Deaths From Vaccine-Preventable Diseases Are At An All-Time Low. - As of 2018, the total world population of children < 5 years of age was roughly estimated at 679. A comparison of the morbidity and mortality before and after widespread. The infectious diseases that remain major causes of mortality for which vaccines.
As of 2018, the total world population of children < 5 years of age was roughly estimated at 679. A comparison of the morbidity and mortality before and after widespread. The infectious diseases that remain major causes of mortality for which vaccines.
The infectious diseases that remain major causes of mortality for which vaccines. As of 2018, the total world population of children < 5 years of age was roughly estimated at 679. A comparison of the morbidity and mortality before and after widespread.
Report Behavior Changes Can Prevent Deaths from Cancer and Other
A comparison of the morbidity and mortality before and after widespread. As of 2018, the total world population of children < 5 years of age was roughly estimated at 679. The infectious diseases that remain major causes of mortality for which vaccines.
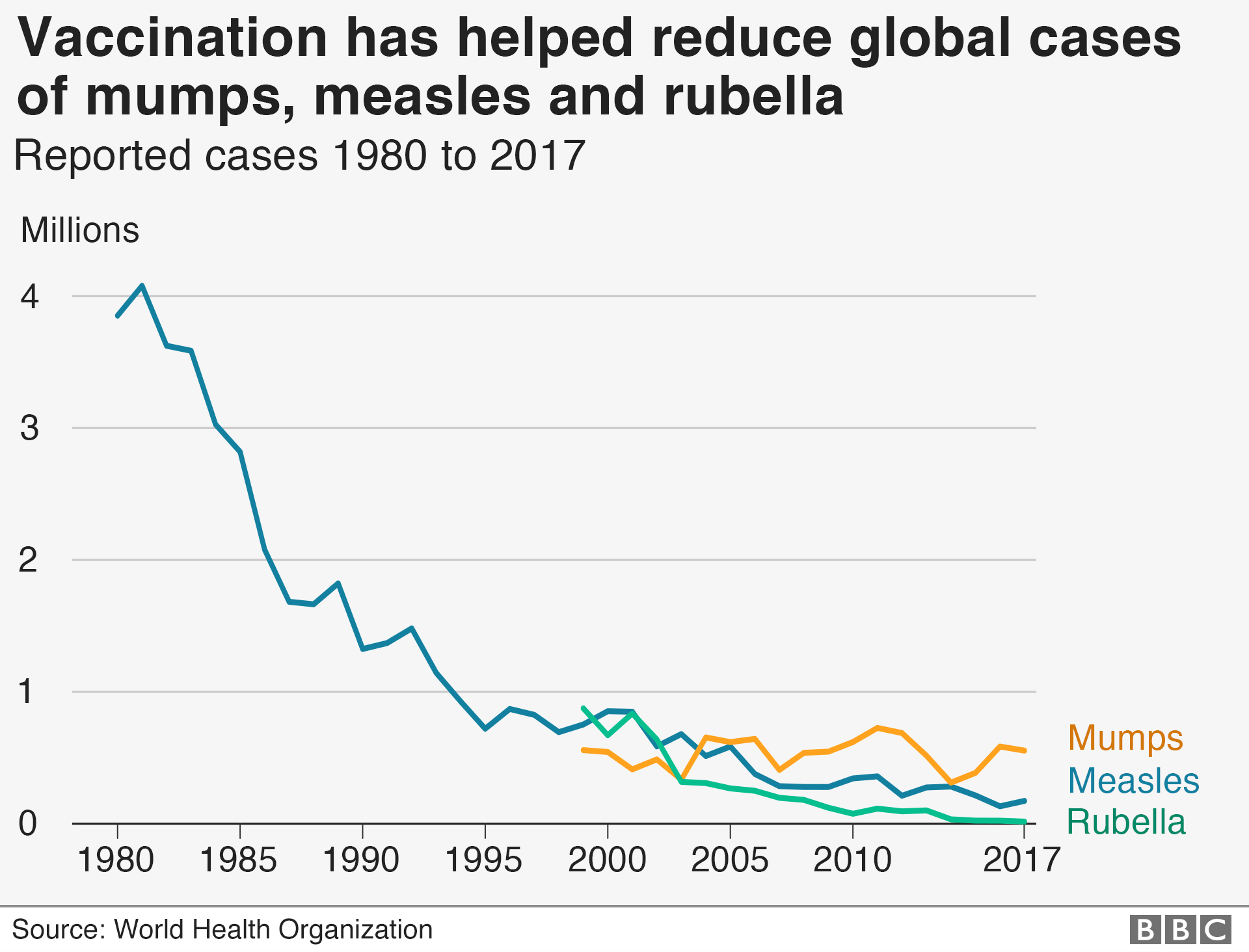
The growth of global immunisation BBC News
The infectious diseases that remain major causes of mortality for which vaccines. A comparison of the morbidity and mortality before and after widespread. As of 2018, the total world population of children < 5 years of age was roughly estimated at 679.
