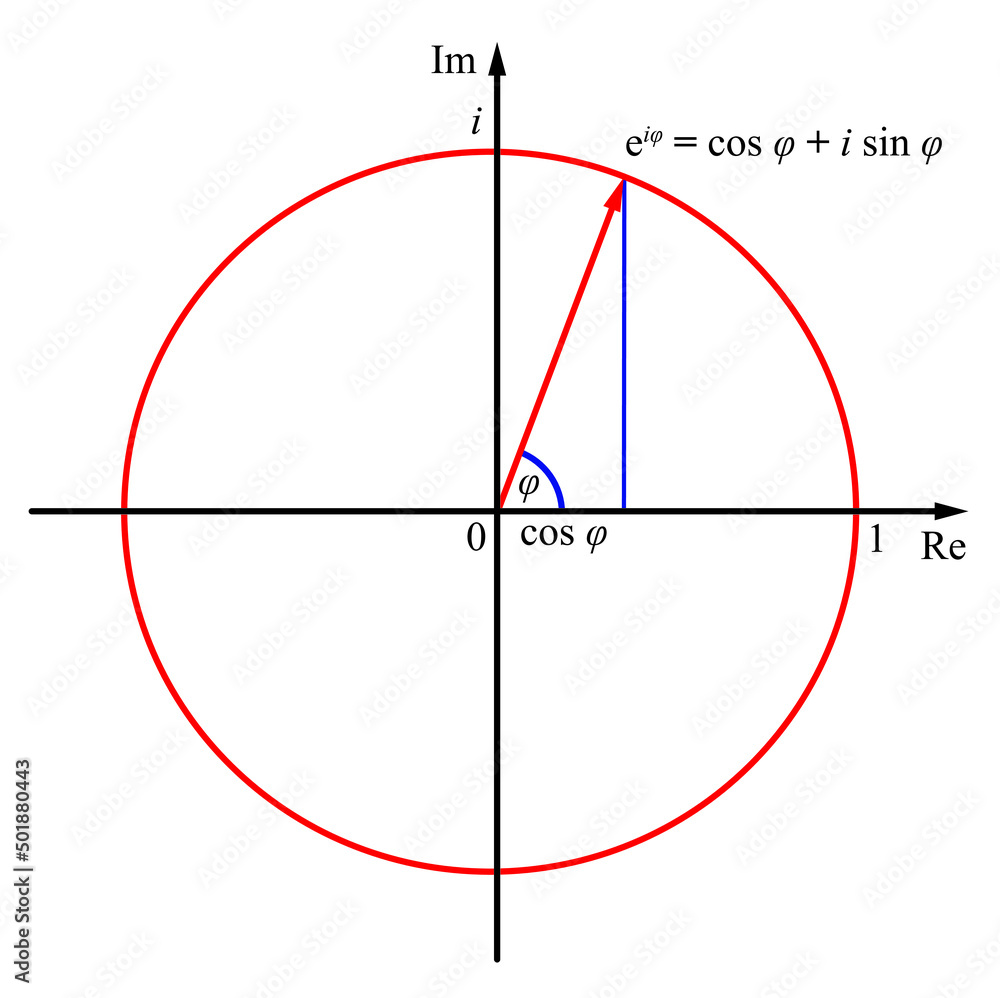
The complex plane complex numbers are represented geometrically by points in the plane: Euler’s formula, polar representation 1. A differential equation is called an euler equation if it can be written in the form $a_nx^ny^{(n)}(x)+\cdots+a_1xy'+a_0y=f(x)$. Note that while this does not involve a. In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy =.
Eulers Formula Mathematics Vector Stock Vector (Royalty Free
Euler’s formula, polar representation 1. Note that while this does not involve a. In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. In general, euler’s method starts with the known value y(x0) = y0 and computes y1, y2,., yn successively by with the formula. A differential equation is called an euler.