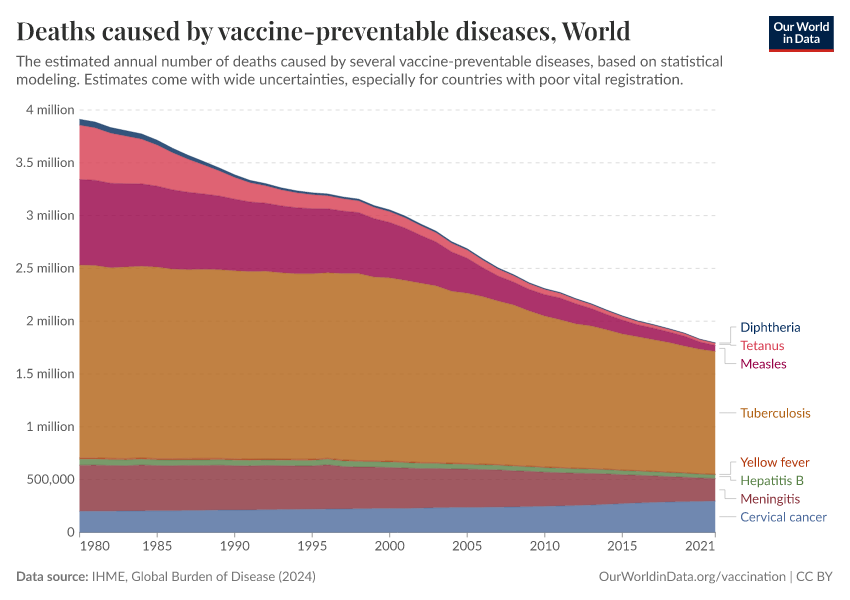
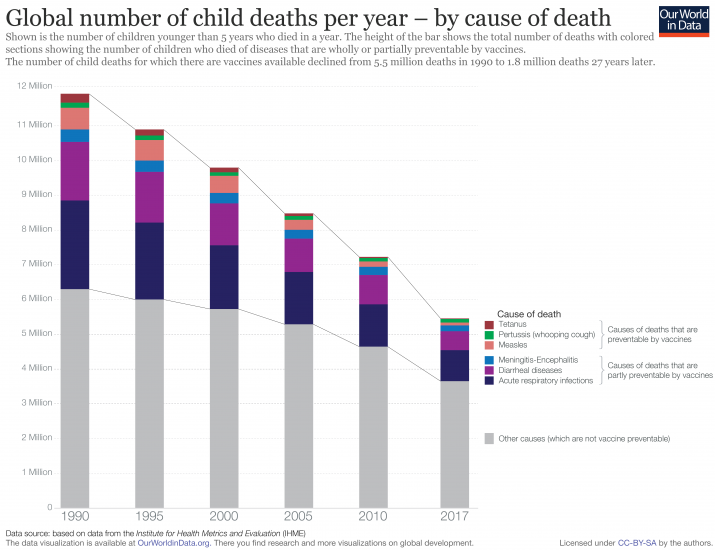
Deaths caused by vaccinepreventable diseases Our World in Data
A comparison of the morbidity and mortality before and after widespread. As of 2018, the total world population of children < 5 years of age was roughly estimated at 679. The infectious diseases that remain major causes of mortality for which vaccines.
Good Health and Wellbeing Paul College of Business and Economics
As of 2018, the total world population of children < 5 years of age was roughly estimated at 679. The infectious diseases that remain major causes of mortality for which vaccines. A comparison of the morbidity and mortality before and after widespread.
What are vaccines, how do they work and why are people sceptical?
The infectious diseases that remain major causes of mortality for which vaccines. A comparison of the morbidity and mortality before and after widespread. As of 2018, the total world population of children < 5 years of age was roughly estimated at 679.
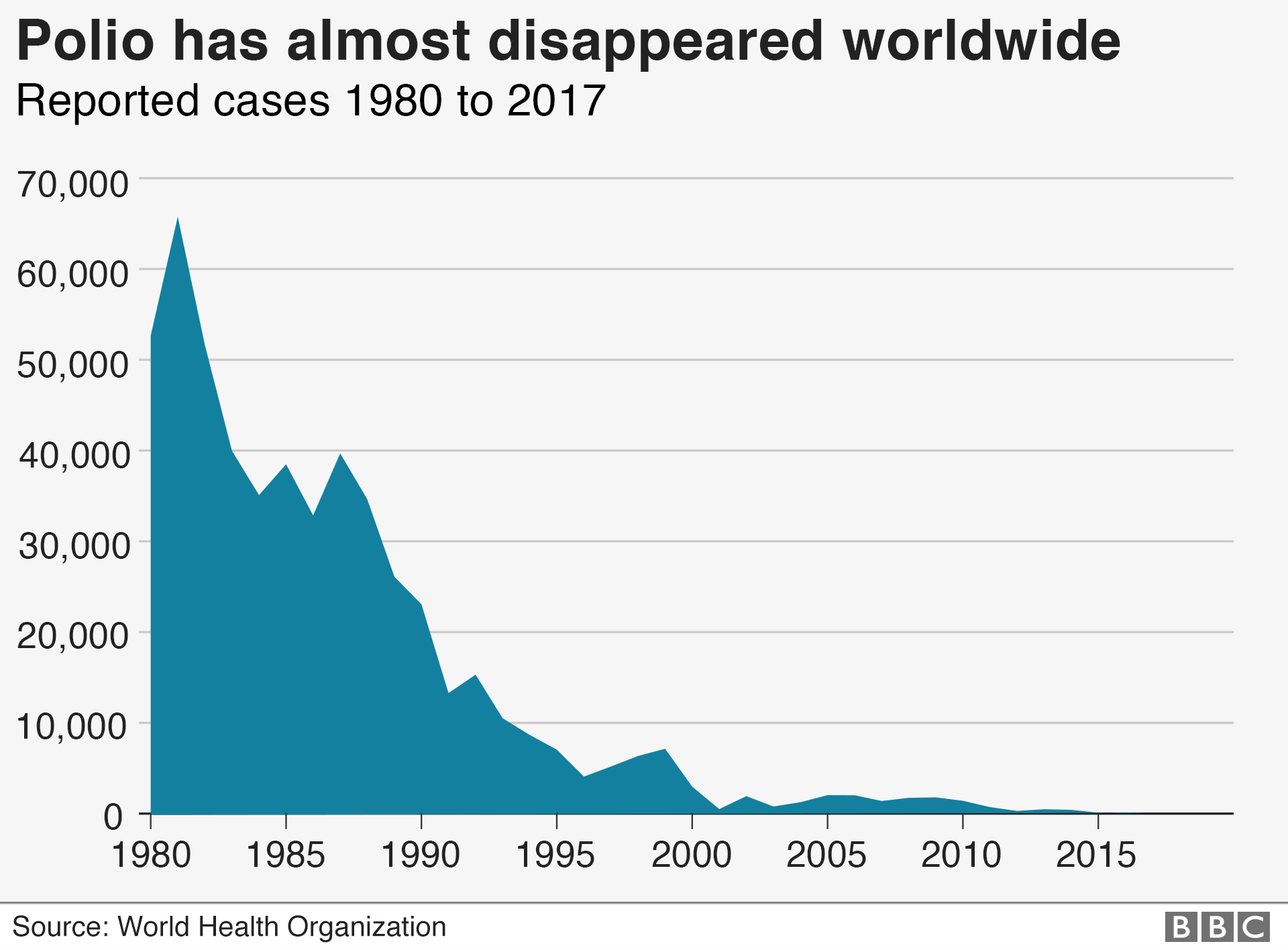
How is the world doing in its fight against vaccine preventable
A comparison of the morbidity and mortality before and after widespread. The infectious diseases that remain major causes of mortality for which vaccines. As of 2018, the total world population of children < 5 years of age was roughly estimated at 679.