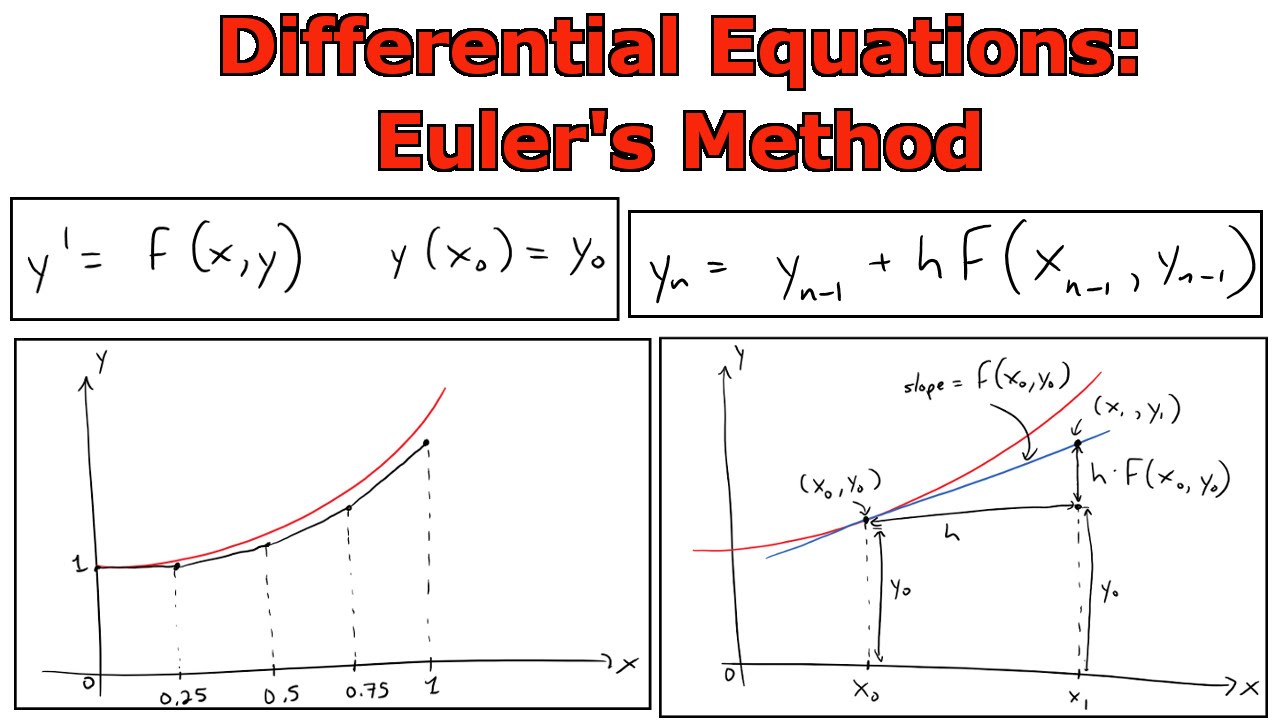
Euler's Method Explained With Examples, 40 OFF
The complex plane complex numbers are represented geometrically by points in the plane: In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. In general, euler’s method starts with the known value y(x0) = y0 and computes y1, y2,., yn successively by with the formula. Note that while this does not involve.
Introduction to Euler's Formula Slideshow PPT
In general, euler’s method starts with the known value y(x0) = y0 and computes y1, y2,., yn successively by with the formula. In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy = 0. Note that while this does not involve a. Euler’s formula, polar representation 1. The complex plane complex numbers are represented.