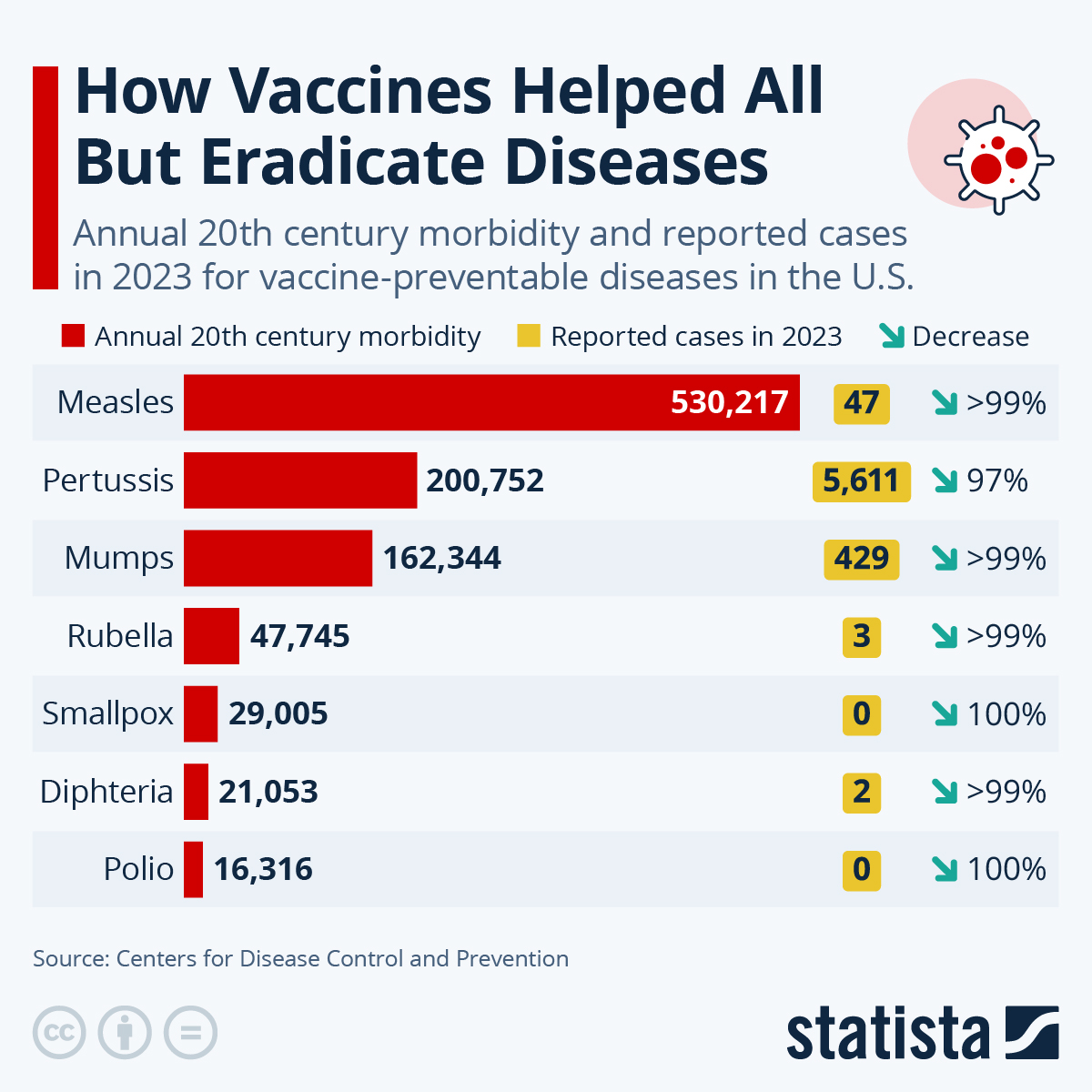
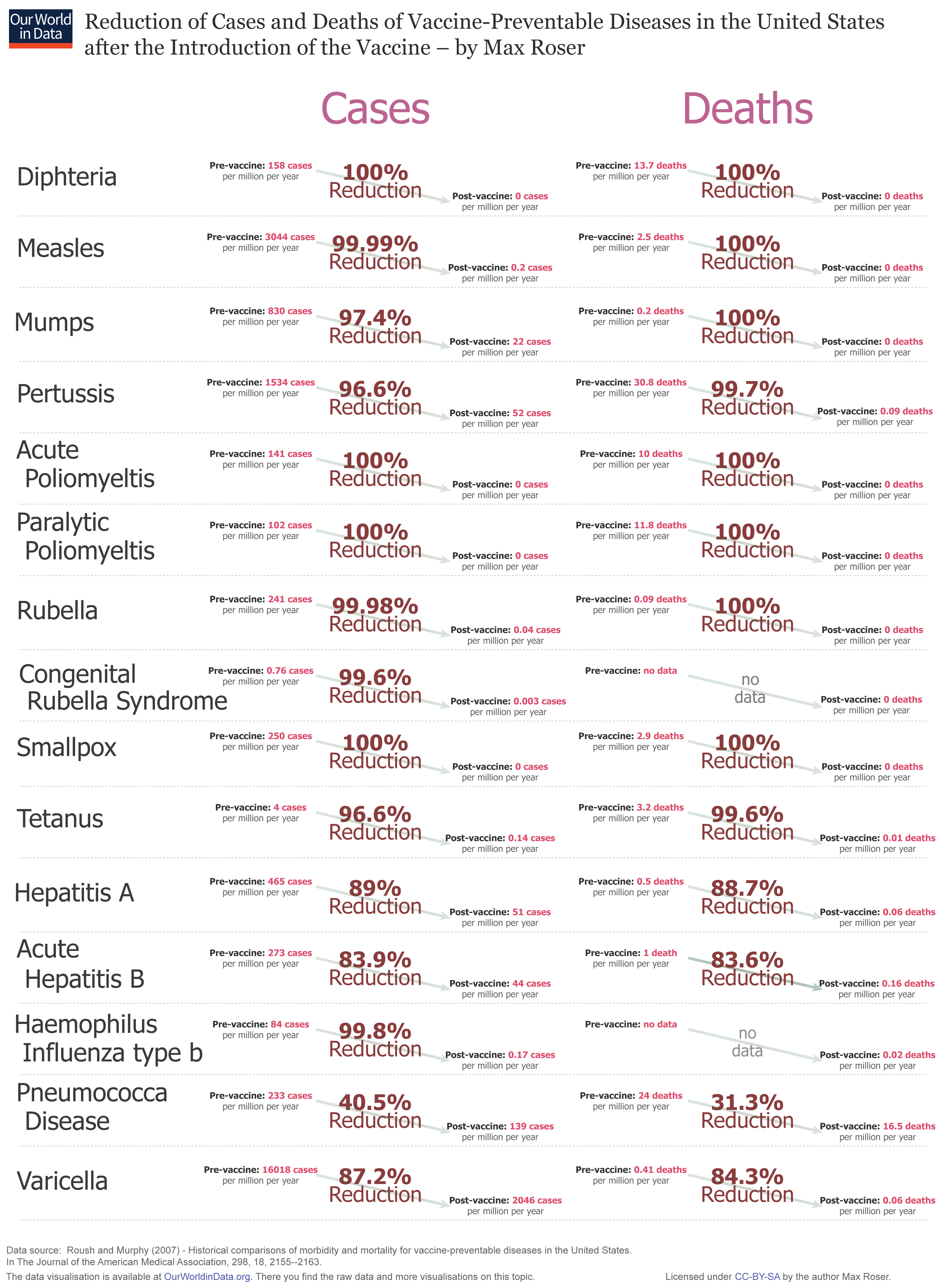
Reduction of Cases and Deaths of VaccinePreventable Diseases in the US
The infectious diseases that remain major causes of mortality for which vaccines. A comparison of the morbidity and mortality before and after widespread. As of 2018, the total world population of children < 5 years of age was roughly estimated at 679.
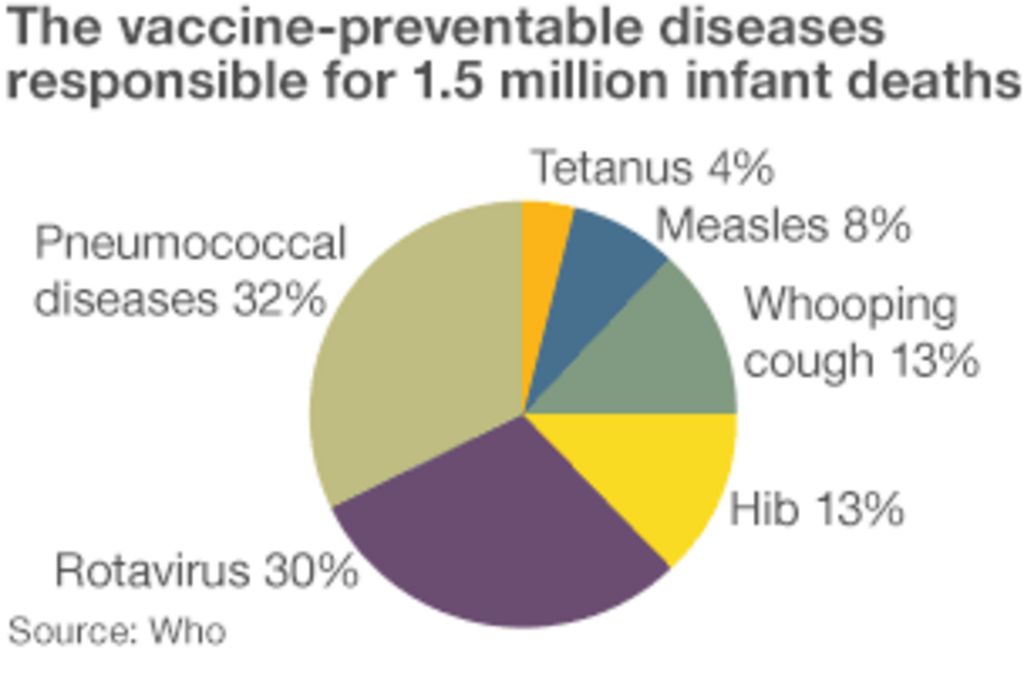
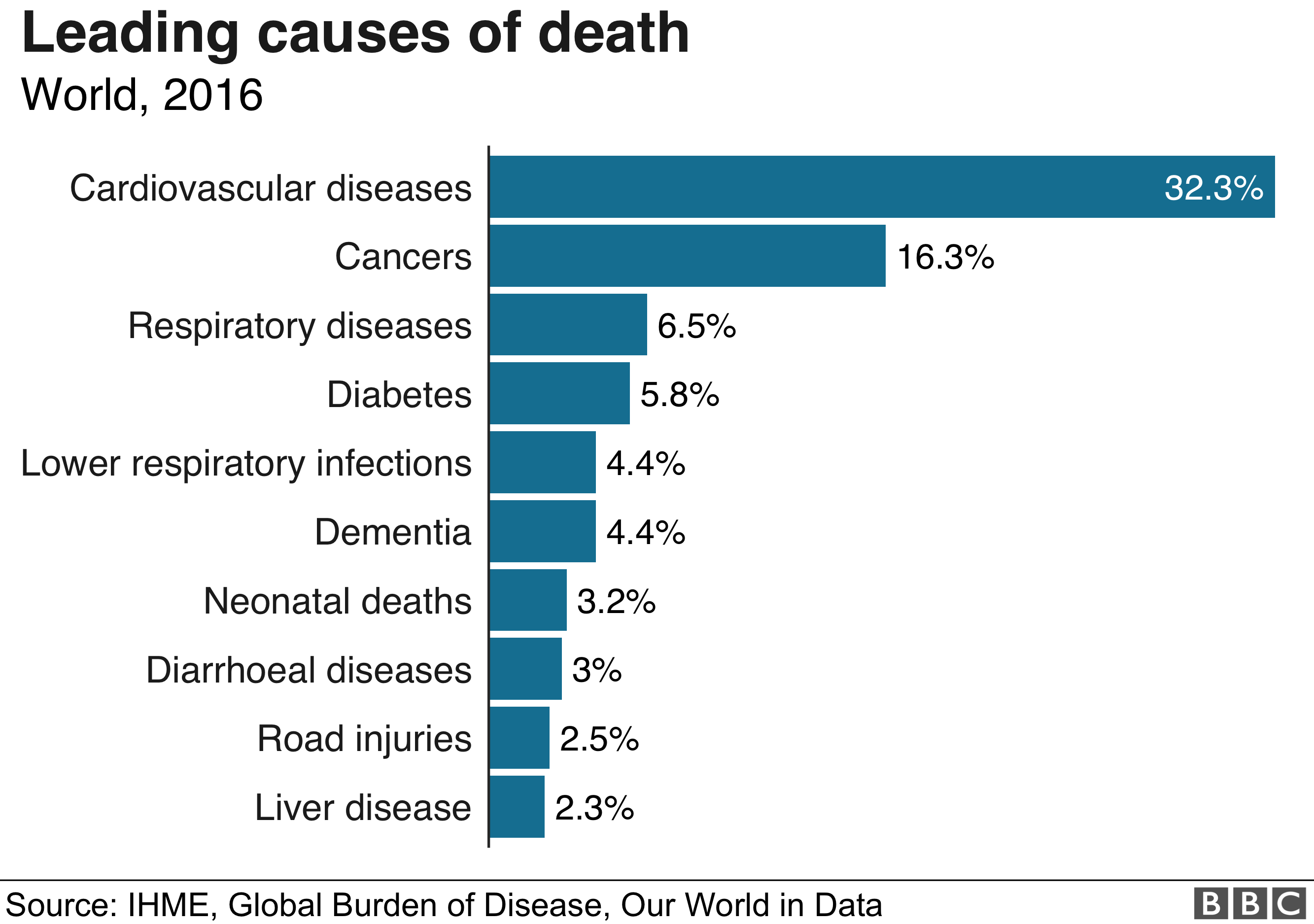
What do the people of the world die from? BBC News
The infectious diseases that remain major causes of mortality for which vaccines. A comparison of the morbidity and mortality before and after widespread. As of 2018, the total world population of children < 5 years of age was roughly estimated at 679.
Epidemiology Unit
The infectious diseases that remain major causes of mortality for which vaccines. A comparison of the morbidity and mortality before and after widespread. As of 2018, the total world population of children < 5 years of age was roughly estimated at 679.
What are vaccines, how do they work and why are people sceptical?
The infectious diseases that remain major causes of mortality for which vaccines. As of 2018, the total world population of children < 5 years of age was roughly estimated at 679. A comparison of the morbidity and mortality before and after widespread.
As Of 2018, The Total World Population Of Children < 5 Years Of Age Was Roughly Estimated At 679.
A comparison of the morbidity and mortality before and after widespread. The infectious diseases that remain major causes of mortality for which vaccines.