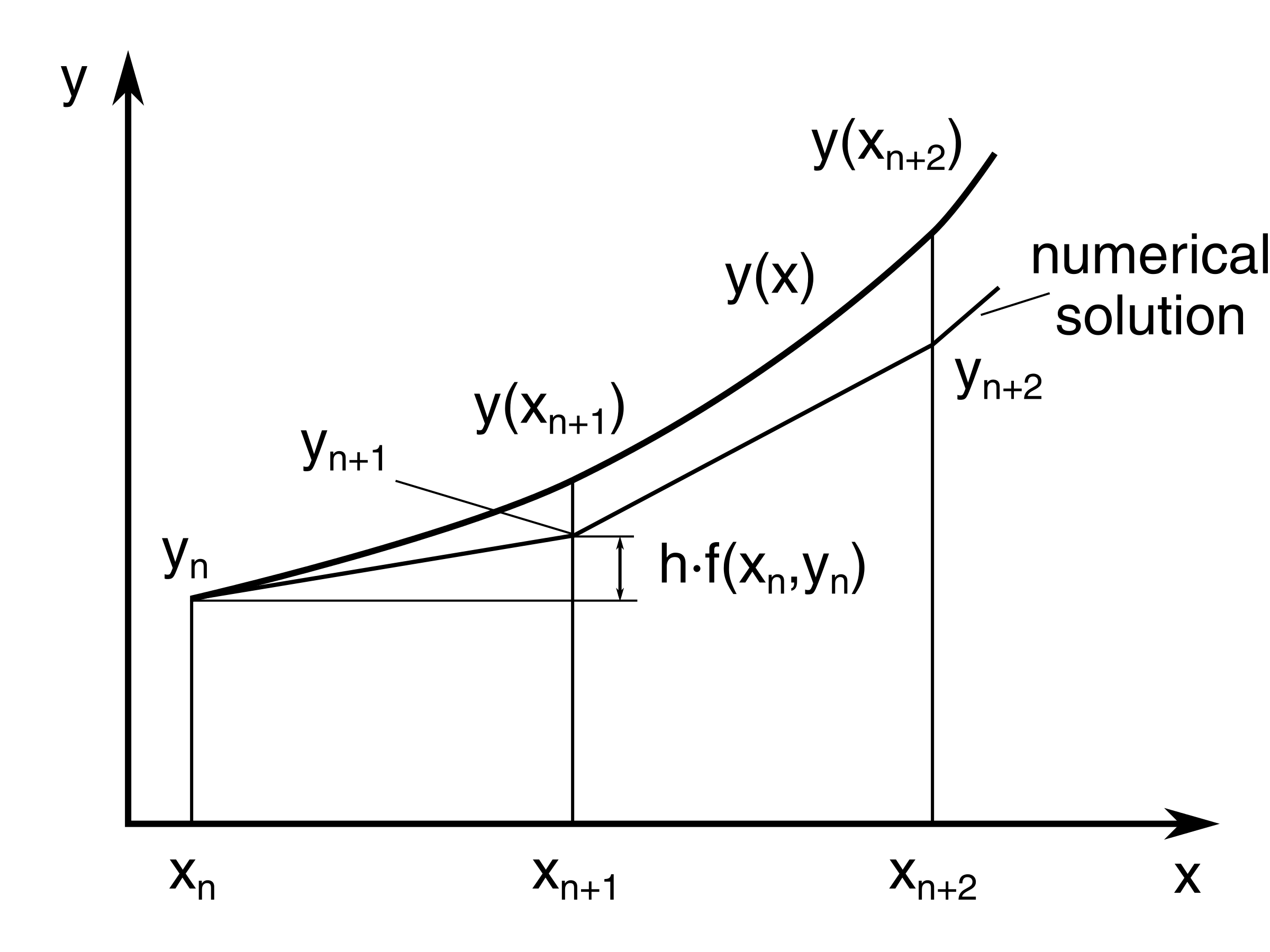
How to do Euler's Method? (Simply Explained in 4 Powerful Examples)
Note that while this does not involve a. In general, euler’s method starts with the known value y(x0) = y0 and computes y1, y2,., yn successively by with the formula. A differential equation is called an euler equation if it can be written in the form $a_nx^ny^{(n)}(x)+\cdots+a_1xy'+a_0y=f(x)$. Euler’s formula, polar representation 1. The complex plane complex numbers are represented geometrically.
Answered Use Euler's method to solve the… bartleby
A differential equation is called an euler equation if it can be written in the form $a_nx^ny^{(n)}(x)+\cdots+a_1xy'+a_0y=f(x)$. Euler’s formula, polar representation 1. In general, euler’s method starts with the known value y(x0) = y0 and computes y1, y2,., yn successively by with the formula. In this section we will discuss how to solve euler’s differential equation, ax^2y'' + bxy' +cy.
Euler's Formula
Euler’s formula, polar representation 1. A differential equation is called an euler equation if it can be written in the form $a_nx^ny^{(n)}(x)+\cdots+a_1xy'+a_0y=f(x)$. The complex plane complex numbers are represented geometrically by points in the plane: In general, euler’s method starts with the known value y(x0) = y0 and computes y1, y2,., yn successively by with the formula. Note that while.
In This Section We Will Discuss How To Solve Euler’s Differential Equation, Ax^2Y'' + Bxy' +Cy = 0.
In general, euler’s method starts with the known value y(x0) = y0 and computes y1, y2,., yn successively by with the formula. Note that while this does not involve a. Euler’s formula, polar representation 1. The complex plane complex numbers are represented geometrically by points in the plane: